Steganography in security refers to the practice of hiding messages or information within other non-secret data to avoid detection. An example includes embedding secret text within an image file by altering the least significant bits of the image's pixel values. This method conceals the message in such a way that it remains invisible to the naked eye and undetectable through casual inspection. Data hidden using steganography can be extracted by specialized software that knows how to read the embedded information. This technique is often used for secure communication, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access while maintaining the appearance of a normal image or file. Detecting steganography requires analyzing the data patterns or using forensic tools designed to uncover hidden content.
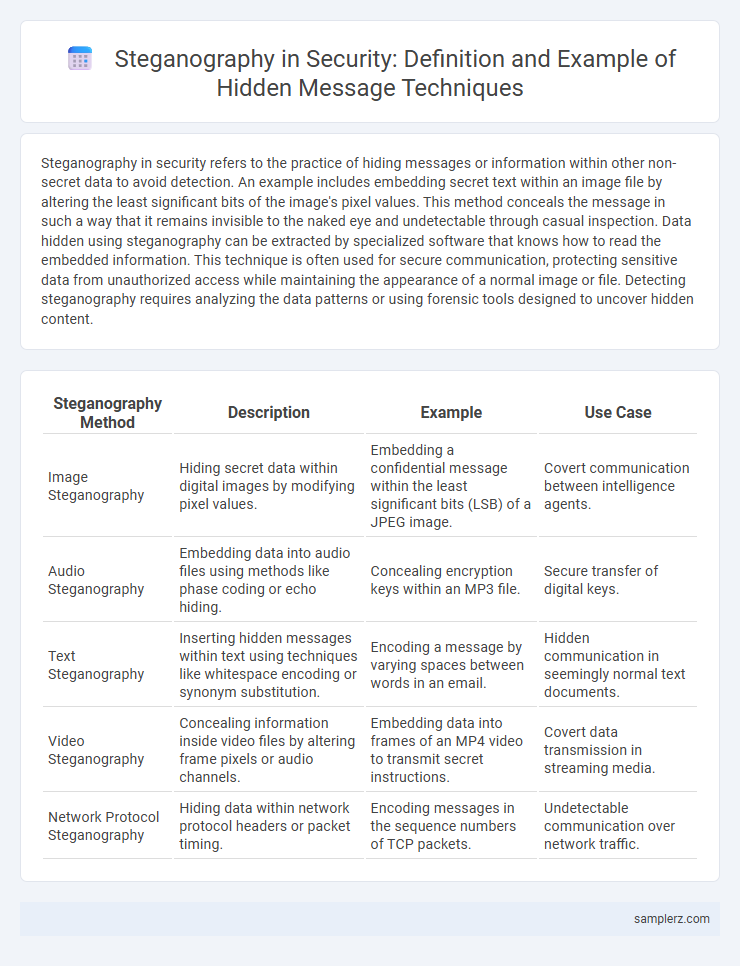
Table of Comparison
| Steganography Method | Description | Example | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Steganography | Hiding secret data within digital images by modifying pixel values. | Embedding a confidential message within the least significant bits (LSB) of a JPEG image. | Covert communication between intelligence agents. |
| Audio Steganography | Embedding data into audio files using methods like phase coding or echo hiding. | Concealing encryption keys within an MP3 file. | Secure transfer of digital keys. |
| Text Steganography | Inserting hidden messages within text using techniques like whitespace encoding or synonym substitution. | Encoding a message by varying spaces between words in an email. | Hidden communication in seemingly normal text documents. |
| Video Steganography | Concealing information inside video files by altering frame pixels or audio channels. | Embedding data into frames of an MP4 video to transmit secret instructions. | Covert data transmission in streaming media. |
| Network Protocol Steganography | Hiding data within network protocol headers or packet timing. | Encoding messages in the sequence numbers of TCP packets. | Undetectable communication over network traffic. |
Classic Historical Examples of Steganography in Messages
Ancient Greeks used steganography by writing secret messages on wooden tablets and then covering them with wax to hide the text. During World War II, spies concealed information within microdots--tiny photographs embedded inside letters or documents. Another notable example is the use of invisible ink in letters to communicate covertly without arousing suspicion.
Digital Image Steganography: Hiding Data in Pictures
Digital Image Steganography embeds secret messages within the pixel values of images, altering the least significant bits to conceal information without noticeable changes to the visual content. This technique enables secure communication by hiding data in common image formats like PNG or BMP, making detection by unauthorized users extremely difficult. Robust algorithms enhance resistance to image compression and cropping, preserving the hidden data's integrity during transmission.
Audio File Steganography: Concealing Information in Sound
Audio file steganography involves embedding secret messages within digital audio signals by altering imperceptible parts of the sound wave, such as the least significant bits (LSB) or frequency components. This technique maintains audio quality while securely transmitting confidential data through formats like WAV or MP3, evading detection from unauthorized listeners. Common applications include covert communication, digital watermarking, and protecting intellectual property rights.
Text Steganography: Hidden Messages in Plain Sight
Text steganography hides secret messages within seemingly innocuous text by altering font styles, inserting invisible characters, or using specific word patterns to encode information. Techniques like zero-width characters or subtle changes in spacing enable covert communication without raising suspicion. These methods ensure that sensitive messages remain concealed while appearing as ordinary text, enhancing security in digital communications.
Social Media Steganography: Secret Communications Online
Social media steganography enables secure communication by embedding hidden messages within images, videos, or text posts shared on platforms like Facebook and Instagram. This technique conceals information in multimedia content, making detection by automated filters or unauthorized users extremely difficult. Users exploit metadata manipulation and pixel alteration methods to transmit covert messages without raising suspicion during routine social media interactions.
Steganography in Video Files: Encoding Covert Data
Steganography in video files involves embedding covert data within video frames by manipulating pixel values or utilizing compression artifacts, making hidden messages imperceptible to viewers. Techniques such as Least Significant Bit (LSB) modification and discrete cosine transform (DCT) alterations enable secure and undetectable communication in video streams. Video steganography is widely used in secure messaging, digital watermarking, and anti-piracy measures to protect sensitive information against unauthorized access.
Steganography Tools: Real-World Application Examples
Steganography tools like OpenPuff and SilentEye enable users to embed secret messages within digital media files such as images, audio, and video, ensuring covert communication in high-security environments. These tools employ techniques like Least Significant Bit (LSB) insertion, which modifies the media's binary data without noticeable quality loss, making detection extremely difficult. Real-world applications include confidential military communications, secure corporate messaging, and digital watermarking for intellectual property protection.
Malware and Steganography: Malicious Message Concealment
Malware often employs steganography to conceal malicious payloads within seemingly innocuous messages, such as embedding harmful code inside image or audio files to evade detection by traditional security systems. This technique enables attackers to bypass firewalls and antivirus software by hiding encrypted commands or executables within the least significant bits of digital media. Detecting such steganographic threats requires advanced analysis methods, including machine learning-based anomaly detection and deep packet inspection to uncover hidden data channels within normal network traffic.
Steganography in Email Communications: Case Studies
Steganography in email communications involves embedding hidden messages within seemingly innocuous email content to evade detection by security filters and adversaries. Case studies reveal techniques such as encoding secret data into image attachments or manipulating text formatting to conceal information without arousing suspicion. These methods highlight the need for advanced threat detection systems equipped to analyze metadata and content patterns for covert communication signals.
Steganography in Cyber Espionage: Notable Incidents
Notable incidents of steganography in cyber espionage include the use of hidden messages within image files by advanced persistent threat (APT) groups like APT28, which embed malicious commands in seemingly innocuous pictures to evade detection. Another significant case involved the Turla group, leveraging steganographic techniques to conceal payloads in social media images for stealthy data exfiltration. These examples highlight steganography as a sophisticated tool for covert communication in state-sponsored cyber espionage campaigns.
example of steganography in message Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com