A logic bomb is a malicious code planted by an insider within an organization's system that triggers a harmful action when specific conditions are met. For example, an employee who has access to critical software might insert a logic bomb set to delete essential files if their user account is terminated. This type of insider threat exploits authorized access to cause data loss, system disruption, or security breaches. Corporations face significant risks from logic bombs because they are difficult to detect and can remain dormant until activated. Monitoring user behavior and implementing strict access controls help in mitigating these threats. Incident response teams use forensic analysis to identify signs of logic bombs and prevent data corruption or operational downtime.
Table of Comparison
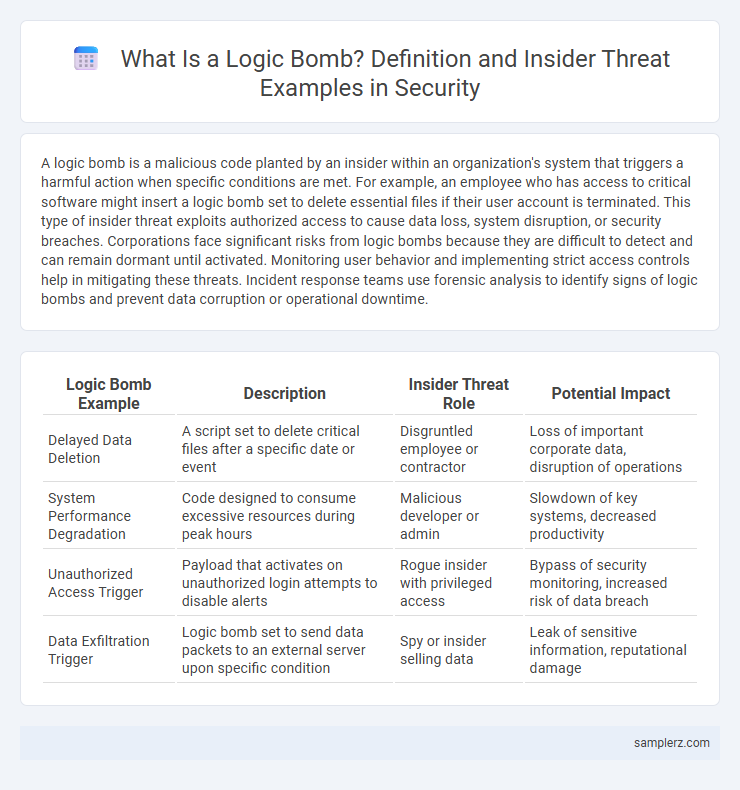
| Logic Bomb Example | Description | Insider Threat Role | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delayed Data Deletion | A script set to delete critical files after a specific date or event | Disgruntled employee or contractor | Loss of important corporate data, disruption of operations |
| System Performance Degradation | Code designed to consume excessive resources during peak hours | Malicious developer or admin | Slowdown of key systems, decreased productivity |
| Unauthorized Access Trigger | Payload that activates on unauthorized login attempts to disable alerts | Rogue insider with privileged access | Bypass of security monitoring, increased risk of data breach |
| Data Exfiltration Trigger | Logic bomb set to send data packets to an external server upon specific condition | Spy or insider selling data | Leak of sensitive information, reputational damage |
Understanding Logic Bombs: A Security Perspective
Logic bombs represent a significant insider threat where malicious code is embedded within software, triggered by specific conditions such as dates, user actions, or system events. For example, an employee with privileged access might insert a logic bomb that activates during a critical financial reporting period, disrupting operations and causing data loss or corruption. Detecting and mitigating these threats requires continuous monitoring of code changes and behavioral analysis to identify unusual triggers before damage occurs.
Insider Threats: How Logic Bombs Are Deployed
Logic bombs are malicious code planted by insiders within an organization's systems, designed to trigger harmful actions when specific conditions are met. These attacks often remain dormant until executed, making detection difficult and allowing insiders to exploit access privileges stealthily. Common deployment tactics include embedding code in routine software updates or exploiting scheduled tasks to activate data breaches or system disruptions.
Real-World Logic Bomb Incidents Involving Employees
Real-world logic bomb incidents involving employees highlight significant insider threats, such as the 2006 case where a former employee of a major telecommunications company planted destructive code that triggered system failures after his termination. Another notable example occurred at a financial firm when a disgruntled IT administrator embedded a logic bomb to corrupt critical databases, causing substantial operational disruptions. These incidents underscore the necessity for rigorous monitoring and access controls to detect and prevent malicious code introduced by insiders.
Common Tactics Used in Insider Logic Bomb Attacks
Insider logic bomb attacks typically exploit privileged access to deploy malicious code triggered by specific conditions such as dates, system events, or user actions. Common tactics include embedding harmful scripts within legitimate software updates, manipulating system configurations to activate destructive processes, and exploiting scheduled tasks to execute payloads at predetermined times. These methods make detection challenging as the malicious code remains dormant until the trigger event occurs, often bypassing traditional security measures.
Case Study: Logic Bomb at a Financial Institution
A logic bomb was implanted by a disgruntled employee at a major financial institution, triggering a malicious script that deleted critical customer transaction records on a specific date. This insider threat exploited privileged access to bypass security controls, causing significant data loss and operational disruption. The incident underscored the necessity for robust monitoring, strict access policies, and anomaly detection systems to prevent similar breaches.
Detecting Logic Bombs Planted by Insiders
Detecting logic bombs planted by insiders requires continuous monitoring of system behaviors and access patterns to identify unusual or unauthorized activity. Implementing advanced analytics and anomaly detection tools helps in recognizing dormant malicious code triggered by specific conditions. Establishing strict access controls and conducting regular audits minimize the risk of insider threats executing logic bombs within critical infrastructures.
Technical Analysis of Logic Bomb Code
A logic bomb in insider threats is a malicious code segment triggered by specific conditions such as dates, user actions, or system events, designed to execute unauthorized activities. Technical analysis reveals embedded logic that monitors system parameters or audit logs, delaying activation until predefined conditions are met to avoid detection. Code dissection often uncovers obfuscated functions and stealth routines that manipulate system processes, delete files, or exfiltrate data once triggered.
Impact of Logic Bombs on Organizational Security
Logic bombs embedded by insider threats can trigger devastating disruptions, such as data corruption, deletion, or unauthorized access, severely compromising organizational security. These malicious codes often activate under specific conditions, making detection difficult and allowing insiders to exploit trusts for espionage or sabotage. The resulting impact includes financial losses, reputational damage, and prolonged recovery efforts, emphasizing the critical need for robust insider threat detection and response systems.
Preventive Measures Against Insider Logic Bombs
Effective preventive measures against insider logic bombs include implementing strict access controls, continuous system monitoring, and regular code audits to detect unauthorized changes. Deploying behavioral analytics helps identify anomalous employee actions indicative of malicious intent. Enforcing comprehensive employee training and a robust incident response plan further mitigate risks associated with insider threats involving logic bombs.
Legal Consequences of Deploying Logic Bombs as an Insider
Deploying logic bombs as an insider constitutes a severe breach of cybersecurity laws, often resulting in criminal charges including unauthorized access, data destruction, and sabotage under statutes such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA). Convictions can lead to heavy fines, imprisonment, and civil lawsuits for damages incurred by the affected organization. Organizations may also seek restitution and implement stricter monitoring to deter future insider threats involving malicious code.
example of logic bomb in insider threat Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com