Steganography is a technique used in security to hide information within other non-secret data, making the presence of the hidden message undetectable. A common example is embedding secret text or binary data within an image file by altering the least significant bits of pixel values. This method ensures the carrier image appears unchanged while securely conveying confidential information. Another example involves hiding data in audio files by slightly modifying sound wave samples imperceptibly to human ears. Video files can also serve as carriers by embedding information in individual frames or their metadata without affecting playback quality. These steganographic techniques help protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and interception during transmission.
Table of Comparison
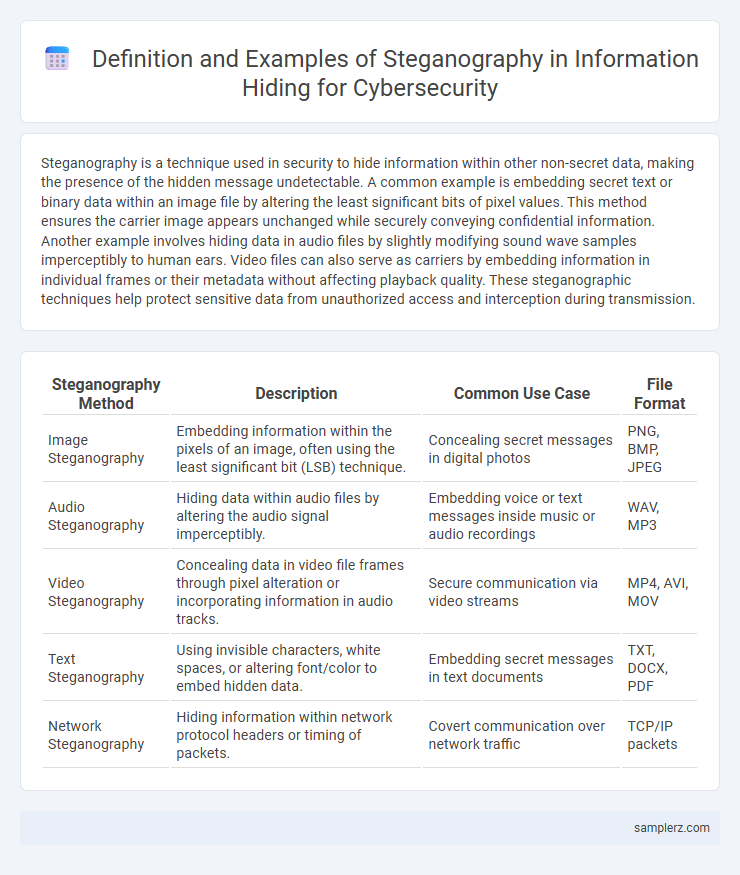
| Steganography Method | Description | Common Use Case | File Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Steganography | Embedding information within the pixels of an image, often using the least significant bit (LSB) technique. | Concealing secret messages in digital photos | PNG, BMP, JPEG |
| Audio Steganography | Hiding data within audio files by altering the audio signal imperceptibly. | Embedding voice or text messages inside music or audio recordings | WAV, MP3 |
| Video Steganography | Concealing data in video file frames through pixel alteration or incorporating information in audio tracks. | Secure communication via video streams | MP4, AVI, MOV |
| Text Steganography | Using invisible characters, white spaces, or altering font/color to embed hidden data. | Embedding secret messages in text documents | TXT, DOCX, PDF |
| Network Steganography | Hiding information within network protocol headers or timing of packets. | Covert communication over network traffic | TCP/IP packets |
Introduction to Steganography in Information Hiding
Steganography in information hiding involves embedding secret data within non-suspicious digital media such as images, audio, or video files to prevent detection. Common examples include hiding text messages within the least significant bits (LSB) of an image's pixel data or embedding confidential audio signals into background music tracks. This technique enhances security by concealing the very existence of the hidden information from unauthorized users and surveillance systems.
Historical Examples of Steganography Techniques
Ancient Greeks used wax tablets to conceal messages by writing on the wood beneath the wax, an early form of steganography. During World War II, invisible ink was extensively employed to hide secret military communications between agents. The use of microdots, tiny photographs embedded within a period or letter, allowed spies to transmit large amounts of information discretely and became a significant technique in espionage history.
Image-Based Steganography Methods
Image-based steganography methods embed secret data within digital images by altering pixel values or utilizing least significant bit (LSB) techniques, enabling covert communication without noticeable changes to the image quality. Techniques such as pixel value differencing (PVD) and discrete cosine transform (DCT) manipulation effectively hide information while maintaining image integrity and resisting visual detection. These methods support secure data transmission in cyber security by concealing sensitive information against unauthorized access or interception.
Audio and Video File Steganography
Audio and video file steganography enables covert communication by embedding secret data within multimedia files without perceptible changes. Techniques such as least significant bit (LSB) modification in audio streams and discrete cosine transform (DCT) manipulation in video frames are commonly used to hide information securely. These methods ensure robust protection against unauthorized access while maintaining the quality and integrity of the original media content.
Steganography in Text Files: Approaches and Examples
Steganography in text files employs techniques such as whitespace manipulation, character substitution, and invisible ink to conceal information within seemingly normal documents. Common methods include using zero-width spaces or altering font formatting to embed hidden messages without altering the visible content. These approaches enable secure data transmission by maintaining the natural appearance of the text while embedding confidential information imperceptibly.
Network Steganography: Hiding Data in Network Protocols
Network steganography involves embedding hidden data within network protocols such as TCP/IP, UDP, or HTTP headers, exploiting unused or redundant fields to transmit covert messages without detection. Techniques like manipulating the IP identification field or using TCP sequence numbers allow secure communication channels that evade traditional security monitoring tools. This method enhances data privacy by hiding information within normal network traffic, making it a critical consideration in advanced cybersecurity defense and threat analysis.
Steganography vs Cryptography: Key Distinctions
Steganography hides information within digital media such as images or audio files, making the existence of the message undetectable, whereas cryptography encrypts the content, rendering it unreadable without the decryption key. Unlike cryptography, which secures data through complex algorithms like AES or RSA, steganography embeds secret data inside benign carriers to maintain covert communication channels. Key distinctions also include steganography's emphasis on concealment of data presence, while cryptography focuses on data confidentiality and integrity.
Tools and Software for Implementing Steganography
Effective tools for implementing steganography include OpenPuff, QuickStego, and Steghide, which allow users to embed hidden data within digital media files such as images, audio, and video. OpenPuff supports multiple layers of encryption and various carriers, enhancing the security of concealed information. Steganography software typically integrates with cryptographic algorithms to ensure covert communication while maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
Real-World Cases of Steganography Usage
Steganography has been employed in real-world cyber espionage campaigns, where malicious actors embed sensitive data within innocuous image or audio files to evade detection. Government agencies and hackers alike have used steganographic techniques to secretly transmit classified information or malware via social media and email attachments. High-profile cases such as the Operation Shady RAT and the Russian Fancy Bear group illustrate how steganography facilitates covert communication and data exfiltration in cyber warfare.
Challenges and Detection of Steganographic Methods
Steganography challenges include the difficulty of detecting hidden information due to the subtle modification of digital media, such as images, audio, or video files. Advanced techniques like adaptive steganography dynamically alter embedding patterns, making traditional statistical detection methods less effective. Detection often requires specialized tools utilizing machine learning algorithms to analyze anomalies in payload distribution and media artifacts.
example of steganography in information hiding Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com