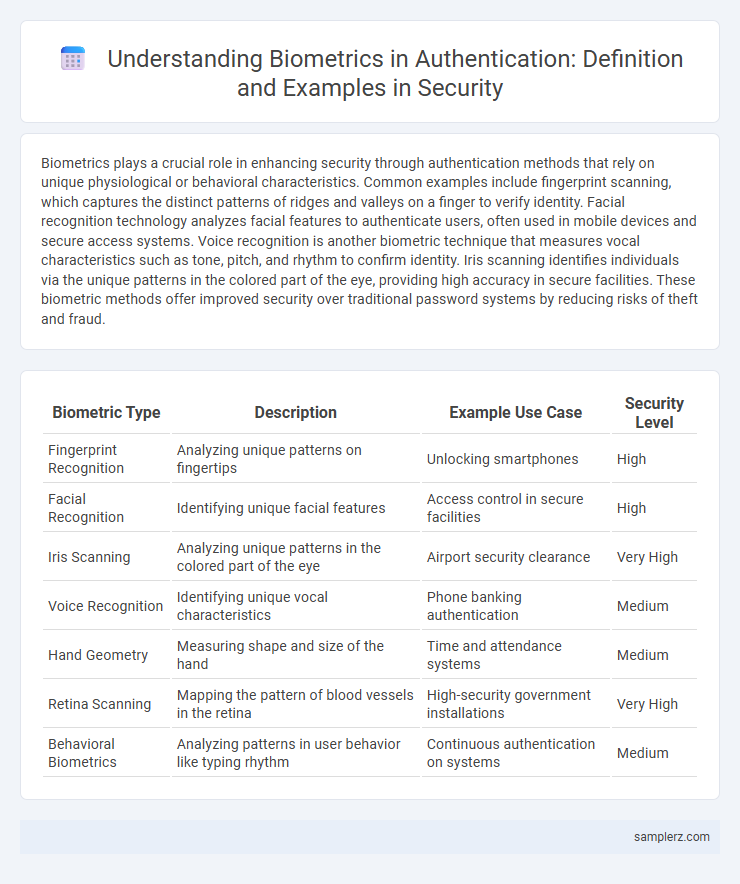
Biometrics plays a crucial role in enhancing security through authentication methods that rely on unique physiological or behavioral characteristics. Common examples include fingerprint scanning, which captures the distinct patterns of ridges and valleys on a finger to verify identity. Facial recognition technology analyzes facial features to authenticate users, often used in mobile devices and secure access systems. Voice recognition is another biometric technique that measures vocal characteristics such as tone, pitch, and rhythm to confirm identity. Iris scanning identifies individuals via the unique patterns in the colored part of the eye, providing high accuracy in secure facilities. These biometric methods offer improved security over traditional password systems by reducing risks of theft and fraud.
Table of Comparison
| Biometric Type | Description | Example Use Case | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fingerprint Recognition | Analyzing unique patterns on fingertips | Unlocking smartphones | High |
| Facial Recognition | Identifying unique facial features | Access control in secure facilities | High |
| Iris Scanning | Analyzing unique patterns in the colored part of the eye | Airport security clearance | Very High |
| Voice Recognition | Identifying unique vocal characteristics | Phone banking authentication | Medium |
| Hand Geometry | Measuring shape and size of the hand | Time and attendance systems | Medium |
| Retina Scanning | Mapping the pattern of blood vessels in the retina | High-security government installations | Very High |
| Behavioral Biometrics | Analyzing patterns in user behavior like typing rhythm | Continuous authentication on systems | Medium |
Introduction to Biometrics in Authentication
Biometrics in authentication leverages unique physiological and behavioral characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans to verify individual identities. These biometric modalities offer heightened security by reducing reliance on traditional passwords and PINs, which are susceptible to theft and guessing. Advanced biometric systems integrate multi-factor authentication and machine learning algorithms to enhance accuracy and prevent spoofing attacks.
Fingerprint Recognition: A Classic Biometric Method
Fingerprint recognition remains a cornerstone biometric method in authentication systems, leveraging the unique ridge patterns on individual fingers for precise identity verification. Its integration into smartphones, access control systems, and secure voting mechanisms highlights its widespread applicability and reliability. Continuous improvements in sensor technology and algorithmic accuracy enhance fingerprint recognition's effectiveness in preventing unauthorized access and identity fraud.
Facial Recognition for Secure Access
Facial recognition technology enhances secure access by analyzing unique facial features to verify identity with high accuracy. This biometric method uses advanced algorithms and AI to detect and match patterns, reducing the risk of unauthorized entry in sensitive environments. Organizations implement facial recognition systems in areas such as corporate buildings, smartphones, and airports to ensure both convenience and robust security.
Iris and Retina Scanning Technologies
Iris and retina scanning are advanced biometric authentication methods used to enhance security by analyzing unique patterns in the eye. Iris scanning captures the detailed texture of the colored ring surrounding the pupil, offering high accuracy and resistance to forgery due to its distinctive and stable features. Retina scanning examines the vascular pattern of blood vessels at the back of the eye, providing an extremely secure identification technique that is difficult to replicate or spoof.
Voice Recognition in Multi-Factor Authentication
Voice recognition enhances multi-factor authentication by using unique vocal characteristics as a secure biometric identifier. It adds an additional layer of security by verifying a user's identity through speech patterns, tone, and cadence. Integrating voice recognition with other factors like passwords or tokens significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access in security systems.
Behavioral Biometrics: Typing Dynamics and Gait Analysis
Behavioral biometrics leverage unique patterns in human behavior for authentication, with typing dynamics analyzing keystroke speed, rhythm, and pressure to identify users accurately. Gait analysis evaluates an individual's walking pattern using motion sensors or cameras to detect identity based on distinctive movement characteristics. These methods enhance security by continuously verifying users without relying solely on static credentials like passwords or fingerprints.
Palm Vein and Hand Geometry Identification
Palm vein and hand geometry identification are advanced biometric authentication methods that utilize unique physical characteristics to enhance security protocols. Palm vein authentication captures the pattern of veins using near-infrared light, providing a highly accurate and forgery-resistant identification process. Hand geometry recognition measures the shape and size of the hand, offering reliable verification with fast processing times, commonly used in access control and time attendance systems.
Ear Shape and Pattern Detection
Ear shape and pattern detection technology provides a unique biometric authentication method by analyzing the distinct contours and curves of an individual's ear. This approach offers high accuracy due to the ear's structural stability over time and resistance to environmental changes. Integrating ear biometrics enhances security systems by enabling non-intrusive, contactless identity verification in secure access control and surveillance applications.
Biometric Authentication in Mobile Devices
Biometric authentication in mobile devices leverages unique physiological features such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans to enhance security and user convenience. Advanced technologies like Apple's Face ID and Samsung's ultrasonic fingerprint sensors provide robust protection against unauthorized access by accurately verifying individual identities. Integration of biometric data with secure elements and encryption protocols ensures that sensitive information remains safeguarded during authentication processes.
Risks and Limitations of Biometric Security Systems
Biometric security systems, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, face risks including false positives and false negatives that can compromise authentication accuracy. These systems are vulnerable to spoofing attacks where attackers use fake biometric samples to bypass security. Additionally, biometric data breaches pose significant privacy concerns since biometric traits are immutable and cannot be changed if compromised.
example of biometrics in authentication Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com