Polyuria is a common symptom in diabetes characterized by excessive urination due to high blood glucose levels. When blood sugar exceeds the renal threshold, the kidneys excrete glucose into the urine, causing an osmotic diuresis. This process increases urine volume significantly, leading to frequent urination in patients with uncontrolled diabetes. In diabetic patients, polyuria can serve as an early indicator of poor glycemic control. Persistent hyperglycemia forces the kidneys to eliminate excess glucose, resulting in continuous fluid loss. Monitoring symptoms such as polyuria helps healthcare professionals adjust treatment plans to manage blood sugar effectively and prevent complications.
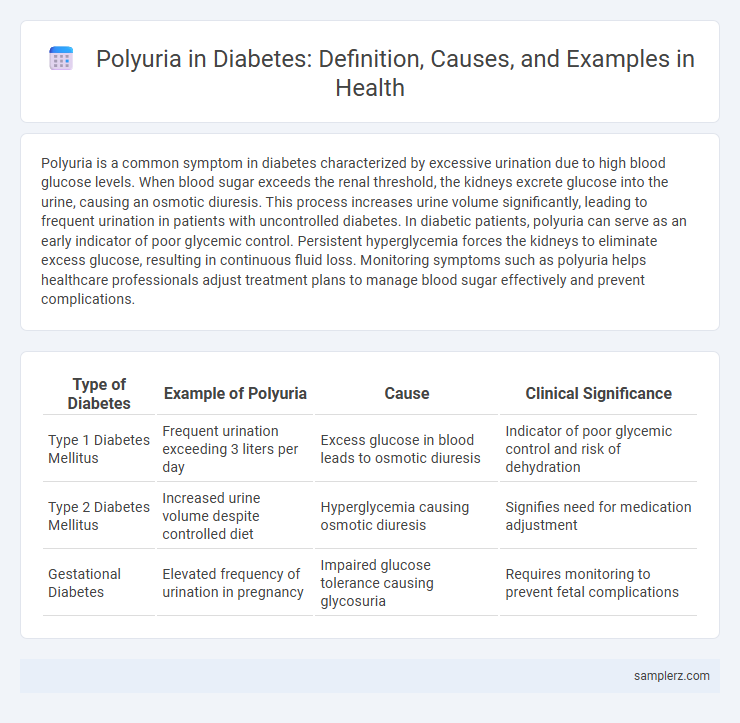
Table of Comparison
| Type of Diabetes | Example of Polyuria | Cause | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus | Frequent urination exceeding 3 liters per day | Excess glucose in blood leads to osmotic diuresis | Indicator of poor glycemic control and risk of dehydration |
| Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Increased urine volume despite controlled diet | Hyperglycemia causing osmotic diuresis | Signifies need for medication adjustment |
| Gestational Diabetes | Elevated frequency of urination in pregnancy | Impaired glucose tolerance causing glycosuria | Requires monitoring to prevent fetal complications |
Understanding Polyuria: A Common Diabetes Symptom
Polyuria in diabetes is characterized by excessive urination, often exceeding 3 liters per day, due to high blood glucose levels causing osmotic diuresis. This symptom commonly occurs in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, where the kidneys expel excess glucose through urine, leading to dehydration and increased thirst. Recognizing polyuria is crucial for early diabetes detection and effective blood sugar management.
How Diabetes Triggers Excessive Urination
Diabetes triggers excessive urination, or polyuria, due to high blood glucose levels causing the kidneys to filter and excrete excess sugar through urine. This osmotic diuresis increases urine volume as water follows glucose out of the body, leading to dehydration and frequent urination. Uncontrolled hyperglycemia in diabetes intensifies this process, resulting in persistent polyuria symptoms.
Classic Examples of Polyuria in Diabetic Patients
Classic examples of polyuria in diabetic patients include frequent urination caused by excessive blood glucose levels leading to osmotic diuresis. Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus results in high plasma glucose concentrations that exceed renal threshold, causing glucose to spill into urine and increase urine volume. This symptom often accompanies polydipsia and is a key indicator of poor glycemic control in diabetes management.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs of Polyuria
Frequent urination, especially producing large volumes of dilute urine, is a key early warning sign of polyuria in diabetes mellitus. Elevated blood glucose levels cause osmotic diuresis, leading to increased urine output that often precedes other symptoms like excessive thirst and fatigue. Timely recognition of these urinary changes enables prompt medical intervention to prevent complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Blood Sugar Levels and Their Link to Polyuria
Elevated blood sugar levels in diabetes cause the kidneys to filter excess glucose, leading to increased urine production, a condition known as polyuria. High glucose concentration in the bloodstream results in osmotic diuresis, where excess sugar pulls water into the urine, increasing volume. Monitoring and managing blood sugar levels is crucial to reduce the risk of polyuria and related dehydration complications.
Day-to-Day Manifestations of Polyuria in Diabetes
Polyuria in diabetes manifests through frequent urination, often exceeding 3 liters per day, disrupting sleep with nocturia and increasing dehydration risk. Elevated blood glucose levels lead to osmotic diuresis, causing excessive fluid loss and electrolyte imbalance, which may result in fatigue and dizziness. Managing daily fluid intake and monitoring blood glucose are essential to control these symptoms and prevent complications.
Differentiating Polyuria from Other Urinary Issues
Polyuria in diabetes is characterized by excessive urination exceeding 3 liters per day, often caused by high blood glucose levels leading to osmotic diuresis. Unlike urinary tract infections or bladder disorders, diabetic polyuria is not accompanied by pain, burning sensation, or urgency but is primarily linked to increased urine volume and thirst. Accurate diagnosis involves measuring blood glucose and urine output to distinguish diabetic polyuria from other urinary problems like cystitis or interstitial cystitis.
Impact of Polyuria on Daily Life with Diabetes
Polyuria in diabetes leads to frequent urination, disrupting sleep patterns and causing dehydration, which impairs concentration and energy levels throughout the day. This increased urinary frequency can interfere with work, social activities, and overall productivity, significantly affecting quality of life. Managing polyuria through proper blood glucose control is essential to minimize its impact on daily routines and maintain optimal health.
Medical Tests for Diagnosing Polyuria in Diabetes
Polyuria in diabetes is often diagnosed through medical tests such as urinalysis, which measures urine volume and glucose levels, and blood tests assessing blood glucose and electrolyte balance. A 24-hour urine collection test helps quantify excessive urine output, confirming polyuria. Monitoring glycosuria and plasma osmolality further supports identifying uncontrolled diabetes causing polyuria.
Managing and Reducing Polyuria in Diabetic Patients
Managing and reducing polyuria in diabetic patients involves maintaining optimal blood glucose levels through consistent insulin therapy and dietary control. Adequate hydration is crucial to prevent dehydration caused by excessive urination, while monitoring electrolyte balance helps avoid complications. Regular consultations with healthcare providers facilitate personalized treatment adjustments to effectively control polyuria and improve overall diabetes management.
example of polyuria in diabetes Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com