Alexithymia is a psychological condition characterized by difficulty in identifying and expressing emotions. Individuals with alexithymia often struggle to recognize their own feelings and may have trouble describing emotions to others. This disorder is commonly identified through clinical assessments that evaluate emotional awareness and verbal expression. Research indicates that alexithymia is linked to various mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Neuroimaging studies show that affected individuals may exhibit reduced activity in brain regions responsible for emotional processing, including the anterior cingulate cortex and insula. Treatment approaches often involve psychotherapy focused on improving emotional recognition and communication skills.
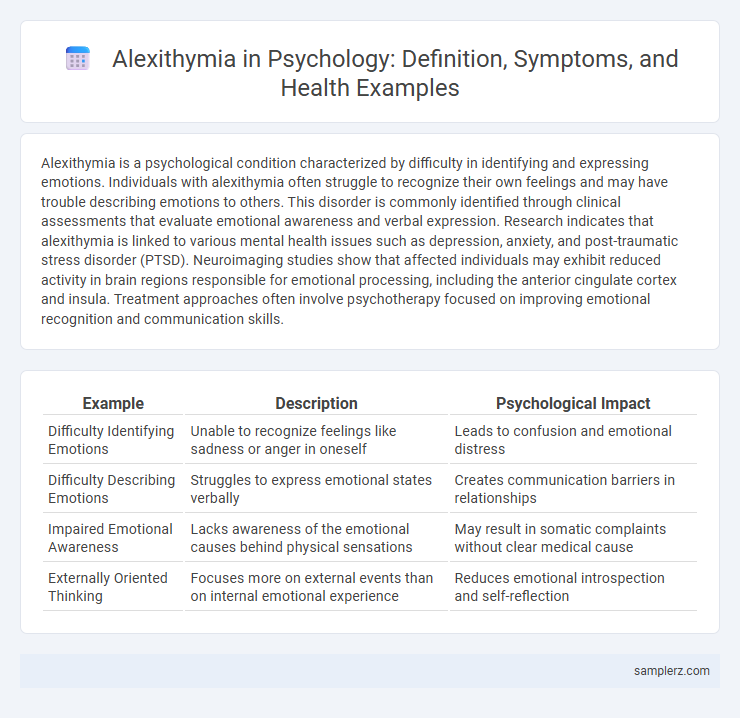
Table of Comparison
| Example | Description | Psychological Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Difficulty Identifying Emotions | Unable to recognize feelings like sadness or anger in oneself | Leads to confusion and emotional distress |
| Difficulty Describing Emotions | Struggles to express emotional states verbally | Creates communication barriers in relationships |
| Impaired Emotional Awareness | Lacks awareness of the emotional causes behind physical sensations | May result in somatic complaints without clear medical cause |
| Externally Oriented Thinking | Focuses more on external events than on internal emotional experience | Reduces emotional introspection and self-reflection |
Understanding Alexithymia: Definition and Core Features
Alexithymia is characterized by difficulty identifying and describing emotions, often leading to challenges in emotional awareness and communication. Core features include a limited ability to verbalize feelings, a constricted imagination, and a tendency to focus on external events rather than internal experiences. This condition can significantly impact interpersonal relationships and mental health, highlighting the importance of targeted psychological interventions.
Common Psychological Signs of Alexithymia
Alexithymia commonly presents with difficulty identifying and describing emotions, leading to challenges in interpersonal communication and emotional regulation. Individuals often exhibit a limited imagination and an externally oriented thinking style, focusing on concrete details rather than feelings. These psychological signs contribute to increased risk of anxiety, depression, and psychosomatic disorders.
Emotional Awareness Deficits in Alexithymia
Alexithymia is characterized by significant emotional awareness deficits, where individuals struggle to identify and describe their own emotions, often leading to impaired emotional processing and interpersonal difficulties. Neuroimaging studies reveal reduced activity in the anterior cingulate cortex and insula, brain regions crucial for emotional awareness and regulation. These deficits contribute to challenges in emotional recognition, limiting effective communication and emotional self-regulation in affected individuals.
Communication Barriers in Individuals with Alexithymia
Individuals with alexithymia often experience significant communication barriers due to difficulties in identifying and expressing emotions, leading to challenges in social interactions and emotional understanding. This impairment in emotional awareness disrupts their ability to convey feelings accurately, resulting in misunderstandings and social isolation. Psychological assessments highlight the need for targeted interventions to improve emotional communication skills and enhance interpersonal relationships in these individuals.
Alexithymia and Its Impact on Mental Health
Alexithymia is characterized by difficulty identifying and expressing emotions, often leading to challenges in emotional regulation and interpersonal relationships. This condition is linked to increased risk of depression, anxiety, and psychosomatic disorders, highlighting its significant impact on overall mental health. Research indicates that individuals with alexithymia may struggle in psychotherapy due to limited emotional insight, necessitating tailored therapeutic approaches for effective treatment.
Real-life Example of Alexithymia in Clinical Settings
In clinical settings, a patient with alexithymia may repeatedly describe physical symptoms like chest pain or fatigue without identifying underlying emotional distress such as anxiety or depression. Therapists often observe difficulties in verbalizing feelings, as the individual struggles to connect bodily sensations to specific emotions, complicating accurate diagnosis and treatment. Effective interventions include cognitive-behavioral therapy aimed at enhancing emotional awareness and communication skills, which improve patient outcomes in managing alexithymia-related challenges.
Alexithymia in Children and Adolescents
Alexithymia in children and adolescents manifests as difficulty identifying and expressing emotions, often leading to social withdrawal and impaired interpersonal relationships. Studies indicate that up to 10% of youth show symptoms consistent with alexithymia, which correlates with increased risks of anxiety, depression, and behavioral problems. Early intervention through emotional awareness training and therapeutic support can significantly improve emotional regulation and psychosocial outcomes in affected young populations.
Relationship Challenges Linked to Alexithymia
Individuals with alexithymia often struggle to identify and express emotions, leading to misunderstandings and emotional distance in romantic relationships. This condition impairs effective communication, causing partners to feel disconnected or unsupported due to the alexithymic individual's difficulty in recognizing their own feelings. Studies reveal that alexithymia is associated with higher rates of relationship dissatisfaction and increased conflict, highlighting the critical need for targeted therapeutic interventions.
Alexithymia and Co-occurring Health Conditions
Alexithymia, characterized by difficulty identifying and expressing emotions, frequently co-occurs with mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Studies reveal a strong correlation between alexithymia and psychosomatic illnesses, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and chronic pain syndromes, highlighting the mind-body connection. Early identification of alexithymia in patients with these co-occurring health conditions can improve therapeutic outcomes through targeted emotional awareness interventions.
Therapeutic Approaches for Managing Alexithymia
Therapeutic approaches for managing alexithymia primarily include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based interventions, which help individuals identify and articulate emotions. Emotion-focused therapy (EFT) also proves effective by encouraging emotional awareness and processing. Structured psychoeducational programs enhance emotional literacy, significantly improving communication and interpersonal functioning in patients with alexithymia.
example of alexithymia in psychology Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com