Pica is a eating disorder characterized by the consumption of non-food items, which can pose serious health risks. Common examples include eating dirt, chalk, or paper, substances that provide no nutritional value and may lead to gastrointestinal blockages or poisoning. This disorder is often observed in individuals with nutritional deficiencies, developmental disorders, or during pregnancy, highlighting the need for medical evaluation and intervention. In clinical settings, pica diagnosis relies on identifying persistent ingestion of inappropriate substances over a period of at least one month. Treatment involves addressing any underlying nutritional deficiencies, such as iron or zinc, and implementing behavioral therapies to reduce harmful eating behaviors. Monitoring the patient's health closely is crucial to prevent complications like lead poisoning or parasitic infections caused by ingestion of contaminated materials.
Table of Comparison
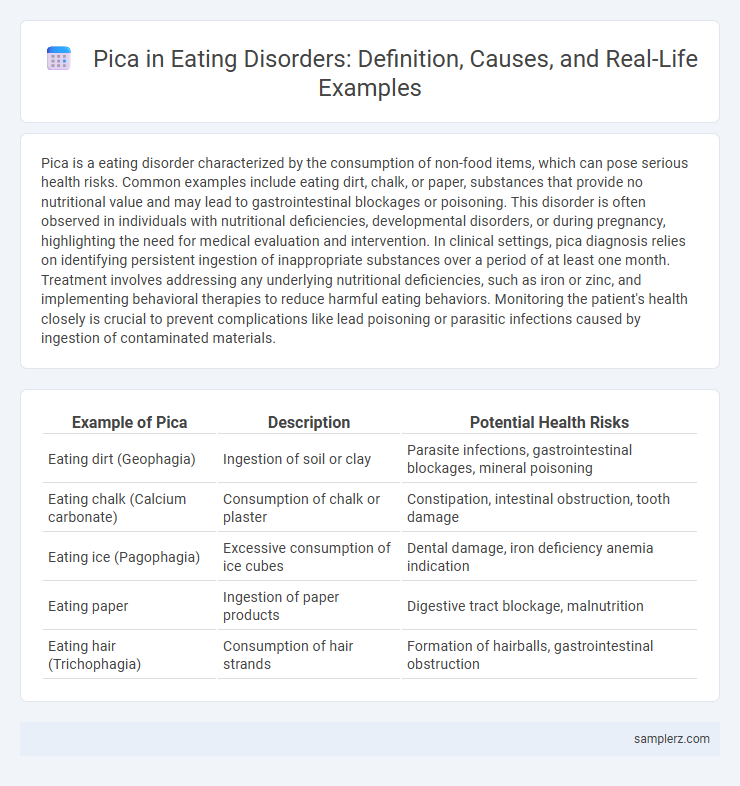
| Example of Pica | Description | Potential Health Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Eating dirt (Geophagia) | Ingestion of soil or clay | Parasite infections, gastrointestinal blockages, mineral poisoning |
| Eating chalk (Calcium carbonate) | Consumption of chalk or plaster | Constipation, intestinal obstruction, tooth damage |
| Eating ice (Pagophagia) | Excessive consumption of ice cubes | Dental damage, iron deficiency anemia indication |
| Eating paper | Ingestion of paper products | Digestive tract blockage, malnutrition |
| Eating hair (Trichophagia) | Consumption of hair strands | Formation of hairballs, gastrointestinal obstruction |
Common Types of Non-Food Items Consumed in Pica
Pica, an eating disorder characterized by the persistent consumption of non-food items, commonly involves substances like dirt, clay, chalk, ice, and paper. These items pose significant health risks such as gastrointestinal blockages, poisoning, and infections. Identifying the typical non-food substances ingested is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment of pica.
Pica in Children: Unusual Eating Habits
Pica in children manifests as the compulsive ingestion of non-food substances like dirt, clay, chalk, or paper, often persisting for at least one month and causing potential nutritional deficiencies or gastrointestinal complications. This unusual eating habit is frequently linked to developmental disorders, iron-deficiency anemia, and environmental factors such as exposure to lead-contaminated soil. Early diagnosis and behavioral interventions are critical to prevent severe health consequences and promote normal dietary patterns.
Geophagy: The Practice of Eating Soil
Geophagy, a form of pica, involves the compulsive consumption of soil or clay and is often observed in individuals with eating disorders. This practice can lead to significant health risks such as gastrointestinal obstruction, parasitic infections, and mineral imbalances like iron-deficiency anemia. Understanding the nutritional deficiencies or psychological triggers behind geophagy is crucial for effective treatment and management in clinical settings.
Pagophagia: Craving and Eating Ice
Pagophagia, a subtype of pica characterized by compulsive ice chewing, is often linked to iron deficiency anemia and nutritional imbalances. This eating disorder manifests as an intense craving for ice despite the absence of thirst, potentially leading to dental damage and disrupted oral health. Recognizing pagophagia early is crucial for diagnosing underlying iron deficiency and preventing related complications.
Amylophagia: Eating Starch-Based Substances
Amylophagia, a subtype of pica, involves the compulsive consumption of starch-based substances like raw potatoes, cornstarch, or flour, often linked to nutritional deficiencies or psychological disorders. This behavior can lead to gastrointestinal complications such as constipation, intestinal obstruction, and malnutrition due to the inability to digest non-food substances. Clinical management requires addressing underlying nutrient deficiencies, behavioral therapy, and monitoring for associated medical conditions like iron-deficiency anemia.
Trichophagia: Ingesting Hair or Fibers
Trichophagia, a rare eating disorder, involves the compulsive ingestion of hair or fibers, often leading to severe digestive complications such as bezoars or intestinal blockages. Patients frequently present with symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, requiring timely medical intervention and behavioral therapy. Effective treatment combines psychiatric support and dietary management to prevent recurrence and promote gastrointestinal health.
Coprophagia: Consuming Fecal Matter
Coprophagia, a rare form of pica, involves the compulsive consumption of fecal matter, often linked to severe psychiatric disorders or extreme nutritional deficiencies. This behavior poses significant health risks including bacterial infections, parasitic infestations, and gastrointestinal complications. Effective treatment requires multidisciplinary intervention combining psychiatric evaluation, nutritional support, and behavioral therapy.
Pica and Pregnancy: Unusual Cravings in Expectant Mothers
Pica during pregnancy involves the compulsive consumption of non-food substances such as dirt, chalk, or ice, which poses significant health risks like anemia and nutritional deficiencies. This eating disorder is often linked to mineral imbalances and heightened nutritional demands in expectant mothers. Proper diagnosis and dietary management are essential to prevent adverse outcomes for both mother and fetus.
Pica in Individuals with Developmental Disorders
Pica, characterized by the persistent ingestion of non-food substances such as dirt, clay, or paper, is frequently observed in individuals with developmental disorders like autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability. This feeding behavior can lead to serious medical complications including gastrointestinal obstruction, poisoning, and malnutrition. Effective management involves multidisciplinary approaches combining behavioral interventions and medical monitoring to ensure safety and nutritional adequacy.
Health Risks Associated with Pica Behaviors
Pica behaviors, such as consuming non-food items like dirt, chalk, or paper, pose significant health risks including intestinal blockages, poisoning, and infections. Nutritional deficiencies and dental injuries are common complications resulting from persistent ingestion of harmful substances. Prompt medical intervention is essential to manage potential toxic exposure and prevent long-term gastrointestinal damage.
example of pica in eating disorder Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com