A prodrome is an early symptom indicating the onset of a disease before more characteristic signs appear. In the case of measles, the prodrome phase typically includes fever, cough, runny nose, and conjunctivitis lasting 2 to 4 days. These early symptoms signal the approaching appearance of the distinctive measles rash, which confirms the diagnosis. Another example of a prodrome occurs in migraine headaches, where patients may experience visual disturbances, such as flashing lights or blind spots, hours to days before the headache starts. This sensory abnormality acts as a warning sign for the subsequent migraine attack. Recognizing these prodromal symptoms can help individuals manage or mitigate the severity of the disease.
Table of Comparison
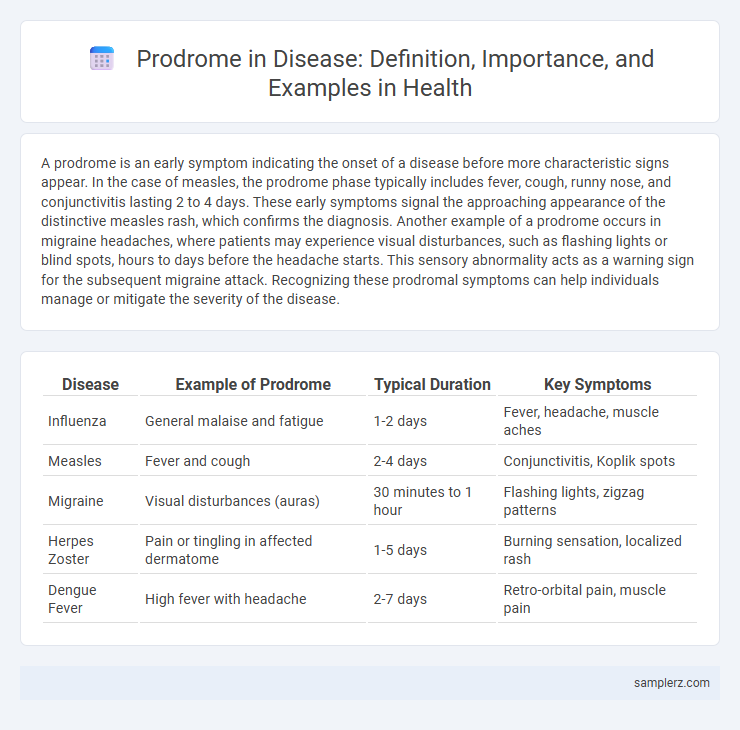
| Disease | Example of Prodrome | Typical Duration | Key Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza | General malaise and fatigue | 1-2 days | Fever, headache, muscle aches |
| Measles | Fever and cough | 2-4 days | Conjunctivitis, Koplik spots |
| Migraine | Visual disturbances (auras) | 30 minutes to 1 hour | Flashing lights, zigzag patterns |
| Herpes Zoster | Pain or tingling in affected dermatome | 1-5 days | Burning sensation, localized rash |
| Dengue Fever | High fever with headache | 2-7 days | Retro-orbital pain, muscle pain |
Understanding Prodrome: Early Warning Signs in Disease
Prodrome refers to the early symptoms or signs indicating the onset of a disease before more specific symptoms appear, such as fatigue, headaches, and mood changes in migraines. Recognizing these prodromal symptoms enables timely intervention and better disease management. In infectious diseases like measles, prodrome typically includes fever, cough, and conjunctivitis preceding the characteristic rash.
Common Diseases and Their Prodromal Symptoms
Prodromal symptoms often signal the onset of common diseases such as influenza, where early signs include fatigue, headache, and muscle aches before fever develops. In infectious mononucleosis, patients frequently experience sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and mild fever during the prodromal phase. Recognizing these early symptoms is critical for prompt diagnosis and effective management of many illnesses.
Migraine: Recognizing the Prodromal Phase
The prodromal phase of migraine often includes early warning signs such as mood changes, food cravings, and increased urination occurring hours to days before headache onset. Identifying these symptoms can help patients initiate preventive measures and manage triggers effectively. Recognizing the migraine prodrome enhances early intervention, potentially reducing attack severity and frequency.
Prodrome in Infectious Diseases: Case Studies
Prodrome in infectious diseases often manifests as early, nonspecific symptoms such as fever, malaise, and headache before the onset of more definitive signs. For example, in measles, the prodromal phase includes Koplik spots and a high fever preceding the characteristic rash. Influenza commonly presents with a prodrome of fatigue, chills, and myalgia, signaling the body's initial response to viral infection.
Prodromal Indicators of Neurological Disorders
Prodromal indicators of neurological disorders often include subtle cognitive impairments, mood changes, and sensory disturbances that precede overt symptoms. For instance, in Parkinson's disease, early signs such as anosmia, REM sleep behavior disorder, and constipation can act as prodromal markers. Identifying these early warning signals facilitates timely diagnosis and intervention, which is crucial for disease management and improving patient outcomes.
Mental Health Conditions with Notable Prodromal Stages
Prodromal stages in mental health conditions often manifest as subtle symptoms such as mood changes, sleep disturbances, or cognitive impairments before the onset of full-blown disorders. Schizophrenia, for instance, frequently presents a prodrome characterized by social withdrawal, decreased motivation, and unusual thought patterns. Early identification of these prodromal signs can facilitate timely intervention, potentially improving long-term outcomes for individuals at risk.
Role of Prodrome in Early Disease Detection
Prodrome symptoms serve as early warning signs in diseases like migraine, herpes zoster, and Parkinson's disease, enabling timely intervention before the full onset of illness. Recognizing prodromal features such as mood changes, muscle weakness, or localized pain enhances early diagnosis and can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Healthcare providers leveraging prodrome identification can reduce disease progression and optimize patient management in clinical practice.
Managing Symptoms During the Prodromal Period
Early detection of prodromal symptoms, such as fatigue and mild fever in diseases like multiple sclerosis or herpes zoster, enables proactive symptom management. Implementing rest, hydration, and appropriate medications during this period can reduce severity and improve patient outcomes. Timely intervention during the prodromal phase is critical for slowing disease progression and enhancing quality of life.
Importance of Patient Awareness About Prodrome
Recognizing prodromal symptoms, such as the aura experienced before a migraine or the early fever and malaise preceding influenza, enables timely intervention and improved disease outcomes. Patient awareness of these initial signs facilitates prompt medical consultation, reducing complications and enhancing treatment effectiveness. Educating patients on common prodromal indicators empowers proactive health management and early detection of serious conditions.
Future Research Directions for Prodromal Markers
Prodromal markers in diseases such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and multiple sclerosis offer critical insights for early diagnosis and intervention. Future research should emphasize identifying reliable biological, neuroimaging, and genetic biomarkers to enhance predictive accuracy and personalized treatment strategies. Advancements in machine learning and longitudinal cohort studies are essential for validating prodromal symptoms and improving prognostic models in clinical practice.
example of prodrome in disease Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com