Sensory reeducation in rehabilitation involves techniques designed to restore and enhance sensory function after nerve injury or stroke. One common example is texture discrimination training, where patients are exposed to various materials such as sandpaper, silk, or cotton to retrain the brain to recognize different tactile sensations. Another method includes using graded stimuli like vibration, temperature changes, or light touch to progressively improve sensory perception. This rehabilitation approach often incorporates repetitive sensory tasks that stimulate the affected area, promoting neuroplasticity and improving sensory processing. Mirror therapy serves as another example, providing visual feedback to help patients regain sensory and motor function by tricking the brain into perceiving movement in an affected limb. Sensory reeducation plays a crucial role in enhancing fine motor skills and reducing sensory deficits, leading to better functional outcomes in health recovery.
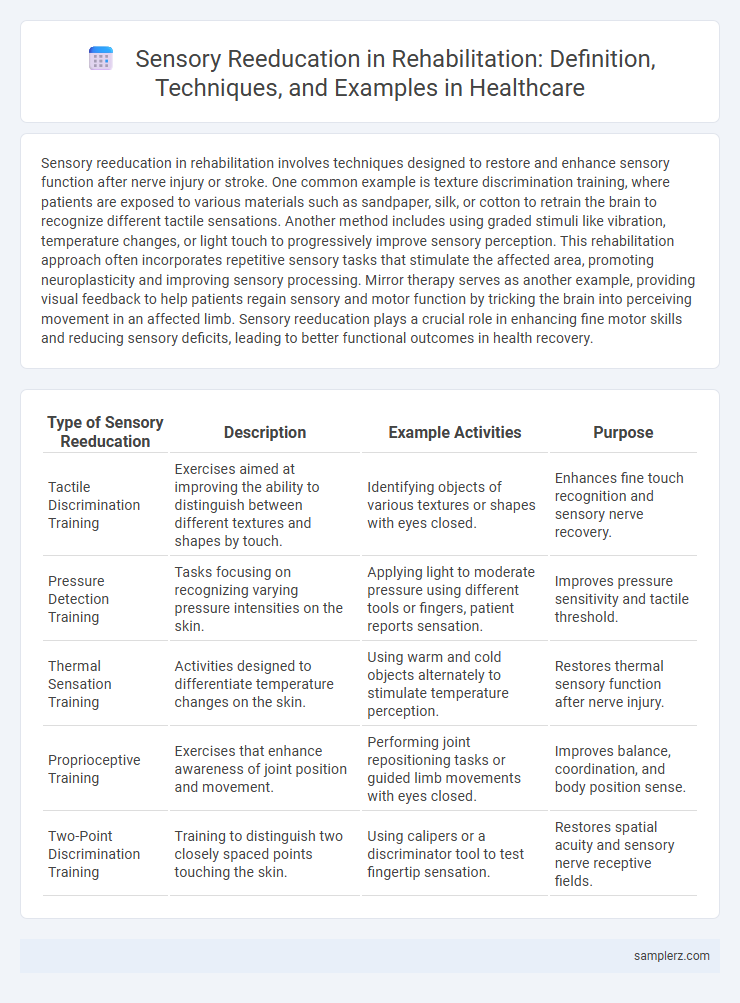
Table of Comparison
| Type of Sensory Reeducation | Description | Example Activities | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tactile Discrimination Training | Exercises aimed at improving the ability to distinguish between different textures and shapes by touch. | Identifying objects of various textures or shapes with eyes closed. | Enhances fine touch recognition and sensory nerve recovery. |
| Pressure Detection Training | Tasks focusing on recognizing varying pressure intensities on the skin. | Applying light to moderate pressure using different tools or fingers, patient reports sensation. | Improves pressure sensitivity and tactile threshold. |
| Thermal Sensation Training | Activities designed to differentiate temperature changes on the skin. | Using warm and cold objects alternately to stimulate temperature perception. | Restores thermal sensory function after nerve injury. |
| Proprioceptive Training | Exercises that enhance awareness of joint position and movement. | Performing joint repositioning tasks or guided limb movements with eyes closed. | Improves balance, coordination, and body position sense. |
| Two-Point Discrimination Training | Training to distinguish two closely spaced points touching the skin. | Using calipers or a discriminator tool to test fingertip sensation. | Restores spatial acuity and sensory nerve receptive fields. |
Introduction to Sensory Reeducation in Rehabilitation
Sensory reeducation in rehabilitation targets the restoration of tactile and proprioceptive functions following nerve injuries or strokes, employing techniques such as texture discrimination, localization exercises, and graded sensory stimuli exposure. Effective sensory reeducation enhances neural plasticity and improves patients' ability to interpret sensory information critical for daily activities and motor control. Clinical studies demonstrate that personalized sensory retraining programs significantly accelerate recovery and functional independence in individuals with peripheral neuropathies or central nervous system damage.
Understanding the Goals of Sensory Reeducation
Sensory reeducation aims to restore functional sensory perception after nerve injury by retraining the brain to interpret tactile stimuli correctly. Techniques such as repetitive touch discrimination tasks and graded exposure to different textures help improve sensory accuracy and enhance neuroplasticity. Achieving improved sensory discrimination supports better motor function and reduces the risk of injury by enhancing protective sensation.
Common Conditions Requiring Sensory Reeducation
Common conditions requiring sensory reeducation in rehabilitation include peripheral nerve injuries, stroke, and diabetic neuropathy, which often result in impaired tactile perception and proprioception. Techniques such as graded texture discrimination, vibration therapy, and sensory threshold training are applied to restore sensory function and enhance motor control. These targeted interventions promote neural plasticity and functional recovery by retraining the brain to interpret sensory input accurately.
Key Principles in Sensory Reeducation Therapy
Sensory reeducation therapy emphasizes the principles of graded exposure, where patients progressively experience different textures and stimuli to enhance neural plasticity. Consistent repetition and focused attention during therapy sessions help retrain sensory pathways and improve tactile discrimination. Integrating patient motivation and functional relevance ensures more effective and sustainable sensory recovery outcomes.
Tactile Discrimination Training Techniques
Tactile discrimination training techniques in sensory reeducation involve exercises that improve the ability to distinguish textures, shapes, and objects through touch, enhancing neural plasticity after nerve injury. Common methods include the use of graded textures, shape sorting, and object identification tasks to refine sensory input processing. These techniques accelerate recovery of tactile function, optimize hand dexterity, and reduce sensory deficits in patients undergoing rehabilitation.
Texture Identification Exercises for Sensory Recovery
Texture identification exercises play a crucial role in sensory reeducation by enhancing the brain's ability to recognize and differentiate various tactile stimuli. Patients engage with materials such as sandpaper, silk, cotton, or rubber to retrain nerve pathways and improve somatosensory perception. Consistent practice with these textures accelerates sensory recovery, particularly following nerve injuries or stroke rehabilitation.
Mirror Therapy as a Sensory Reeducation Tool
Mirror therapy serves as an effective sensory reeducation tool in rehabilitation by using visual feedback to retrain the brain and restore sensory perception in patients with phantom limb pain or stroke-induced hemiparesis. This technique involves placing a mirror between limbs, allowing the patient to observe the reflection of the healthy limb performing movements, which helps rewire neural pathways and improve motor function. Research indicates significant improvements in sensory discrimination and reduction of pain symptoms when mirror therapy is integrated into rehabilitation programs.
Use of Graded Sensory Stimulation in Practice
Graded sensory stimulation in rehabilitation involves systematically exposing patients to varying intensities of tactile, thermal, or proprioceptive stimuli to enhance sensory recovery after nerve injury or stroke. Techniques include using textured materials, temperature variations, and vibration devices to progressively retrain sensory pathways and improve functional outcomes. Research demonstrates that consistent graded stimulation promotes cortical reorganization and better integration of sensory input, crucial for restoring hand dexterity and tactile discrimination.
Home-Based Sensory Reeducation Activities
Home-based sensory reeducation activities in rehabilitation often include tactile discrimination tasks such as identifying objects of varying textures, temperatures, and weights using the affected limb to enhance neural plasticity. Patients may perform sensory threshold training by using graded stimulation tools like brushes or vibration devices to improve sensory perception and nerve function recovery. Incorporating proprioceptive exercises, such as joint position matching or mirror therapy, further supports functional motor integration and sensory pathway remodeling.
Monitoring Progress and Outcomes in Sensory Rehabilitation
Monitoring progress in sensory rehabilitation involves regular assessments using standardized tools like the Semmes-Weinstein Monofilaments for touch sensitivity and the Two-Point Discrimination test to evaluate spatial acuity recovery. Objective measures such as neurophysiological recordings and patient-reported outcome scales help track improvements and adapt therapeutic interventions for optimal sensory reeducation. These methods provide quantifiable data essential for tailoring rehabilitation strategies and maximizing functional recovery.
example of sensory reeducation in rehabilitation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com