Comorbidity in diabetes often includes hypertension, which significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular complications. Data from the American Diabetes Association reveal that nearly 70% of adults with diabetes also suffer from high blood pressure. This combination exacerbates the management challenges and contributes to higher morbidity rates. Another common comorbidity is diabetic retinopathy, affecting approximately one-third of diabetic patients worldwide. Studies show that prolonged hyperglycemia leads to microvascular damage in the retina, resulting in vision impairment or blindness. Monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels are critical to reducing the incidence of these diabetic complications.
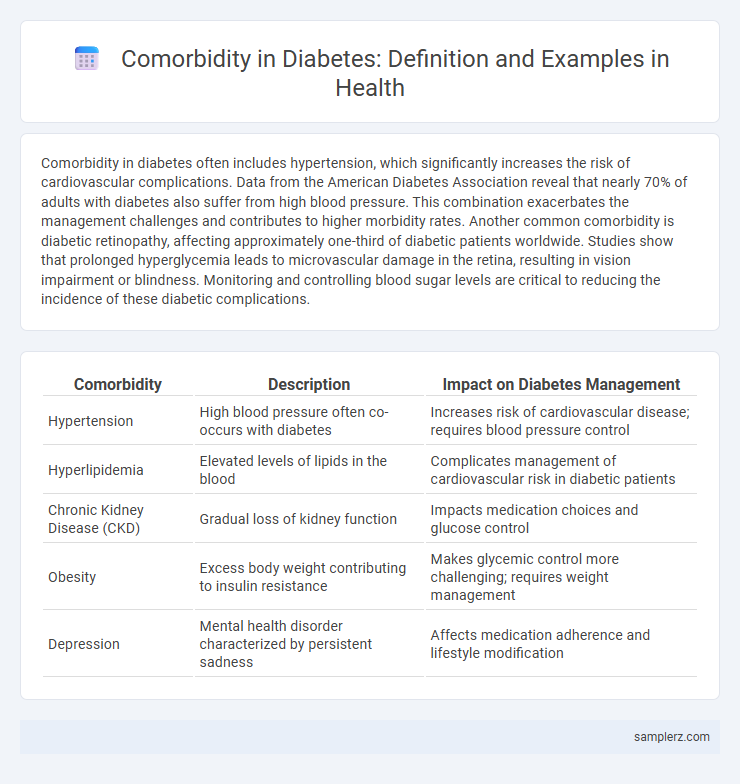
Table of Comparison
| Comorbidity | Description | Impact on Diabetes Management |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | High blood pressure often co-occurs with diabetes | Increases risk of cardiovascular disease; requires blood pressure control |
| Hyperlipidemia | Elevated levels of lipids in the blood | Complicates management of cardiovascular risk in diabetic patients |
| Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | Gradual loss of kidney function | Impacts medication choices and glucose control |
| Obesity | Excess body weight contributing to insulin resistance | Makes glycemic control more challenging; requires weight management |
| Depression | Mental health disorder characterized by persistent sadness | Affects medication adherence and lifestyle modification |
Common Comorbidities Associated with Diabetes
Common comorbidities associated with diabetes include hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease, which significantly increase morbidity and mortality risks. Diabetic patients frequently present with obesity and dyslipidemia, further complicating glycemic control and overall health management. Effective treatment plans require addressing these interconnected conditions to reduce complications and improve patient outcomes.
Hypertension: A Frequent Companion to Diabetes
Hypertension frequently coexists with diabetes, affecting approximately 60-80% of diabetic patients and significantly increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. The interplay between elevated blood glucose and high blood pressure accelerates endothelial dysfunction and promotes atherosclerosis. Effective management of both conditions through lifestyle modification and pharmacotherapy is crucial to reduce morbidity and mortality in diabetic populations.
Cardiovascular Disease Risks in Diabetic Patients
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a common comorbidity in diabetic patients, significantly increasing morbidity and mortality rates. Elevated blood glucose levels contribute to endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerosis, and hypertension, which are key risk factors for heart attacks and strokes in this population. Effective management of diabetes includes controlling blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol to reduce cardiovascular risks.
Obesity and Its Link to Diabetes Comorbidity
Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by promoting insulin resistance and chronic inflammation. Excess adipose tissue alters glucose metabolism and impairs pancreatic beta-cell function, exacerbating diabetic conditions. Managing obesity through lifestyle interventions is crucial in preventing and controlling diabetes comorbidity, improving overall metabolic health.
Diabetic Nephropathy and Chronic Kidney Disease
Diabetic nephropathy is a common comorbidity in patients with diabetes, characterized by progressive kidney damage due to high blood sugar levels. This condition often leads to chronic kidney disease (CKD), marked by a gradual loss of kidney function and increased risk of end-stage renal disease. Early detection and management of diabetic nephropathy are crucial to slowing CKD progression and reducing the burden of complications in diabetic patients.
Mental Health Disorders in People with Diabetes
People with diabetes commonly experience comorbid mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety, which can significantly impact disease management and treatment adherence. Studies indicate that the prevalence of depression in diabetic patients is nearly twice that of the general population, highlighting the critical need for integrated mental health screening. Addressing these comorbid conditions through multidisciplinary care improves glycemic control and overall quality of life.
Diabetic Retinopathy: Eye Complications in Diabetes
Diabetic retinopathy is a common comorbidity in patients with diabetes, characterized by damage to the blood vessels in the retina due to prolonged high blood sugar levels. This condition can lead to vision impairment and is a leading cause of blindness among working-age adults. Regular eye screenings and tight glycemic control are essential to prevent the progression of diabetic retinopathy and preserve visual health.
Peripheral Neuropathy Among Diabetic Patients
Peripheral neuropathy is a common comorbidity in diabetic patients, characterized by nerve damage due to chronic high blood glucose levels. This condition leads to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities, significantly impacting quality of life and increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections. Effective management includes strict glycemic control, regular foot examinations, and pharmacological treatments to alleviate neuropathic pain.
Dyslipidemia as a Coexisting Condition in Diabetes
Dyslipidemia is a common comorbidity in diabetes, characterized by abnormal lipid profiles including elevated triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, and increased LDL cholesterol. This lipid imbalance significantly raises the risk of cardiovascular diseases in diabetic patients, complicating disease management and outcomes. Addressing dyslipidemia through targeted lipid-lowering therapies is critical for reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular events in individuals with diabetes.
The Impact of Sleep Apnea in Individuals with Diabetes
Sleep apnea significantly worsens glycemic control in individuals with diabetes by increasing insulin resistance and oxidative stress. This comorbidity elevates the risk of cardiovascular complications, making blood sugar management more challenging. Effective diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea are crucial to improving health outcomes and reducing hospitalizations in diabetic patients.
example of comorbidity in diabetes Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com