Xerostomia, or dry mouth, is a common symptom observed in patients with Sjogren's syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that targets the salivary glands. In Sjogren's syndrome, immune cells attack and damage the glands responsible for saliva production, leading to significant decreases in saliva flow. This reduction in saliva causes difficulties in speaking, swallowing, and increases the risk of dental caries and oral infections. Patients with Sjogren's syndrome experiencing xerostomia often report a persistent dry sensation and changes in taste perception. Diagnostic tests such as salivary flow rate measurements and labial salivary gland biopsies are used to confirm glandular dysfunction. Management includes saliva substitutes, stimulating agents, and strict oral hygiene to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Table of Comparison
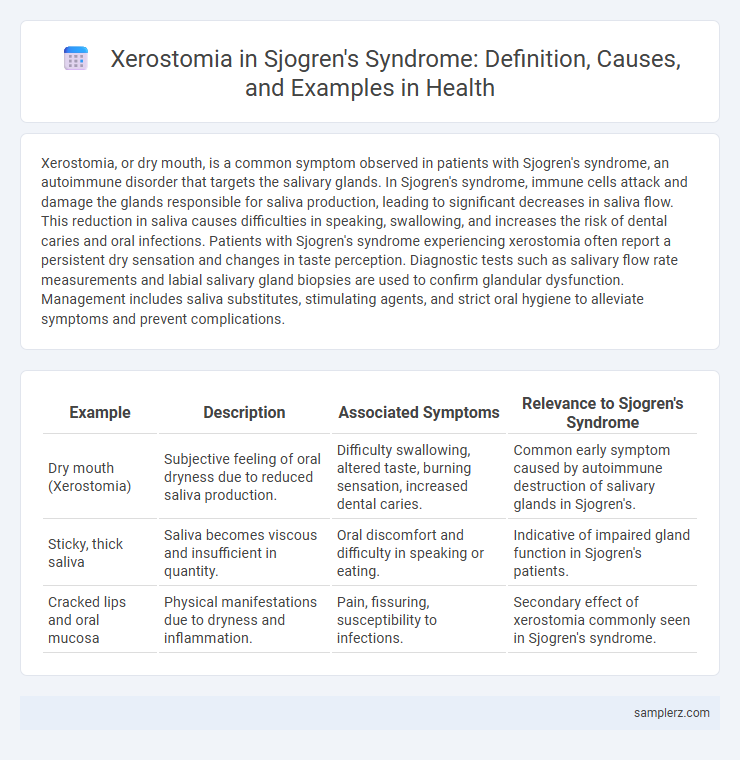
| Example | Description | Associated Symptoms | Relevance to Sjogren's Syndrome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry mouth (Xerostomia) | Subjective feeling of oral dryness due to reduced saliva production. | Difficulty swallowing, altered taste, burning sensation, increased dental caries. | Common early symptom caused by autoimmune destruction of salivary glands in Sjogren's. |
| Sticky, thick saliva | Saliva becomes viscous and insufficient in quantity. | Oral discomfort and difficulty in speaking or eating. | Indicative of impaired gland function in Sjogren's patients. |
| Cracked lips and oral mucosa | Physical manifestations due to dryness and inflammation. | Pain, fissuring, susceptibility to infections. | Secondary effect of xerostomia commonly seen in Sjogren's syndrome. |
Understanding Xerostomia in Sjogren’s Syndrome
Xerostomia in Sjogren's syndrome manifests as persistent dry mouth due to autoimmune destruction of salivary glands, leading to decreased saliva production and impaired oral lubrication. This dryness increases the risk of dental caries, oral infections such as candidiasis, and difficulties in swallowing and speaking. Effective management requires both symptom relief through saliva substitutes and addressing the underlying autoimmune activity to preserve gland function.
Common Symptoms of Xerostomia in Sjogren’s
Common symptoms of xerostomia in Sjogren's syndrome include persistent dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, and altered taste perception. Patients often experience increased dental caries and oral infections due to reduced saliva production. These symptoms significantly impact oral health and quality of life in individuals with Sjogren's.
Causes of Xerostomia in Sjogren’s Patients
Xerostomia in Sjogren's syndrome primarily results from autoimmune destruction of salivary glands, leading to reduced saliva production and glandular dysfunction. Inflammatory infiltration by lymphocytes causes glandular tissue damage, impairing the secretion of saliva. Concomitant factors such as medication use and other systemic autoimmune conditions further exacerbate xerostomia in Sjogren's patients.
Clinical Indicators of Dry Mouth in Sjogren’s
Patients with Sjogren's syndrome commonly present with xerostomia, characterized by persistent dry mouth due to salivary gland dysfunction. Clinical indicators include reduced salivary flow rate, erythematous and atrophic oral mucosa, fissured tongue, and increased dental caries risk. Objective measurements such as sialometry combined with patient-reported symptoms aid in confirming the diagnosis of dry mouth in Sjogren's syndrome.
Impact of Xerostomia on Oral Health in Sjogren’s
Xerostomia in Sjogren's syndrome significantly impairs oral health by reducing saliva flow, which is essential for maintaining the natural balance of oral flora and protecting against dental caries. The decreased saliva production leads to increased risk of fungal infections like oral candidiasis, mucosal irritation, and difficulty in swallowing and speaking. Chronic dry mouth also promotes periodontal disease progression and accelerates tooth decay, severely affecting patients' quality of life.
Diagnostic Methods for Xerostomia in Sjogren’s Syndrome
Diagnostic methods for xerostomia in Sjogren's syndrome include salivary flow rate measurement, sialometry, and salivary gland biopsy to assess glandular dysfunction and lymphocytic infiltration. Imaging techniques such as salivary gland ultrasonography and scintigraphy provide detailed visualization of gland structure and function. Serological tests detecting anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB antibodies support diagnosis by indicating autoimmune activity characteristic of Sjogren's syndrome.
Real-Life Examples of Xerostomia in Sjogren’s
Patients with Sjogren's syndrome frequently experience xerostomia, leading to difficulties in speaking, swallowing, and increased dental caries risk. Real-life cases highlight severe dry mouth symptoms causing disrupted sleep and reliance on saliva substitutes or frequent hydration. Clinical reports underscore the impact of diminished salivary gland function on oral health, necessitating multidisciplinary management approaches.
Managing Xerostomia Symptoms in Sjogren’s Patients
Managing xerostomia symptoms in Sjogren's patients involves regular use of saliva substitutes and stimulants to alleviate oral dryness and improve comfort. Frequent dental check-ups and meticulous oral hygiene practices reduce the risk of caries and oral infections associated with decreased saliva flow. Hydration, sugar-free chewing gum, and medications like pilocarpine can effectively enhance salivary gland function and provide symptom relief.
Treatment Options for Xerostomia in Sjogren’s Syndrome
Treatment options for xerostomia in Sjogren's syndrome primarily include saliva substitutes, artificial saliva sprays, and frequent sipping of water to maintain oral moisture. Prescription medications such as pilocarpine and cevimeline stimulate saliva production by targeting muscarinic receptors, improving comfort and oral health. Regular dental care and the use of fluoride treatments also help prevent complications caused by dry mouth in Sjogren's patients.
Preventive Tips for Xerostomia in Sjogren’s Disease
Xerostomia in Sjogren's disease significantly increases the risk of dental caries and oral infections due to reduced saliva production. Effective preventive tips include maintaining rigorous oral hygiene with fluoride toothpaste, regular dental check-ups, and frequent sips of water to keep the mouth moist. Using saliva substitutes or stimulants like sugar-free chewing gum can also alleviate dryness and protect oral health.
example of xerostomia in Sjogren Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com