Orthorexia in adolescents often presents as an obsessive focus on healthy eating, leading to restrictive dietary patterns that exclude entire food groups. These teens may spend excessive time researching food quality, obsess over ingredients, and experience anxiety if their dietary rules are violated. This behavior can result in nutritional deficiencies, weight loss, and social isolation due to rigid eating habits. Healthcare professionals identify orthorexia in adolescents through symptoms such as extreme food avoidance, preoccupation with purity of food, and distress related to eating "unhealthy" options. Data indicates that this condition is more common in teenagers involved in fitness communities or those with a history of anxiety disorders. Early intervention focusing on balanced nutrition and psychological support is critical to prevent long-term health complications linked to orthorexia.
Table of Comparison
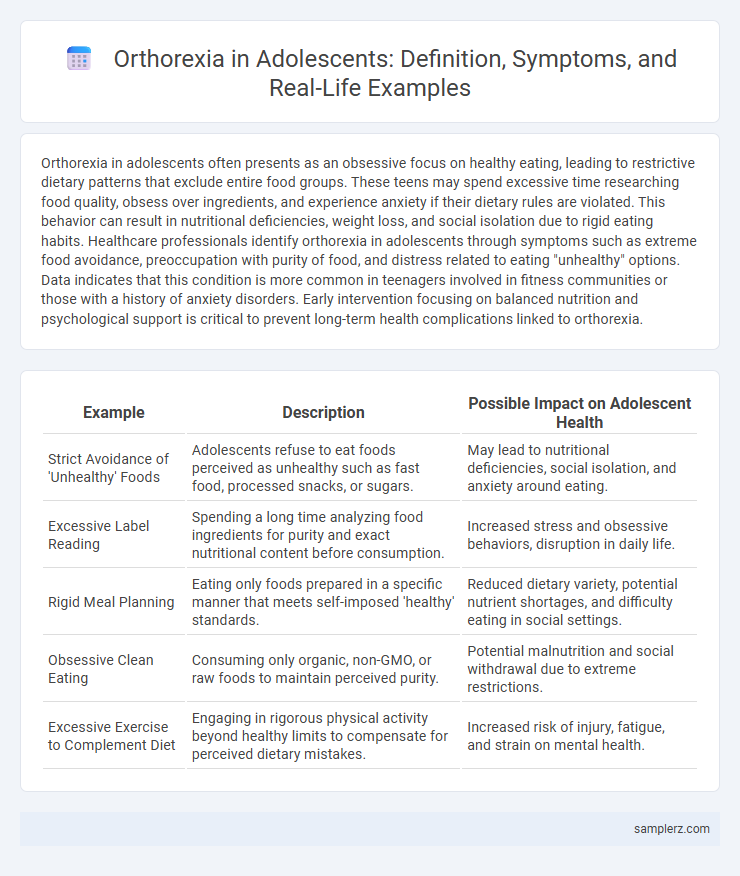
| Example | Description | Possible Impact on Adolescent Health |
|---|---|---|
| Strict Avoidance of 'Unhealthy' Foods | Adolescents refuse to eat foods perceived as unhealthy such as fast food, processed snacks, or sugars. | May lead to nutritional deficiencies, social isolation, and anxiety around eating. |
| Excessive Label Reading | Spending a long time analyzing food ingredients for purity and exact nutritional content before consumption. | Increased stress and obsessive behaviors, disruption in daily life. |
| Rigid Meal Planning | Eating only foods prepared in a specific manner that meets self-imposed 'healthy' standards. | Reduced dietary variety, potential nutrient shortages, and difficulty eating in social settings. |
| Obsessive Clean Eating | Consuming only organic, non-GMO, or raw foods to maintain perceived purity. | Potential malnutrition and social withdrawal due to extreme restrictions. |
| Excessive Exercise to Complement Diet | Engaging in rigorous physical activity beyond healthy limits to compensate for perceived dietary mistakes. | Increased risk of injury, fatigue, and strain on mental health. |
Understanding Orthorexia: Definition and Relevance in Adolescents
Orthorexia in adolescents manifests as an obsessive focus on healthy eating, characterized by rigid dietary rules and an intense fear of consuming "impure" foods, leading to nutritional deficiencies and social isolation. This condition is increasingly relevant as teens face growing exposure to health trends through social media, often confusing mindful eating with pathological behaviors. Early recognition and intervention are critical to prevent long-term physical and psychological consequences associated with orthorexia in this vulnerable age group.
Common Signs of Orthorexia in Teenagers
Common signs of orthorexia in teenagers include an obsessive focus on healthy eating, rigid dietary restrictions, and an intense fear of foods perceived as unhealthy. Adolescents may spend excessive time planning, purchasing, and preparing meals, which can interfere with social activities and academic performance. Physical symptoms often involve unintentional weight loss, nutrient deficiencies, and fatigue due to limited food variety.
Social Media’s Role in Adolescent Orthorexia
Social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok significantly influence adolescent orthorexia by promoting unrealistic health and diet standards that encourage obsessive healthy eating behaviors. Adolescents exposed to constant streams of "clean eating" content often develop anxiety around food purity and nutrient quality, leading to restrictive eating patterns. Research shows a strong correlation between frequent social media use and increased risk of orthorexia symptoms among teenagers, highlighting the need for media literacy interventions.
Real-life Cases of Orthorexia Among Teens
Cases of orthorexia among adolescents often involve teenagers who strictly avoid foods they perceive as unhealthy, leading to nutritional deficiencies and social isolation. For instance, a 15-year-old girl eliminated all processed foods and consumed only raw vegetables and fruits, resulting in significant weight loss and fatigue. Such real-life examples highlight the need for early intervention and education on balanced eating habits in teens.
Impact of Orthorexia on Adolescent Physical Health
Orthorexia in adolescents often leads to severe nutritional deficiencies, resulting in weakened immune function and stunted growth. Prolonged restrictive eating habits can cause anemia, fatigue, and hormonal imbalances, negatively affecting overall physical development. Chronic malnutrition from orthorexia increases the risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular issues during critical growth periods.
Psychological Effects of Orthorexia in Youth
Orthorexia in adolescents often manifests as an obsessive fixation on healthy eating, leading to severe anxiety and social isolation. Youth struggling with orthorexia may experience heightened stress, distorted body image, and compulsive behaviors related to food choices. These psychological effects can disrupt academic performance, peer relationships, and overall mental well-being.
Warning Behaviors: Identifying Orthorexic Tendencies
Adolescents with orthorexia often exhibit warning behaviors such as an excessive preoccupation with healthy eating, rigid food rules, and severe anxiety when their dietary standards are compromised. These warning signs may include obsessive meal planning, social withdrawal to avoid eating non-approved foods, and pervasive guilt or shame about food choices. Early identification of these behaviors is critical to preventing long-term physical and psychological health consequences associated with orthorexia nervosa.
Peer and Family Influence on Adolescent Orthorexia
Orthorexia in adolescents often manifests through behaviors influenced by peer pressure and family attitudes toward healthy eating, with teens adopting rigid dietary restrictions to gain social acceptance or approval. Research indicates that adolescents are more susceptible to orthorexia when surrounded by peers or family members who emphasize perfectionism in diet and body image. This dynamic reinforces obsessive eating patterns, elevating the risk of developing orthorexia nervosa during critical developmental stages.
School Environment and the Rise of Orthorexia in Teens
School cafeterias and peer influences in the school environment often contribute significantly to the rise of orthorexia in adolescents. Teens may develop an obsessive focus on eating "pure" or "healthy" foods, exacerbated by social pressures to conform to health trends and the availability of information on strict dietary rules. This behavior can lead to malnutrition, anxiety, and impaired social functioning during critical developmental years.
Strategies for Early Detection and Support in Adolescents
Orthorexia in adolescents often manifests as obsessive behavior toward healthy eating, leading to nutritional deficiencies and social isolation. Early detection strategies include monitoring sudden changes in eating patterns, excessive preoccupation with food quality, and increased anxiety related to meal times. Support interventions involve multidisciplinary approaches combining nutritional counseling, psychological therapy, and family education to promote balanced eating habits and emotional well-being.
example of orthorexia in adolescent Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com