Captive insurance in risk management refers to a company creating its own insurance subsidiary to insure its risks rather than purchasing insurance from third-party providers. This approach allows businesses to tailor coverage to specific risks, reduce insurance costs, and gain greater control over claims management. For example, a manufacturing firm may establish a captive insurer to cover product liability and workers' compensation risks, optimizing risk retention and improving cash flow. In finance, captive insurance entities often serve as strategic tools for managing unpredictable risks and stabilizing insurance expenses. Corporations in sectors such as energy, construction, and healthcare frequently use captives to mitigate operational risks while benefiting from potential tax advantages and increased underwriting profits. Data trends indicate that captive insurance structures can lead to improved risk transparency and better capital allocation within corporate risk management programs.
Table of Comparison
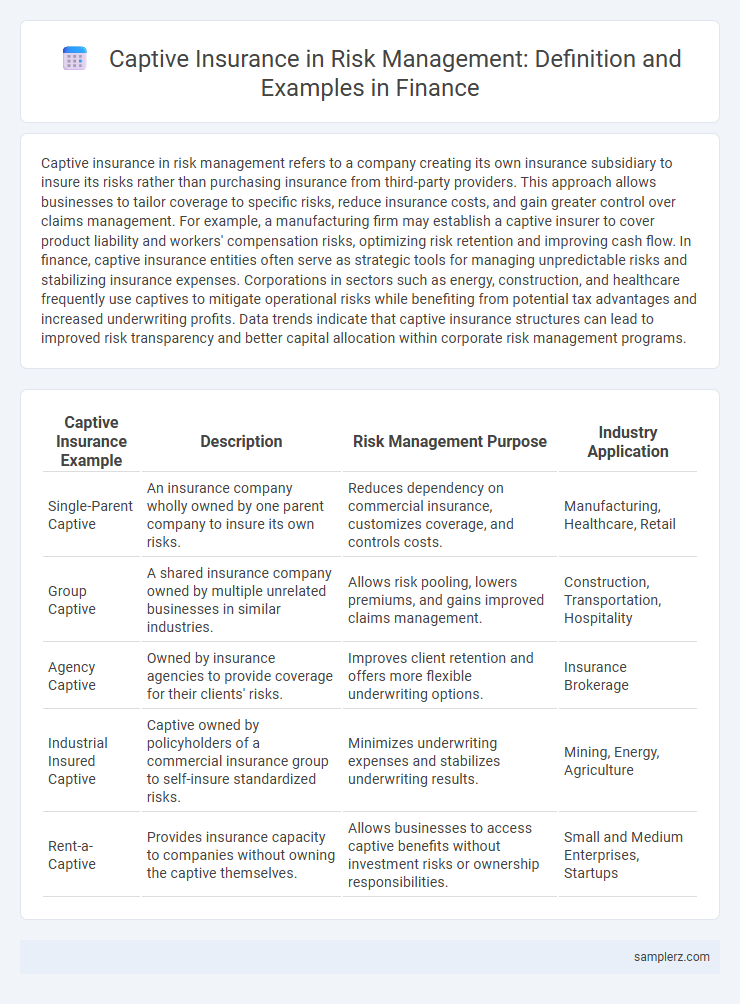
| Captive Insurance Example | Description | Risk Management Purpose | Industry Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Parent Captive | An insurance company wholly owned by one parent company to insure its own risks. | Reduces dependency on commercial insurance, customizes coverage, and controls costs. | Manufacturing, Healthcare, Retail |
| Group Captive | A shared insurance company owned by multiple unrelated businesses in similar industries. | Allows risk pooling, lowers premiums, and gains improved claims management. | Construction, Transportation, Hospitality |
| Agency Captive | Owned by insurance agencies to provide coverage for their clients' risks. | Improves client retention and offers more flexible underwriting options. | Insurance Brokerage |
| Industrial Insured Captive | Captive owned by policyholders of a commercial insurance group to self-insure standardized risks. | Minimizes underwriting expenses and stabilizes underwriting results. | Mining, Energy, Agriculture |
| Rent-a-Captive | Provides insurance capacity to companies without owning the captive themselves. | Allows businesses to access captive benefits without investment risks or ownership responsibilities. | Small and Medium Enterprises, Startups |
Introduction to Captive Insurance in Risk Management
Captive insurance serves as a strategic risk management tool where a company creates its own insurance subsidiary to finance risks internally. This approach enhances control over insurance coverage, reduces costs, and improves cash flow compared to traditional insurance policies. Companies in industries with significant risk exposure, such as manufacturing and healthcare, frequently adopt captive insurance to tailor risk transfer solutions and optimize their overall risk management framework.
Key Benefits of Using Captive Insurance
Captive insurance provides companies with enhanced risk control and customized coverage tailored to specific operational needs, reducing reliance on traditional insurers. It offers significant cost savings through lower premiums and improved cash flow management by retaining underwriting profits. Tax advantages and increased financial flexibility further strengthen a firm's overall risk management strategy.
Common Structure of Captive Insurance Companies
Captive insurance companies typically follow a common structure involving a parent company creating a wholly owned subsidiary to provide tailored insurance coverage for its own risks. This structure enables risk retention, improved cash flow management, and potential cost savings by reducing reliance on traditional insurance carriers. Common types include pure captives, association captives, and group captives, each offering varying degrees of risk sharing and regulatory compliance tailored to the parent entity's risk management strategy.
Real-World Example: Fortune 500 Captive Insurance Implementation
A Fortune 500 company established a captive insurance subsidiary to manage risks related to cybersecurity and product liability, reducing third-party insurer dependency and lowering premiums by 15%. This captive enabled the firm to customize coverage, enhance claims control, and improve cash flow through retained premiums. Such implementation illustrates strategic risk financing, optimizing operational resilience and cost-efficiency in corporate risk management.
Captive Insurance in Healthcare: Practical Applications
Captive insurance in healthcare provides customized risk financing solutions for hospitals and medical groups, allowing them to retain premiums and control claims management effectively. By establishing a captive, healthcare organizations can mitigate malpractice risks, manage employee health benefit costs, and enhance cash flow stability through tailored insurance coverage. This approach reduces reliance on traditional insurers, improves risk pooling, and facilitates proactive loss prevention strategies specific to healthcare operations.
How Multinational Corporations Leverage Captive Insurance
Multinational corporations leverage captive insurance to mitigate risks by establishing wholly-owned insurance subsidiaries that provide tailored coverage for complex, global exposures such as political risk, foreign exchange fluctuations, and trade credit risk. This strategic use of captive insurance enhances risk retention capabilities, reduces reliance on traditional insurance markets, and improves cash flow management by capturing underwriting profits in-house. Captive insurance also facilitates centralized risk analytics and compliance with diverse regulatory environments across multiple jurisdictions.
Case Study: Captive Insurance for Employee Benefits
A large multinational corporation established a captive insurance company to underwrite employee health and wellness benefits, effectively reducing external insurance costs and gaining greater control over claims management. By self-insuring through its captive, the company tailored coverage to employee needs, mitigated volatility in premium pricing, and improved cash flow predictability. This strategic use of captive insurance enhanced risk management efficiency while supporting employee retention and satisfaction.
Risk Financing Through Captives: Industry Examples
Risk financing through captives allows industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and construction to retain and control their risk exposure by establishing wholly-owned insurance subsidiaries. For instance, major corporations such as DuPont and Johnson & Johnson utilize captive insurance to underwrite their unique operational risks, reduce third-party insurer reliance, and achieve tailored risk coverage. These captives enhance financial stability by managing claims internally and optimizing loss reserves, providing a strategic risk management advantage.
Regulatory Considerations in Captive Insurance Structures
Regulatory considerations in captive insurance structures are crucial for ensuring compliance and operational legitimacy, with specific requirements varying by jurisdiction, such as minimum capital reserves and solvency margins mandated by regulatory bodies like the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) in the United States. Captive insurers must navigate complex licensing procedures, including detailed business plans and periodic financial reporting, to maintain regulatory approval and avoid penalties. Effective risk management relies on aligning captive insurance frameworks with local and international regulatory standards to optimize tax treatment and risk retention strategies.
Lessons Learned from Successful Captive Insurance Programs
Successful captive insurance programs demonstrate the importance of customizing risk retention strategies to align with company-specific exposures and operational goals. Effective risk management through captives often involves meticulous regulatory compliance, robust capital adequacy, and proactive claims management to optimize cost savings and improve coverage stability. Data from industry benchmarks reveal that companies achieving significant cost reductions and enhanced risk control typically invest in comprehensive analytics and governance frameworks within their captive operations.
example of captive insurance in risk management Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com