Zombie firms are companies that continue operating despite being unable to cover their debt servicing costs from current profits. In the manufacturing industry, a notable example is Toshiba, which has struggled with significant debt and declining profitability over recent years. Despite these challenges, Toshiba has managed to sustain operations through government support and creditor leniency, highlighting its status as a zombie firm. In the retail sector, Sears Holdings represents another classic zombie firm example. The company has endured years of losses, declining sales, and store closures but remained operational due to continuous financial backing and restructuring efforts. Both Toshiba and Sears illustrate how zombie firms persist, tying up capital and resources that could otherwise be allocated to more productive businesses, ultimately impacting economic growth.
Table of Comparison
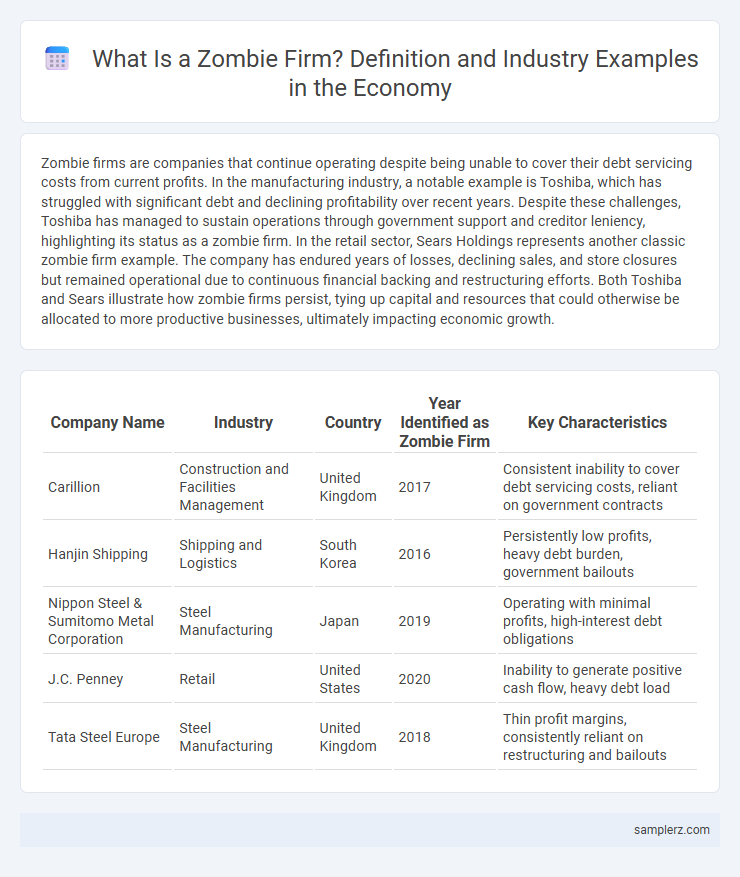
| Company Name | Industry | Country | Year Identified as Zombie Firm | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carillion | Construction and Facilities Management | United Kingdom | 2017 | Consistent inability to cover debt servicing costs, reliant on government contracts |
| Hanjin Shipping | Shipping and Logistics | South Korea | 2016 | Persistently low profits, heavy debt burden, government bailouts |
| Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation | Steel Manufacturing | Japan | 2019 | Operating with minimal profits, high-interest debt obligations |
| J.C. Penney | Retail | United States | 2020 | Inability to generate positive cash flow, heavy debt load |
| Tata Steel Europe | Steel Manufacturing | United Kingdom | 2018 | Thin profit margins, consistently reliant on restructuring and bailouts |
Defining Zombie Firms in Modern Industries
Zombie firms in modern industries are companies that generate just enough revenue to cover operating costs and interest payments but lack the capacity to invest or innovate, effectively stalling economic growth. For example, in the manufacturing sector, certain steel producers continue to operate despite obsolete technology and declining demand, relying on debt restructuring and government subsidies to survive. These firms drain resources, distort market competition, and hinder the reallocation of capital to more productive enterprises within the economy.
Notable Zombie Firms Across Key Sectors
Toshiba Corporation in the technology sector stands out as a notable zombie firm, burdened by persistent debt and sluggish growth despite continuous government support. In the automotive industry, Nissan Motors exemplifies a zombie company struggling with legacy costs and declining market share. The steel industry features companies like ArcelorMittal, which face ongoing financial distress but remain operational through bailout measures and creditor leniency.
Case Study: Zombie Companies in the Retail Industry
A prominent example of a zombie firm in the retail industry is Sears Holdings Corporation, which struggled under heavy debt despite generating insufficient cash flow to cover interest payments. This prolonged financial distress prevented necessary investments in modernization and innovation, leading to declining market relevance. The case of Sears highlights how zombie companies can drain industry resources and hinder economic growth by occupying market space without contributing to productivity.
Impacts of Zombie Firms on Manufacturing Sectors
Zombie firms in the manufacturing sector, such as Japan's longstanding cases in the steel and textile industries, drain economic resources by maintaining unproductive operations through continuous debt refinancing. These companies distort market competition by crowding out more innovative firms and impede technological advancements critical for sectoral growth. Persistent zombie firms also reduce overall productivity growth, leading to stagnation in manufacturing output and employment opportunities.
Real Estate Industry: Examples of Zombie Enterprises
In the real estate industry, zombie firms persist due to stagnant property values and excessive debt servicing, exemplified by companies like WeWork during its financial struggles prior to restructuring. These enterprises survive on continual refinancing despite generating insufficient cash flow to cover operational costs, distorting market efficiency. The presence of such zombie firms contributes to reduced capital availability for healthier real estate developers, hindering overall sector growth.
How Banking Harbors Zombie Firms
Zombie firms, such as Japan's long-standing steel manufacturer, Nippon Steel, survive primarily due to continued bank support despite weak profitability and outdated technology. Banking institutions often extend credit to these underperforming companies to avoid recognizing loan losses, thereby sustaining inefficient capital allocation within the economy. This phenomenon contributes to resource misallocation, dampening overall economic growth and innovation by crowding out healthier enterprises.
Energy Sector: Identifying Zombie Corporations
In the energy sector, zombie firms such as Chesapeake Energy illustrate the challenges of sustaining operations amid heavy debt and declining profitability despite ongoing market pressures. These companies often rely on refinancing to avoid bankruptcy, draining resources and impeding industry innovation. Identifying such zombie corporations is crucial for investors and policymakers aiming to enhance sector efficiency and promote economic resilience.
Technology Industry’s Struggles with Zombie Entities
The technology industry faces significant challenges from zombie firms like Toshiba, which continues operating despite chronic financial difficulties and outdated product lines. These companies drain resources by occupying market share without driving innovation or growth, hindering overall sector productivity. The persistence of such zombie entities slows technological advancement and deters investment in truly competitive and innovative startups.
Global Examples: Zombie Firms in International Markets
ZZZ Best, a once-notorious American company in the restoration industry, exemplifies a zombie firm that survived through deceptive accounting before collapsing. In Japan, corporations like Toshiba have struggled with prolonged financial underperformance yet remained operational due to government and bank support, highlighting systemic issues in managing zombie firms. South Korea's airline industry witnessed Asiana Airlines facing persistent losses while relying heavily on government bailouts, illustrating the global prevalence and economic impact of zombie firms.
Lessons Learned from Zombie Firms in Different Industries
The retail sector provides a notable example of zombie firms, with businesses like Sears struggling under massive debt and declining sales yet continuing operations due to creditor forbearance. Lessons learned highlight the importance of timely restructuring and innovation to prevent resource misallocation and foster industry competitiveness. Policymakers and investors must prioritize early intervention strategies to mitigate the economic drag caused by prolonged zombie firm activity.
example of zombie firm in industry Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com