The Triffin dilemma highlights a conflict between national and global economic interests when a country's currency serves as the world's primary reserve currency. For example, the United States dollar faces this issue as it must supply enough dollars to meet global demand while maintaining domestic economic stability. This creates a tension between running trade deficits to provide liquidity and preserving confidence in the dollar's value. In practice, the Triffin dilemma manifested during the Bretton Woods era, where the U.S. had to convert dollars into gold at a fixed rate. Foreign nations accumulated large dollar reserves but doubted the U.S.'s ability to back these reserves, causing global economic uncertainty. This crisis ultimately led to the collapse of the gold standard in 1971 and the shift to fiat currencies, illustrating the intrinsic challenges of maintaining an international reserve currency.
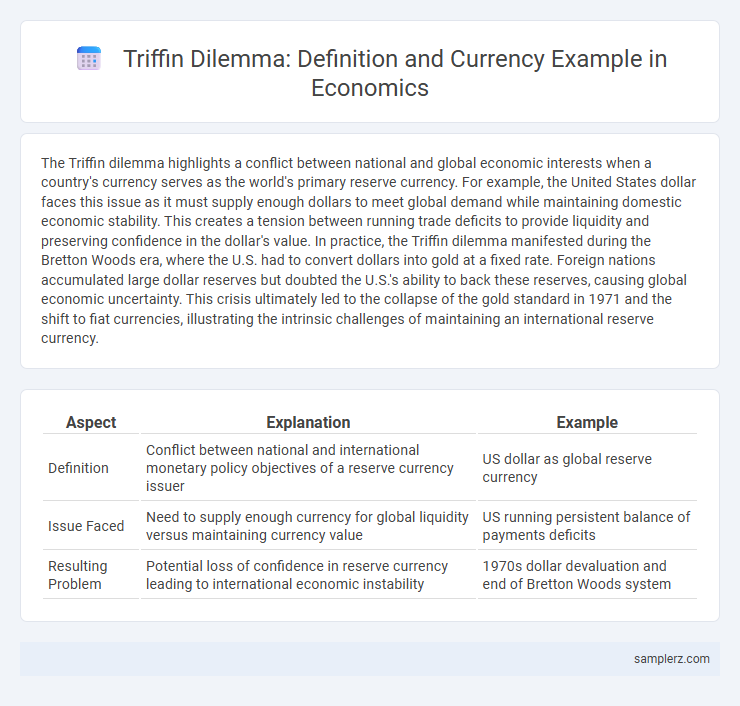
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conflict between national and international monetary policy objectives of a reserve currency issuer | US dollar as global reserve currency |
| Issue Faced | Need to supply enough currency for global liquidity versus maintaining currency value | US running persistent balance of payments deficits |
| Resulting Problem | Potential loss of confidence in reserve currency leading to international economic instability | 1970s dollar devaluation and end of Bretton Woods system |
Understanding the Triffin Dilemma in Modern Currency Systems
The Triffin dilemma highlights the inherent conflict between national monetary policy and global liquidity needs when a country's currency serves as the world reserve currency, exemplified by the US dollar's role in international trade and finance. This conflict arises because issuing sufficient dollars to meet global demand can lead to a trade deficit and undermine confidence in the currency's value. Understanding this dilemma is crucial for analyzing the stability challenges faced by modern currency systems and the potential risks of persistent imbalances in reserve currencies.
Historical Examples: The Bretton Woods Era and the U.S. Dollar
The Triffin dilemma was prominently illustrated during the Bretton Woods era when the U.S. dollar served as the world's primary reserve currency, linking domestic monetary policy to global liquidity demands. As confidence in the dollar's convertibility to gold waned due to persistent U.S. balance of payments deficits, countries questioned the sustainability of dollar dominance. This tension ultimately contributed to the collapse of the Bretton Woods system in 1971, highlighting the inherent conflict between national economic policy and international reserve currency obligations.
Euro as a Reserve Currency: Triffin Dilemma in the European Union
The Euro faces a Triffin dilemma as it strives to balance its role as a global reserve currency with the European Union's economic stability. To maintain international confidence, the Eurozone must supply sufficient liquidity, often requiring current account deficits that can undermine domestic economic health. This tension challenges the EU's ability to sustain the Euro's reserve status without jeopardizing long-term fiscal sustainability.
Petrodollar System: An Extension of the Triffin Dilemma
The Petrodollar system exemplifies an extension of the Triffin dilemma by creating a persistent global demand for US dollars to price and trade oil, thus sustaining the dollar's reserve currency status despite growing US external deficits. This structural tension forces the United States to run balance of payments deficits to supply petrodollars, while undermining confidence in dollar stability over time. As a result, the global economy faces a paradox where the dollar must remain abundant for liquidity yet scarce enough to preserve its value, intensifying systemic vulnerabilities inherent in the Triffin dilemma.
Chinese Yuan and SDR: New Faces of the Triffin Dilemma
The Chinese Yuan's increasing inclusion in the International Monetary Fund's Special Drawing Rights (SDR) basket exemplifies the modern Triffin dilemma, where China's role as a global reserve currency provider creates tension between domestic monetary policy and international liquidity demands. As the Yuan gains prominence, China faces pressure to supply sufficient liquidity to support global financial stability while maintaining control over its currency and economy. This dual responsibility highlights the evolving challenges of the Triffin dilemma in a multipolar currency system.
Central Banks’ Dilemma: Balancing Domestic Policy and Global Demand
Central banks face the Triffin dilemma when their currency serves as a global reserve, forcing a balance between domestic monetary policy and international liquidity needs. For example, the U.S. Federal Reserve must accommodate global demand for dollars by running persistent deficits, which can conflict with its mandate to control inflation and support economic growth. This tension complicates policy decisions, as maintaining global trust in the currency may undermine domestic economic stability.
Impact of the Triffin Dilemma on Global Trade Imbalances
The Triffin dilemma highlights how the reliance on a reserve currency, such as the US dollar, creates persistent global trade imbalances as issuing countries must run deficits to supply liquidity while eroding confidence in their currency's stability. These imbalances contribute to fluctuating capital flows and increased vulnerability to financial crises in emerging markets heavily dependent on stable reserve currencies. Consequently, the dilemma exacerbates the challenge of maintaining sustainable international trade and financial stability in the global economy.
Cryptocurrency and the Future of the Triffin Dilemma
The Triffin dilemma illustrates the inherent conflict between a national currency's role as a global reserve and domestic economic policy, which cryptocurrency challenges by offering decentralized alternatives without centralized control. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies reduce dependency on traditional reserve currencies like the US dollar, potentially mitigating the Triffin dilemma's impact by eliminating the need for a single dominant reserve currency. The future of the Triffin dilemma may evolve as digital currencies and blockchain technologies create a more diversified and resilient global monetary system.
Lessons from the 2008 Financial Crisis and the Triffin Dilemma
The 2008 financial crisis exposed vulnerabilities linked to the Triffin dilemma, highlighting the conflict between national monetary policy objectives and the global demand for the U.S. dollar as a reserve currency. Countries holding large dollar reserves faced risks of currency instability and balance-of-payment imbalances, illustrating how reliance on a single currency can exacerbate systemic financial crises. This experience underscores the need for diversified reserve assets and international monetary cooperation to mitigate the risks inherent in the Triffin dilemma.
Policy Solutions and Reforms to Address the Triffin Dilemma
Policy solutions to the Triffin dilemma involve diversifying international reserve currencies to reduce reliance on a single national currency, such as the US dollar. Reforms in global financial governance propose establishing a supranational currency issued by institutions like the International Monetary Fund to provide stability without national debt constraints. Strengthening coordination among central banks and implementing measures to balance reserve currency supply with global economic growth are critical to addressing inherent imbalances in the current system.
example of Triffin dilemma in currency Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com