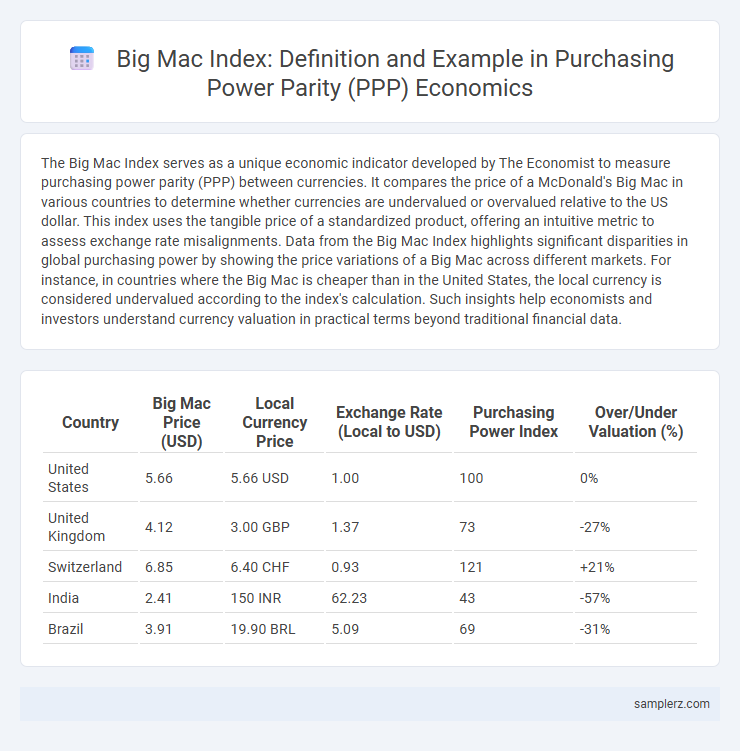
The Big Mac Index serves as a unique economic indicator developed by The Economist to measure purchasing power parity (PPP) between currencies. It compares the price of a McDonald's Big Mac in various countries to determine whether currencies are undervalued or overvalued relative to the US dollar. This index uses the tangible price of a standardized product, offering an intuitive metric to assess exchange rate misalignments. Data from the Big Mac Index highlights significant disparities in global purchasing power by showing the price variations of a Big Mac across different markets. For instance, in countries where the Big Mac is cheaper than in the United States, the local currency is considered undervalued according to the index's calculation. Such insights help economists and investors understand currency valuation in practical terms beyond traditional financial data.
Table of Comparison
| Country | Big Mac Price (USD) | Local Currency Price | Exchange Rate (Local to USD) | Purchasing Power Index | Over/Under Valuation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 5.66 | 5.66 USD | 1.00 | 100 | 0% |
| United Kingdom | 4.12 | 3.00 GBP | 1.37 | 73 | -27% |
| Switzerland | 6.85 | 6.40 CHF | 0.93 | 121 | +21% |
| India | 2.41 | 150 INR | 62.23 | 43 | -57% |
| Brazil | 3.91 | 19.90 BRL | 5.09 | 69 | -31% |
Understanding the Big Mac Index: A Global Price Comparison
The Big Mac Index compares the price of a McDonald's Big Mac across countries to measure purchasing power parity (PPP), serving as an accessible indicator of currency valuation. By analyzing the cost differences, economists identify whether a currency is undervalued or overvalued relative to the US dollar, reflecting economic disparities. This index highlights inflation rates, cost of living variations, and market-efficient currency adjustments in a globally recognizable product.
How the Big Mac Index Measures Purchasing Power Parity
The Big Mac Index measures purchasing power parity (PPP) by comparing the price of a McDonald's Big Mac burger across different countries, reflecting the relative cost of living and currency valuation. By analyzing the price variations, this index highlights whether a currency is undervalued or overvalued in comparison to the US dollar. Economists use this practical example to assess the real purchasing power of currencies beyond traditional exchange rate metrics.
Real-World Examples: Big Mac Prices Across Countries
The Big Mac Index reveals significant purchasing power disparities by comparing the cost of a Big Mac in various countries, highlighting currency under- or overvaluation. In 2023, a Big Mac cost $5.66 in the United States, $3.45 in India, and $8.12 in Switzerland, demonstrating considerable variance. These real-world price differences illustrate the practical application of the Big Mac Index in assessing exchange rate misalignments and living cost variations globally.
Analyzing Currency Overvaluation with the Big Mac Index
The Big Mac Index offers a practical method for analyzing currency overvaluation by comparing the price of a Big Mac in different countries against the U.S. dollar baseline. A currency is considered overvalued if the local Big Mac price, when converted to dollars, is significantly higher than the price in the United States. This index provides insights into purchasing power parity and helps identify misalignments in exchange rates affecting international trade and investment decisions.
The Big Mac Index: Findings and Economic Insights
The Big Mac Index reveals notable disparities in purchasing power parity by comparing the price of a standardized Big Mac burger across countries. For instance, lower prices in nations like India and South Africa indicate undervalued currencies, while higher costs in Switzerland and Norway suggest overvaluation relative to the US dollar. This index provides an accessible, real-world illustration of currency valuation, inflation differences, and consumer price levels impacting global economic decisions.
Big Mac Index Trends: Emerging vs. Developed Markets
The Big Mac Index reveals significant disparities in purchasing power between emerging and developed markets, with emerging economies often showing undervalued currencies relative to the US dollar. Trends indicate that while developed markets tend to have more stable Big Mac prices, emerging markets experience greater fluctuations influenced by inflation, currency volatility, and economic reforms. This index serves as a practical tool for assessing currency misalignment and purchasing power parity across different economic contexts.
Cost of Living Through the Big Mac Lens
The Big Mac Index provides a practical benchmark for comparing purchasing power and cost of living across countries by analyzing the price of a standardized product--the Big Mac. This index highlights disparities in local currency valuation and living expenses by reflecting the relative cost of goods and services in different economies. Economists use this measure to gauge whether a currency is undervalued or overvalued in terms of buying power parity, offering insights into global economic conditions and consumer price levels.
Fluctuations in Exchange Rates and Burger Buying Power
The Big Mac Index illustrates fluctuations in exchange rates by comparing the cost of a McDonald's Big Mac across countries, highlighting differences in purchasing power parity. Variations in local currency values directly impact the burger buying power, revealing undervalued or overvalued currencies. This index serves as a simple yet effective economic indicator of currency strength relative to the US dollar.
Limitations and Criticisms of the Big Mac Index
The Big Mac Index, while popular for comparing purchasing power parity across countries, faces criticism for oversimplifying complex economic conditions by relying solely on the price of a single product. Limitations include the exclusion of non-traded goods and services, differences in local production costs, taxes, and market competition, which can distort true currency valuation. Moreover, cultural and consumer preference variations affect Big Mac prices, undermining its reliability as a definitive economic indicator.
Future Implications of the Big Mac Index in Economic Analysis
The Big Mac Index, a benchmark for assessing purchasing power parity, offers future implications in economic analysis by revealing currency valuation trends and underlying market dynamics. Integrating this index with advanced data analytics can enhance forecasting accuracy for exchange rate fluctuations and inflationary pressures. Policymakers and investors gain a practical tool for evaluating economic stability and guiding fiscal strategies in a globalized economy.
example of Big Mac index in purchasing power Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com