Gig work in labor refers to short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated through digital platforms. Common examples include ride-sharing drivers for companies like Uber and Lyft, delivery couriers for services such as DoorDash and Postmates, and freelance professionals offering tasks via platforms like Upwork and Fiverr. These roles emphasize on-demand availability and task-based compensation, differing from traditional full-time employment. The gig economy significantly contributes to labor market dynamics by providing alternative income sources for millions of workers globally. Data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that approximately 36% of the workforce engaged in gig work during 2023. This segment reflects broader shifts toward digital integration in economic activities and evolving employment preferences among younger demographics.
Table of Comparison
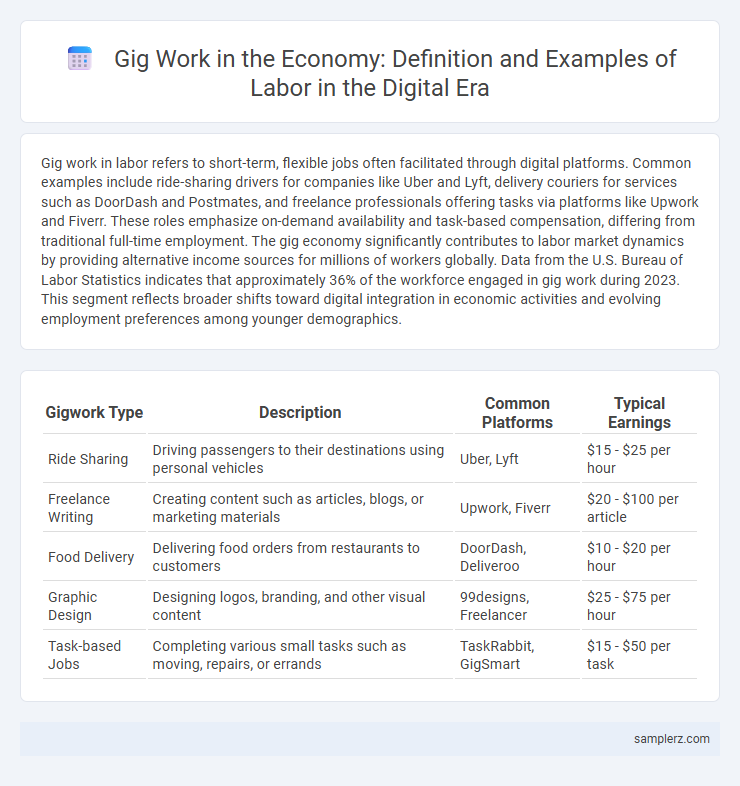
| Gigwork Type | Description | Common Platforms | Typical Earnings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ride Sharing | Driving passengers to their destinations using personal vehicles | Uber, Lyft | $15 - $25 per hour |
| Freelance Writing | Creating content such as articles, blogs, or marketing materials | Upwork, Fiverr | $20 - $100 per article |
| Food Delivery | Delivering food orders from restaurants to customers | DoorDash, Deliveroo | $10 - $20 per hour |
| Graphic Design | Designing logos, branding, and other visual content | 99designs, Freelancer | $25 - $75 per hour |
| Task-based Jobs | Completing various small tasks such as moving, repairs, or errands | TaskRabbit, GigSmart | $15 - $50 per task |
Understanding Gigwork: Defining the Modern Labor Shift
Gigwork represents a pivotal shift in the labor market by offering flexible, short-term contracts typically facilitated through digital platforms such as Uber, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit. This model emphasizes task-based employment over traditional full-time roles, enabling workers to leverage skills in areas like delivery, freelance design, and ride-sharing. Understanding gigwork involves recognizing its impact on employment patterns, income stability, and labor rights within the evolving gig economy landscape.
Rise of Freelancing in the Digital Economy
The rise of freelancing in the digital economy exemplifies gigwork transforming labor markets, with platforms like Upwork and Fiverr enabling millions of professionals to offer specialized services worldwide. This shift boosts economic flexibility by allowing workers to engage in diverse projects without long-term commitments, contributing to a dynamic labor supply. Increased adoption of remote work technologies and digital payment systems further accelerates the expansion of gig-based freelancing, impacting income patterns and employment structures globally.
Ride-Sharing and Delivery Services as Gigwork Models
Ride-sharing platforms like Uber and Lyft exemplify gigwork by connecting independent drivers with passengers, offering flexible income opportunities while affecting urban transportation patterns. Delivery services such as DoorDash and Instacart rely on gig workers to meet increasing consumer demands for rapid and convenient food and grocery delivery, driving growth in the on-demand economy. These gigwork models highlight the shift toward decentralized labor markets and the challenges related to worker classification, earnings variability, and regulatory frameworks.
Online Platforms: Task-Based Jobs and Their Economic Impact
Online platforms such as Upwork, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit facilitate gig work by connecting freelancers with clients for task-based jobs like graphic design, writing, and home repairs. These platforms contribute significantly to the gig economy, generating billions in revenue and offering flexible income opportunities to millions of workers globally. The economic impact includes increased labor market participation and shifts toward decentralized, on-demand employment models that influence traditional labor dynamics.
The Role of Gig Economy Apps in Shaping Employment
Gig economy apps like Uber, Lyft, and TaskRabbit have revolutionized labor markets by offering flexible work opportunities that cater to diverse skill sets and schedules. These platforms leverage technology to connect workers directly with consumers, reducing traditional employment barriers and fostering a shift towards independent contracting. The rapid growth of gig work influences employment patterns, income stability, and regulatory frameworks worldwide.
Creative and Specialized Gigwork: Designers, Writers, and More
Creative and specialized gigwork includes roles such as graphic designers, content writers, video editors, and digital marketers who offer expertise on freelance platforms like Upwork and Fiverr. These professionals often leverage advanced skills in software tools like Adobe Creative Suite and SEO strategies to meet specific client needs. The rise of remote work has further expanded opportunities for these creatives to participate in the global gig economy, generating significant income streams outside traditional employment.
Temporary Labor: Construction, Events, and Seasonal Gigs
Temporary labor in construction includes short-term projects like site preparation and equipment handling, often hired through staffing agencies or direct contracts. Event-based gigs involve roles such as setup, catering, and security for concerts, festivals, and corporate functions, providing flexible labor solutions. Seasonal gigs in retail and agriculture respond to peak demand periods, offering workers temporary opportunities aligned with market fluctuations.
Remote Virtual Assistance and Administrative Gigwork
Remote virtual assistance exemplifies gig work by enabling professionals to provide administrative support such as email management, scheduling, and data entry from any location, reducing the need for physical office presence. This sector of gig labor leverages digital platforms like Upwork and Fiverr to connect clients with skilled assistants on a project or hourly basis. Growth in remote virtual administrative gigs reflects increasing demand for flexible workforce solutions and cost-effective business operations globally.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities for Gig Workers
Gig work in labor, such as ride-sharing and freelance digital services, presents both economic challenges and opportunities for workers. Inconsistent income streams and lack of traditional employment benefits create financial instability for many gig workers, while the flexibility and access to diverse job markets offer potential for increased earnings and entrepreneurial growth. Understanding these dynamics is essential for policymakers aiming to balance worker protection with fostering innovation in the gig economy.
The Future of Labor: Trends in Gigwork and Economic Growth
Gigwork platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit exemplify the shift toward flexible labor arrangements driving economic growth by enabling workers to monetize diverse skills on demand. This labor model supports income diversification and reduces unemployment rates by connecting a global workforce with localized job opportunities in real time. As digital infrastructure improves and AI integration advances, gigwork is forecast to become a significant contributor to GDP by expanding micro-entrepreneurship and stimulating consumer spending.
example of gigwork in labor Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com