Menu costs in a restaurant refer to the expenses associated with changing prices on physical menus, which can include printing new menus, updating digital displays, and re-training staff on new pricing. For example, when a restaurant experiences rising food supply costs, it may need to increase menu prices to maintain profit margins, incurring menu costs in the process. These costs can affect the frequency and speed at which a restaurant adjusts its prices, impacting overall pricing strategy and revenue management. Restaurants face tangible expenses such as graphic design fees, printing, and lamination when modifying paper menus to reflect new prices. In addition, operational costs arise from informing staff and customers about price changes, which may temporarily slow down service. Menu costs thus represent a critical factor in decision-making for restaurant pricing policies, especially in environments with volatile input prices.
Table of Comparison
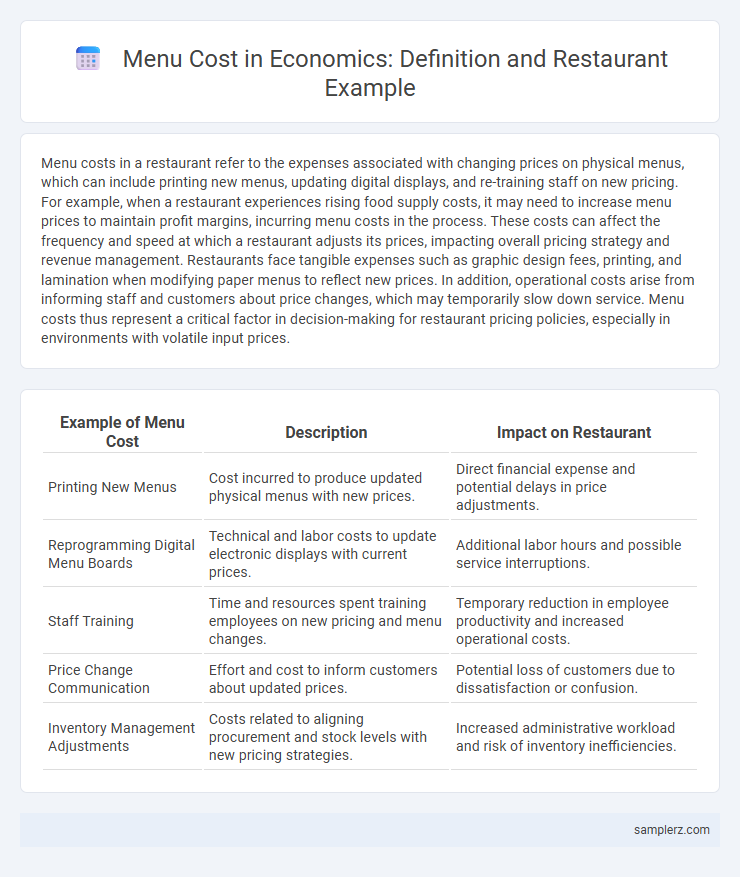
| Example of Menu Cost | Description | Impact on Restaurant |
|---|---|---|
| Printing New Menus | Cost incurred to produce updated physical menus with new prices. | Direct financial expense and potential delays in price adjustments. |
| Reprogramming Digital Menu Boards | Technical and labor costs to update electronic displays with current prices. | Additional labor hours and possible service interruptions. |
| Staff Training | Time and resources spent training employees on new pricing and menu changes. | Temporary reduction in employee productivity and increased operational costs. |
| Price Change Communication | Effort and cost to inform customers about updated prices. | Potential loss of customers due to dissatisfaction or confusion. |
| Inventory Management Adjustments | Costs related to aligning procurement and stock levels with new pricing strategies. | Increased administrative workload and risk of inventory inefficiencies. |
Understanding Menu Costs in Restaurant Operations
Menu costs in restaurant operations refer to the expenses incurred when updating physical menus, including printing new menus, redesign costs, and staff training on new pricing. Frequent price changes can lead to increased menu costs, impacting overall profitability and operational efficiency. Understanding these costs helps restaurants balance the need for price adjustments against maintaining customer satisfaction and controlling overhead expenses.
Real-Life Examples of Menu Cost Impacts
Menu costs in restaurants often manifest as the expenses incurred when updating printed menus due to price changes in ingredients like beef or dairy. Frequent fluctuations in supplier costs compel establishments to reprint menus, leading to material, design, and labor expenses that accumulate significantly over time. This phenomenon directly impacts pricing strategies, influencing profit margins and customer perception in competitive dining markets.
How Restaurants Face Menu Cost Challenges
Restaurants encounter menu cost challenges when frequent price adjustments require reprinting menus, retraining staff, and updating digital platforms, leading to increased operational expenses. To mitigate these costs, many establishments adopt digital menus or use menu inserts to enable flexible pricing without incurring high reprinting fees. Strategic pricing models and demand forecasting also help restaurants minimize the frequency of menu changes while maintaining profitability.
Revising Printed Menus: Financial and Labor Implications
Revising printed menus in restaurants incurs significant menu costs, encompassing both direct financial expenses for reprinting and indirect labor costs for updating menu designs and training staff. Frequent changes lead to increased operational spending, impacting overall profitability due to material, design, and employee time investments. Understanding these costs helps restaurants balance menu flexibility with economic efficiency to optimize revenue.
Digital Menus as Solutions to Traditional Menu Costs
Digital menus significantly reduce traditional menu costs in restaurants by eliminating printing expenses and allowing instant updates to prices and offerings. This technology improves operational efficiency by minimizing labor associated with manual menu changes and reducing waste from discarded paper menus. Adoption of digital menus also enhances customer experience with interactive features, driving increased sales and lowering overall menu management costs.
Price Adjustment Costs during Economic Fluctuations
Restaurants face significant menu costs when adjusting prices during economic fluctuations, such as the expense of reprinting physical menus and retraining staff on new pricing structures. These price adjustment costs often lead to delayed or infrequent price changes despite shifts in supply costs or demand, causing temporary mismatches in pricing efficiency. For example, during inflation, a restaurant may hesitate to update menu prices promptly due to the operational costs associated with frequent changes, impacting profitability and customer perception.
Case Study: Menu Updates after Supply Price Changes
Restaurant menu costs increase when supply price fluctuations require frequent updates, as seen in a case study where rising ingredient expenses forced multiple menu reprints within a month. These updates involve not only printing costs but also staff training on new pricing and potential customer dissatisfaction due to frequent changes. The case highlights the economic impact of supply volatility on operational expenses and price rigidity in the food service industry.
Indirect Costs of Menu Changes on Customer Perception
Frequent menu changes in restaurants impose indirect costs by disrupting customer perception, leading to potential dissatisfaction and decreased loyalty. These adjustments can confuse patrons who rely on familiar choices, ultimately impacting repeat business and brand reputation. The hidden expenses include retraining staff and redesigning marketing materials, which further strain operational efficiency.
Strategies to Minimize Menu Cost in Restaurants
Restaurants minimize menu costs by utilizing digital menus that allow instant price updates without reprinting expenses. Implementing seasonal menus reduces frequent price changes, lowering the need for constant physical menu alterations. Bulk ordering and long-term supplier contracts stabilize ingredient costs, indirectly reducing the frequency and scale of menu price adjustments.
The Economic Significance of Menu Costs in the Hospitality Industry
Menu costs in the hospitality industry represent the expenses restaurants incur when changing prices, including printing new menus, updating digital platforms, and training staff on revised pricing. These costs influence pricing strategies, often causing delays in adjusting to fluctuating food supply prices or labor costs, which affects profitability and market responsiveness. Understanding menu costs is vital for restaurateurs to optimize revenue in dynamic economic environments, balancing cost efficiency with customer satisfaction.
example of menu cost in restaurant Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com