A spin-off in a business context occurs when a parent company creates a new, independent company by separating a portion of its existing subsidiary. For example, eBay spun off PayPal in 2015, establishing it as a standalone publicly traded company. This strategic move allowed PayPal to focus exclusively on its digital payments platform while eBay concentrated on its core e-commerce operations. Another notable example involves Hewlett-Packard, which executed a spin-off by separating its enterprise services division into a new company called Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) in 2015. This allowed HPE to specialize in IT infrastructure and consulting services independently from HP's focus on personal computers and printers. Spin-offs like these enable both entities to pursue tailored growth strategies and improve shareholder value.
Table of Comparison
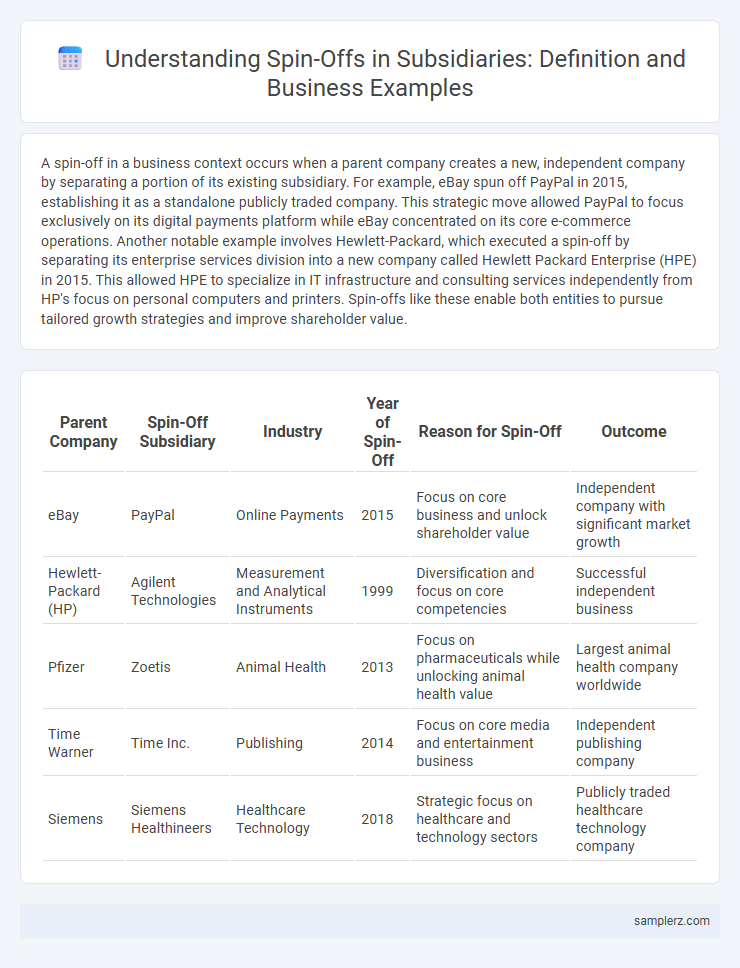
| Parent Company | Spin-Off Subsidiary | Industry | Year of Spin-Off | Reason for Spin-Off | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eBay | PayPal | Online Payments | 2015 | Focus on core business and unlock shareholder value | Independent company with significant market growth |
| Hewlett-Packard (HP) | Agilent Technologies | Measurement and Analytical Instruments | 1999 | Diversification and focus on core competencies | Successful independent business |
| Pfizer | Zoetis | Animal Health | 2013 | Focus on pharmaceuticals while unlocking animal health value | Largest animal health company worldwide |
| Time Warner | Time Inc. | Publishing | 2014 | Focus on core media and entertainment business | Independent publishing company |
| Siemens | Siemens Healthineers | Healthcare Technology | 2018 | Strategic focus on healthcare and technology sectors | Publicly traded healthcare technology company |
Introduction to Spin-Offs in Subsidiaries
A spin-off in a subsidiary occurs when a parent company separates a part of its subsidiary into an independent entity, allowing focused management and unlocking shareholder value. For example, PayPal was spun off from eBay in 2015 to operate as a standalone company, enabling more targeted growth strategies in digital payments. Spin-offs facilitate strategic realignment and can improve operational efficiency by concentrating on core business areas within the subsidiary structure.
Key Characteristics of Subsidiary Spin-Offs
Subsidiary spin-offs typically involve a parent company creating an independent company by separating a subsidiary, allowing focused strategic direction and enhanced operational efficiency. Key characteristics include the transfer of assets, liabilities, and personnel from the parent to the new entity, along with the distribution of shares to existing shareholders. These spin-offs enable targeted capital allocation, unlock subsidiary value, and often improve market valuation by clarifying business segments.
Famous Global Examples of Subsidiary Spin-Offs
Tesla's spin-off of its energy storage division into Tesla Energy illustrates successful subsidiary restructuring, enabling focused innovation in renewable solutions. Similarly, eBay's separation of PayPal allowed both entities to pursue tailored growth strategies, boosting shareholder value significantly. Disney's decision to spin off its publishing arm into a separate company enhanced operational efficiency and market responsiveness within each business unit.
Notable Technology Industry Spin-Offs
Notable technology industry spin-offs include Agilent Technologies, which was spun off from Hewlett-Packard in 1999 to focus on test and measurement equipment. Another example is PayPal, initially a subsidiary of eBay before becoming an independent entity in 2015, specializing in digital payments. These spin-offs illustrate how parent companies restructure to unlock value and enhance specialization within the tech sector.
Pharmaceutical Companies with Successful Spin-Offs
Pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer have executed successful spin-offs, such as the creation of Viatris, which allowed Pfizer to focus on innovative drug development while Viatris specialized in generic medications and biosimilars. GlaxoSmithKline's spin-off of its consumer healthcare division into Haleon enabled both companies to streamline operations and enhance shareholder value. These strategic moves demonstrate how spin-offs in the pharmaceutical industry can optimize resource allocation and drive focused growth in specialized market segments.
Spin-Offs in the Retail and Consumer Goods Sector
Spin-offs in the retail and consumer goods sector often reshape competitive landscapes by enabling subsidiaries to operate as independent entities, such as when PepsiCo spun off its grocery business to focus exclusively on beverages and snacks. This strategic separation enhances agility and allows targeted investment, exemplified by eBay's spin-off of StubHub to streamline its marketplace operations. Retail giants also leverage spin-offs to unlock shareholder value and innovate within niche markets, as seen in Walgreens Boots Alliance's divestiture of its wholesale distribution unit.
Financial Services Firms’ Subsidiary Spin-Off Cases
Financial services firms like JPMorgan Chase and Citigroup have executed subsidiary spin-offs to enhance shareholder value and streamline operations. For instance, Citigroup's spin-off of its brokerage division, Smith Barney, formed a joint venture with Morgan Stanley, allowing both firms to focus on core banking and wealth management services. These spin-offs enable clearer financial structures, improved regulatory compliance, and targeted strategic growth within specialized market segments.
Impact of Spin-Offs on Parent and Subsidiary Growth
Spin-offs in subsidiaries often lead to increased focus and agility for both parent and spun-off companies, driving specialized innovation and market responsiveness. The parent company benefits from streamlined operations and enhanced shareholder value, while the new entity gains independence to pursue targeted growth strategies. Empirical studies reveal spin-offs can boost revenue growth rates by 10-15% for subsidiaries and improve return on equity by 5-8% for parent firms.
Strategic Motives Behind Subsidiary Spin-Offs
Subsidiary spin-offs often occur to enhance strategic focus on core competencies, allowing the parent company to streamline operations and unlock shareholder value. For example, eBay's spin-off of PayPal in 2015 enabled both entities to pursue independent growth strategies tailored to their distinct markets. This strategic move capitalized on the divergent business models and accelerated innovation in digital payments separate from e-commerce activities.
Lessons Learned from Real-World Spin-Off Examples
Real-world spin-offs such as PayPal from eBay highlight the importance of strategic focus and operational independence for subsidiaries, enabling tailored growth and value creation. Lessons learned emphasize clear governance structures and transparent communication as critical factors in managing stakeholder expectations during the transition. Effective spin-offs often result in enhanced innovation and market responsiveness by allowing the new entity to align closely with its core competencies.
example of spin-off in subsidiary Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com