The term "dragon" in private equity refers to highly successful and influential investment firms or individuals that demonstrate exceptional growth and deal-making prowess. These entities often lead large funding rounds, drive innovation, and shape industry trends through strategic acquisitions and portfolio management. Dragon investors are known for their ability to identify high-potential startups and scale them rapidly into market leaders. Private equity dragons typically manage billions of dollars in assets under management (AUM) and maintain a diverse portfolio across multiple sectors including technology, healthcare, and consumer goods. Their investments generate significant returns by deploying capital efficiently and leveraging operational expertise to enhance company value. Recognized examples include firms like Sequoia Capital and Blackstone Group, which consistently outperform peers and influence global private equity markets.
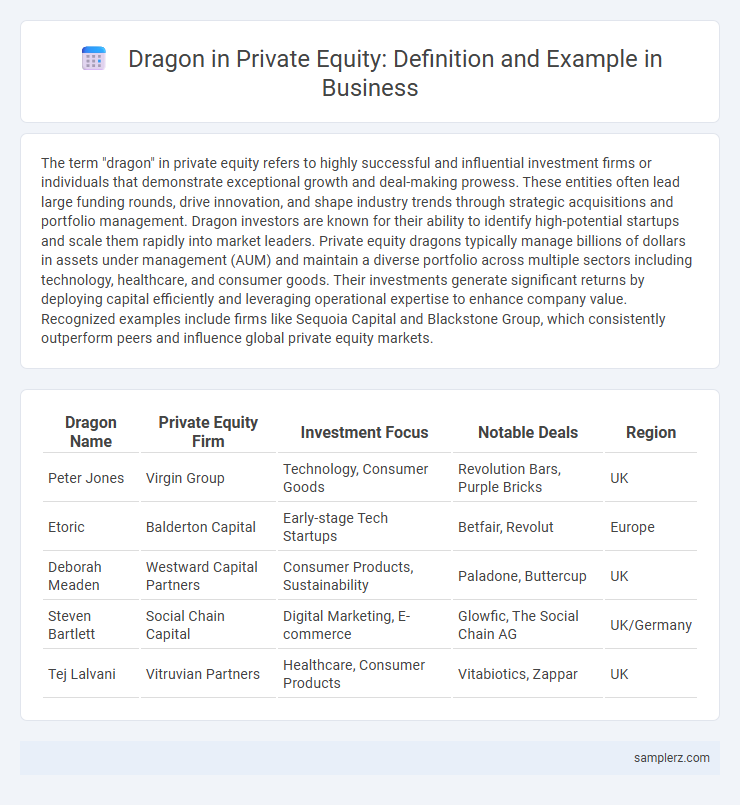
Table of Comparison
| Dragon Name | Private Equity Firm | Investment Focus | Notable Deals | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peter Jones | Virgin Group | Technology, Consumer Goods | Revolution Bars, Purple Bricks | UK |
| Etoric | Balderton Capital | Early-stage Tech Startups | Betfair, Revolut | Europe |
| Deborah Meaden | Westward Capital Partners | Consumer Products, Sustainability | Paladone, Buttercup | UK |
| Steven Bartlett | Social Chain Capital | Digital Marketing, E-commerce | Glowfic, The Social Chain AG | UK/Germany |
| Tej Lalvani | Vitruvian Partners | Healthcare, Consumer Products | Vitabiotics, Zappar | UK |
Defining "Dragons" in Private Equity
Dragons" in private equity refer to high-performing investors or firms that consistently generate exceptional returns by identifying undervalued assets and driving value creation through strategic management. These entities possess strong sector expertise, extensive networks, and a track record of successful exits, setting them apart from typical private equity players. Examples of dragons include firms like Blackstone, KKR, and Carlyle Group, known for their ability to scale businesses rapidly and maximize portfolio value.
Key Characteristics of Dragon Investments
Dragon investments in private equity are distinguished by their aggressive growth strategies, significant capital infusion, and high tolerance for risk. These investments often target early-stage companies with scalable business models and innovative technologies, aiming for exponential returns. Strong management involvement and a focus on rapid market expansion further define the key characteristics of dragon investments.
Notable Examples of Dragons in Private Equity History
Chris Sacca, founder of Lowercase Capital, is a notable dragon in private equity known for early investments in Uber and Twitter, generating massive returns. Another example is John Doerr of Kleiner Perkins, whose strategic funding of Google and Amazon significantly shaped the private equity landscape. These dragons exemplify vision-driven investment that transforms industries and delivers substantial value creation.
How Dragons Differ from Unicorns in Private Equity
Dragons in private equity represent companies generating over $100 million in annual profit, showcasing sustained profitability rather than just high valuation growth. Unlike unicorns, which are startups valued above $1 billion often based on future potential, dragons emphasize cash flow and operational efficiency. This focus on measurable earnings makes dragons more attractive to investors seeking stable returns and long-term value creation.
Case Study: A Dragon Deal That Transformed a Portfolio
A landmark example of a dragon deal in private equity is Silver Lake Partners' $12.5 billion investment in Dell Technologies, which reshaped the firm's portfolio by driving a strategic transition from hardware to cloud computing. This transaction not only enhanced Dell's market position but also delivered substantial returns by capitalizing on emerging tech trends and operational efficiencies. The deal exemplifies how targeted private equity investments can transform traditional companies into innovative market leaders.
Factors Leading to Dragon-Level Returns
Dragon-level returns in private equity are often driven by factors such as sector expertise, strategic operational improvements, and timely market entry. Successful funds leverage deep industry knowledge, aggressive cost management, and value creation through active portfolio management to outperform benchmarks. Access to proprietary deal flow and strong alignment of interests between investors and management teams also plays a critical role in achieving exceptional multiple expansions.
Sectors Most Likely to Produce Dragons
Sectors most likely to produce dragons in private equity include technology, healthcare, and renewable energy due to their high growth potential and innovation capacity. Technology companies, especially those involved in AI, SaaS, and cybersecurity, often scale rapidly, attracting significant investment and delivering substantial returns. Healthcare innovations in biotech and digital health also drive market disruption, while renewable energy benefits from global trends toward sustainability and regulatory support.
Risks and Rewards of Chasing Dragons in Private Equity
Investing in high-growth startups, often called "dragons" for their potential to deliver massive returns, carries substantial risks including valuation bubbles, illiquidity, and operational challenges. Private equity firms chasing these dragons must conduct rigorous due diligence to mitigate risks like market volatility and over-leveraging, balancing the possibility of exponential gains against potential significant losses. Successful investments in dragon companies can result in outsized rewards, including rapid scaling and dominant market positioning, but require sophisticated risk management strategies to navigate uncertainties effectively.
Strategies for Identifying Potential Dragon Investments
Top private equity firms identify potential dragon investments by analyzing market disruption potential, strong management teams, and scalable business models that drive exponential growth. They leverage data-driven due diligence, industry trends, and competitive positioning to uncover undervalued companies with high return prospects. Strategic partnerships and deep sector expertise enhance their ability to spot emerging leaders capable of delivering outsized value.
Lessons Learned from Successful Dragon Exits
Successful dragon exits in private equity, such as the Alibaba IPO and the Flipkart acquisition by Walmart, demonstrate the importance of market timing and strategic positioning. These cases highlight the critical role of strong governance structures and robust operational improvements in maximizing exit valuations. Data-driven decision-making and early identification of growth catalysts consistently contribute to delivering high returns for investors.
example of dragon in private equity Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com