A spin-off in business occurs when a company creates a new independent entity by separating part of its operations, assets, or divisions. An example is PayPal's spin-off from eBay in 2015, where PayPal became a standalone company focused on digital payments. This move allowed PayPal to pursue growth opportunities independently while eBay concentrated on its core e-commerce business. Another example is Hewlett-Packard's split in 2015 into two separate companies: HP Inc., which handles personal computers and printers, and Hewlett Packard Enterprise, which focuses on enterprise products and services. This spin-off strategy aimed to enhance operational efficiency and better serve distinct customer segments. The separation provided clarity in business focus and improved investor value by targeting specific market needs.
Table of Comparison
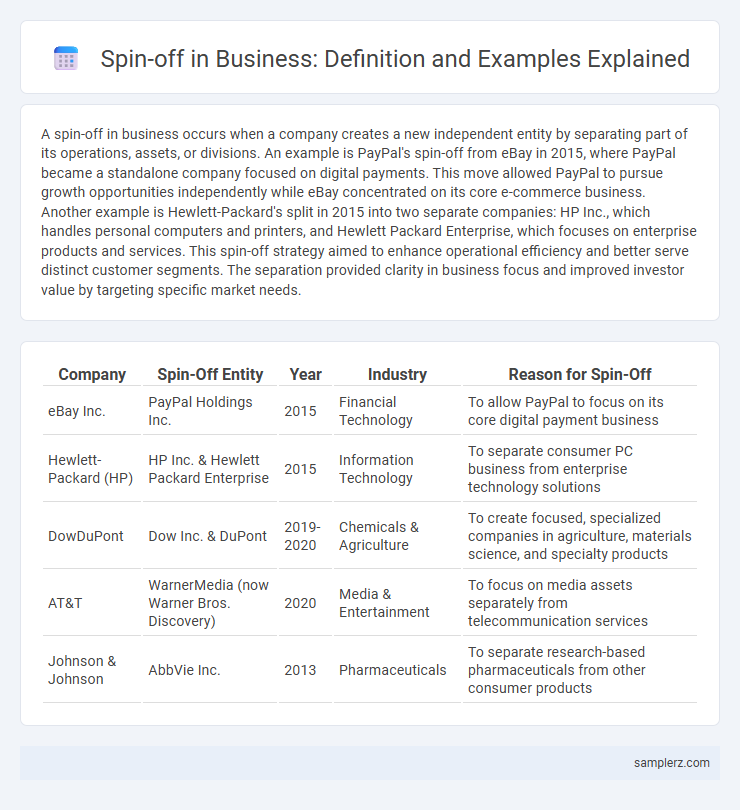
| Company | Spin-Off Entity | Year | Industry | Reason for Spin-Off |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eBay Inc. | PayPal Holdings Inc. | 2015 | Financial Technology | To allow PayPal to focus on its core digital payment business |
| Hewlett-Packard (HP) | HP Inc. & Hewlett Packard Enterprise | 2015 | Information Technology | To separate consumer PC business from enterprise technology solutions |
| DowDuPont | Dow Inc. & DuPont | 2019-2020 | Chemicals & Agriculture | To create focused, specialized companies in agriculture, materials science, and specialty products |
| AT&T | WarnerMedia (now Warner Bros. Discovery) | 2020 | Media & Entertainment | To focus on media assets separately from telecommunication services |
| Johnson & Johnson | AbbVie Inc. | 2013 | Pharmaceuticals | To separate research-based pharmaceuticals from other consumer products |
Introduction to Business Spin-offs
Business spin-offs occur when a parent company creates a new independent entity by separating a division or subsidiary. A notable example is PayPal's spin-off from eBay in 2015, allowing PayPal to focus solely on digital payments while eBay concentrated on its marketplace platform. Spin-offs often enhance shareholder value by enabling each entity to pursue specialized strategies and operational efficiencies.
Key Features of Successful Spin-offs
Successful spin-offs, such as PayPal emerging from eBay, demonstrate clear strategic focus on core competencies, enabling the new entity to innovate freely while leveraging established resources. Key features include autonomous management teams, well-defined financial structures, and a strong alignment with market opportunities that drive growth and shareholder value. These elements empower spin-offs to operate with agility, attract dedicated investment, and capitalize on niche markets efficiently.
Notable Corporate Spin-off Examples
Notable corporate spin-off examples include PayPal's separation from eBay in 2015, which allowed PayPal to focus exclusively on digital payments and expand its market presence. Another significant case is Hewlett-Packard's 2015 split into HP Inc. and Hewlett Packard Enterprise, enabling both entities to specialize in personal computing and enterprise services respectively. These spin-offs often unlock shareholder value and increase operational efficiency by allowing the new companies to focus on core competencies.
Technology Sector Spin-off Case Studies
Technology sector spin-off case studies highlight companies like PayPal, which originated as a division of Confinity before becoming a standalone entity specializing in digital payments. Another example is NVIDIA's creation of Mellanox Technologies to focus on high-performance interconnect solutions, enhancing innovations in data centers. These spin-offs demonstrate strategic moves to unlock specialized growth and technological advancements within diverse market segments.
Pharmaceutical Industry Spin-offs
Pharmaceutical industry spin-offs often occur when large corporations create independent companies to focus on specialized drug development, such as Pfizer's spin-off of Viatris, which concentrates on generic and biosimilar medicines. These spin-offs enable more agile research and targeted innovation in areas like oncology, vaccines, or rare diseases. By separating non-core assets, parent companies optimize resource allocation and enhance shareholder value in the pharmaceutical sector.
Spin-offs in Retail and Consumer Goods
Spin-offs in retail and consumer goods often involve large corporations separating a specific brand or product line to create a more focused and agile company, such as PepsiCo spinning off its bottling operations into Pepsi Bottling Group. This strategic move allows the new entity to concentrate on core competencies, improve operational efficiency, and unlock shareholder value. For example, the separation of Kraft Foods Group from Mondelez International enabled each company to tailor strategies for distinct market segments in snacks and grocery products.
Strategic Reasons Behind Business Spin-offs
Business spin-offs often occur to enhance strategic focus by allowing the parent company to concentrate on its core operations while the new entity targets specialized markets or innovations. These spin-offs enable improved resource allocation, operational efficiencies, and the unlocking of shareholder value through clearer business models. By separating distinct business units, companies can respond faster to market changes, attract tailored investments, and pursue growth opportunities specific to each entity's strategic goals.
Financial Impact of Spin-offs on Parent Companies
Spin-offs often lead to significant financial impacts on parent companies by unlocking shareholder value and improving operational focus. For example, when eBay spun off PayPal in 2015, the parent company experienced a surge in stock performance, reflecting enhanced market valuations and clearer business strategies. This financial separation allowed both entities to attract targeted investments and optimize capital allocation effectively.
Lessons Learned from Spin-off Success Stories
Successful spin-offs like PayPal from eBay highlight the importance of strategic focus and operational independence in driving growth and innovation. Companies learn that clear vision alignment and dedicated leadership empower the spin-off to adapt quickly to market demands and unlock shareholder value. Effective communication with stakeholders and robust financial planning are critical lessons from these business transformations.
Future Trends in Business Spin-offs
Business spin-offs are increasingly leveraged to unlock innovation by creating agile, independent entities focused on emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and renewable energy. Companies such as Siemens Energy and PayPal have successfully executed spin-offs to capitalize on future market trends, enhancing shareholder value and operational efficiency. This strategic separation allows parent firms to concentrate on core competencies while enabling spin-offs to rapidly adapt to evolving industry demands and digital transformation.
example of spin-off in business Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com