Sweat equity in business refers to the non-monetary investment that founders or employees contribute through hard work, time, and effort to build a company. For example, a startup founder who works for months developing a prototype without drawing a salary is earning sweat equity. This type of investment increases the value of the business and can result in ownership shares or equity stakes. An illustration of sweat equity is a team of software developers who create a new app while holding other jobs. They invest hundreds of hours without immediate pay, aiming to gain equity once the product is launched or sold. Such sweat equity incentivizes commitment and aligns the team's interests with the long-term success of the business.
Table of Comparison
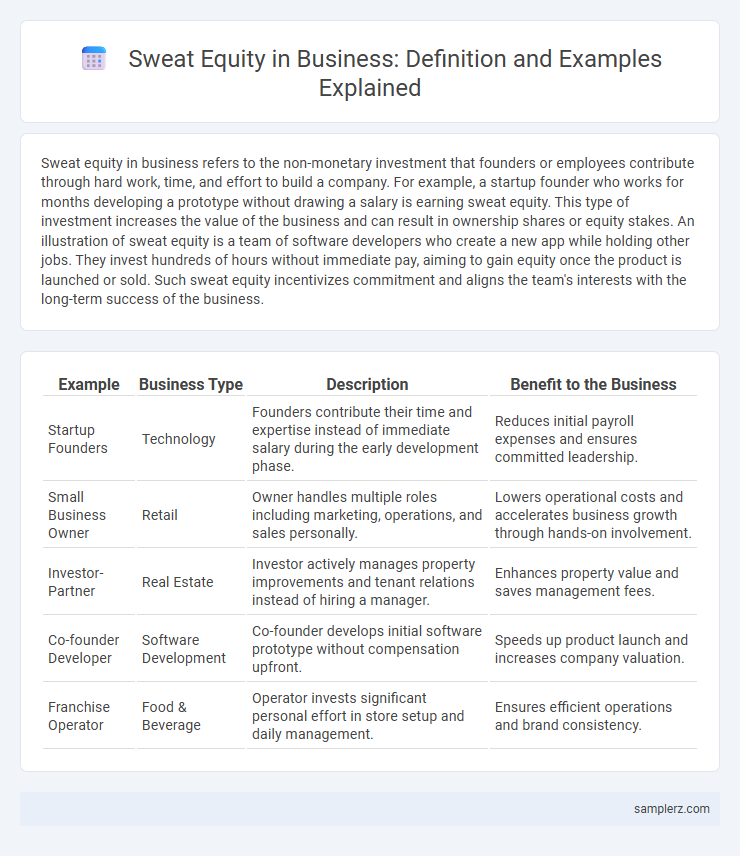
| Example | Business Type | Description | Benefit to the Business |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Founders | Technology | Founders contribute their time and expertise instead of immediate salary during the early development phase. | Reduces initial payroll expenses and ensures committed leadership. |
| Small Business Owner | Retail | Owner handles multiple roles including marketing, operations, and sales personally. | Lowers operational costs and accelerates business growth through hands-on involvement. |
| Investor-Partner | Real Estate | Investor actively manages property improvements and tenant relations instead of hiring a manager. | Enhances property value and saves management fees. |
| Co-founder Developer | Software Development | Co-founder develops initial software prototype without compensation upfront. | Speeds up product launch and increases company valuation. |
| Franchise Operator | Food & Beverage | Operator invests significant personal effort in store setup and daily management. | Ensures efficient operations and brand consistency. |
Understanding Sweat Equity in Business
Sweat equity in business represents the non-monetary investment made by founders or employees through hard work, time, and effort to build the company's value. For example, a startup founder may forgo a salary while developing a product, earning ownership shares based on their contributions rather than cash investment. Recognizing sweat equity is crucial for valuing contributions in businesses where initial capital is limited but intellectual effort and skills drive growth.
Why Sweat Equity Matters for Startups
Sweat equity represents the non-monetary investment founders and early employees contribute through time, effort, and skills to build a startup's value, often resulting in significant ownership stakes. This form of equity is crucial for startups lacking substantial capital, enabling them to attract talent and motivate team members aligned with the company's vision. Recognizing sweat equity's role empowers startups to allocate shares fairly, fostering commitment and driving long-term growth without upfront financial expenditure.
Classic Examples of Sweat Equity Agreements
Classic examples of sweat equity agreements include startup founders contributing time and expertise in exchange for ownership shares, often seen in technology companies like Google and Facebook during their early stages. Small business partnerships frequently rely on sweat equity, where one partner invests labor instead of capital and receives a percentage of profits or equity. Real estate development projects also utilize sweat equity when investors or developers perform physical work or management roles to reduce cash investment and gain ownership stakes.
Sweat Equity Among Co-Founders
Sweat equity among co-founders often manifests as unpaid labor, product development, and strategic planning invested during the startup phase, directly increasing the company's valuation. Founders contribute their expertise and time instead of capital, earning ownership stakes proportional to their input, which aligns incentives and drives long-term commitment. Examples include a technical co-founder developing the initial software platform or a marketing co-founder establishing brand presence before external funding.
Employee Compensation Through Sweat Equity
Employee compensation through sweat equity involves granting employees ownership stakes in a company as a reward for their hard work and contributions instead of traditional salaries. Startups often use sweat equity to motivate key team members by allocating stock options or shares, aligning employees' interests with long-term company growth. This approach fosters loyalty and incentivizes performance, especially when cash flow is limited during early-stage development.
Sweat Equity in Small Family Businesses
Small family businesses often rely on sweat equity when family members contribute labor, skill, and time instead of financial capital to grow the company. For example, a family-run restaurant may have members handling daily operations, marketing, and bookkeeping without formal salaries, increasing the business's value through their dedicated efforts. This non-monetary investment builds ownership stakes and fosters long-term commitment, essential for sustaining and expanding small family enterprises.
Sweat Equity in Franchises and Partnerships
Sweat equity in franchises often involves owners investing significant time and effort to build brand recognition and operational efficiency, which increases the franchise's overall value without immediate cash input. In partnerships, sweat equity is commonly allocated to partners who contribute expertise, management, or labor instead of capital, reflecting their ownership stake and influence on business growth. This non-monetary investment aligns incentives and drives long-term commitment, enhancing valuation during future funding rounds or exit events.
Real-Life Sweat Equity Success Stories
Tech startups like Airbnb and Dropbox demonstrate the power of sweat equity, where founders invested countless hours instead of capital to develop their platforms. In small businesses, restaurant owners often trade a reduced salary for equity stakes, aligning long-term growth with their personal effort. Real-life examples confirm sweat equity as a key driver for building value and securing stakeholder commitment.
Legal Considerations in Sweat Equity Deals
Sweat equity agreements require clear legal documentation outlining roles, responsibilities, and valuation methods to prevent disputes between founders and investors. Intellectual property rights and equity distribution must be explicitly addressed in contracts to protect contributions and ownership stakes. Ensuring compliance with securities laws and employment regulations is crucial to maintain the validity and enforceability of sweat equity arrangements.
Maximizing Sweat Equity Value in Your Business
Maximizing sweat equity value in your business involves strategically investing time and expertise to enhance company growth and profitability without immediate financial expenditure. Founders often increase sweat equity by developing proprietary technology, building a robust customer base, or refining operational processes that significantly boost valuation. Transparent documentation and clear agreements on equity distribution ensure that contributions are recognized and incentivized, fostering long-term commitment and business success.
example of sweat equity in business Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com