A Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC) is an investment vehicle designed to take companies public without going through the traditional initial public offering (IPO) process. One notable example of a SPAC investment is the merger of Virgin Galactic with Social Capital Hedosophia, which allowed the spaceflight company to be listed on the New York Stock Exchange in 2019. This SPAC transaction raised approximately $450 million, providing Virgin Galactic with capital to fund its commercial spaceflight operations. SPACs have become a popular alternative for businesses seeking faster access to public markets and capital. The Social Capital Hedosophia SPAC demonstrated how high-profile entities can leverage these blank-check companies to bypass regulatory hurdles typically encountered in conventional IPOs. Investors benefit from the potential upside in companies like Virgin Galactic, whose valuation soared post-merger, highlighting SPACs as a significant trend in contemporary investment strategies.
Table of Comparison
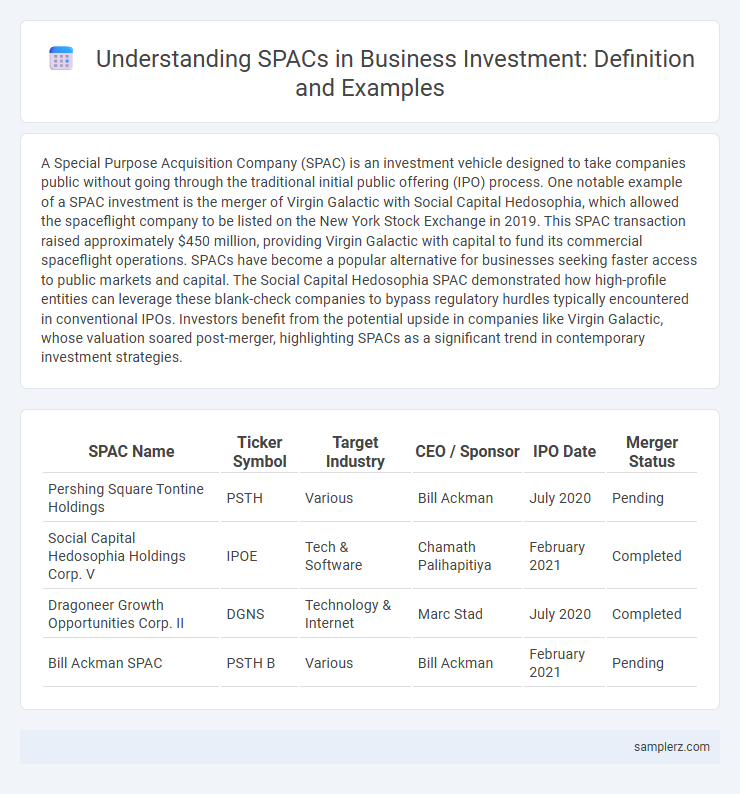
| SPAC Name | Ticker Symbol | Target Industry | CEO / Sponsor | IPO Date | Merger Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pershing Square Tontine Holdings | PSTH | Various | Bill Ackman | July 2020 | Pending |
| Social Capital Hedosophia Holdings Corp. V | IPOE | Tech & Software | Chamath Palihapitiya | February 2021 | Completed |
| Dragoneer Growth Opportunities Corp. II | DGNS | Technology & Internet | Marc Stad | July 2020 | Completed |
| Bill Ackman SPAC | PSTH B | Various | Bill Ackman | February 2021 | Pending |
Introduction to SPACs in Investment
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) have become a popular investment vehicle for raising capital through public markets without undergoing the traditional IPO process. Investors typically buy shares in a SPAC, which then seeks a private company to merge with, enabling that company to become publicly traded. The surge in SPAC activity since 2020 highlights their importance in alternative investment strategies, offering both liquidity and growth opportunities.
How SPACs Work: Key Mechanisms
A Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC) raises capital through an initial public offering (IPO) to acquire a private company, enabling the target to go public without a traditional IPO process. Investors initially buy shares in the SPAC, which are held in a trust until a merger or acquisition is completed. This structure accelerates market entry for private firms while providing investors with redemption rights and potential upside from the merged entity.
Notable SPAC Examples in Recent Years
Notable SPAC examples in recent years include the merger of Social Capital Hedosophia with Virgin Galactic, which raised over $800 million to fund the space tourism company's public listing. Another significant deal was the $4 billion combination of Churchill Capital Corp IV with Lucid Motors, accelerating the electric vehicle manufacturer's market entry. These high-profile transactions highlight the growing influence of SPACs in providing alternative capital for emerging and high-growth companies.
High-Profile Companies That Went Public via SPAC
DraftKings exemplifies a high-profile company that went public via a SPAC merger, achieving rapid market entry through its 2020 deal with Diamond Eagle Acquisition Corp. Virgin Galactic also demonstrated how space tourism innovation attracted significant SPAC investments, merging with Social Capital Hedosophia in 2019. These examples highlight SPAC's role in accelerating public listings for disruptive companies seeking capital infusion and market visibility.
Success Stories: SPAC Investment Outcomes
DraftKings' merger with Diamond Eagle Acquisition Corp. exemplifies a successful SPAC investment, resulting in a significant market capitalization increase and expanded capital access. Virgin Galactic's partnership with Social Capital Hedosophia showcases how SPACs can accelerate space tourism ventures by providing public market entry with substantial funding. Churchill Capital Corp IV's acquisition of Lucid Motors highlights SPACs' role in advancing electric vehicle innovation while generating notable shareholder value.
Risks and Challenges in SPAC Investments
SPAC investments carry significant risks such as inflated valuations, potential conflicts of interest between sponsors and public investors, and a compressed timeline to identify and complete acquisitions, which can pressure deal quality. Regulatory scrutiny has increased, heightening disclosure requirements and legal uncertainties that may impact deal execution and investor protections. Market volatility and lack of historical performance data for many SPAC targets further complicate investment decisions, resulting in increased uncertainty for investors.
Comparing SPACs to Traditional IPOs
SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) offer a faster route to public markets with less regulatory scrutiny compared to traditional IPOs, often completing the process in 3 to 6 months versus 6 to 12 months for IPOs. While traditional IPOs provide immediate capital infusion and established market credibility, SPACs allow private companies to negotiate valuations directly with sponsors, potentially reducing market volatility risks. Investors should consider the higher due diligence requirements and post-merger performance variability associated with SPAC transactions relative to conventional IPO outcomes.
Regulatory Developments Affecting SPACs
The rise of Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) has prompted regulatory bodies like the SEC to implement stricter disclosure requirements and enhanced investor protections. Key regulatory developments include mandates for clearer financial disclosures, detailed risk assessments, and timelines for completing mergers to mitigate risks inherent in SPAC transactions. These regulatory measures aim to increase transparency and safeguard investors while maintaining the viability of SPACs as alternative investment vehicles in the capital markets.
Lessons Learned from Prominent SPAC Deals
Prominent SPAC deals like DraftKings' merger with Diamond Eagle Acquisition highlighted the importance of thorough due diligence and transparent financial disclosures to avoid valuation bubbles. The Nikola SPAC deal demonstrated risks related to management credibility and the necessity of robust corporate governance structures. These cases emphasize careful investor scrutiny and regulatory compliance as critical factors for successful SPAC investments.
Future Trends for SPACs in the Investment Landscape
SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) continue to reshape the investment landscape by offering alternative pathways for companies to access public markets, with sectors like technology, renewable energy, and biotechnology attracting significant SPAC capital. Future trends indicate increased regulatory scrutiny and investor demand for transparency will drive more rigorous due diligence and enhanced governance standards in SPAC transactions. The evolving market dynamics suggest SPACs will increasingly focus on sustainable investments and long-term value creation to appeal to institutional investors and align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
example of SPAC in investment Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com