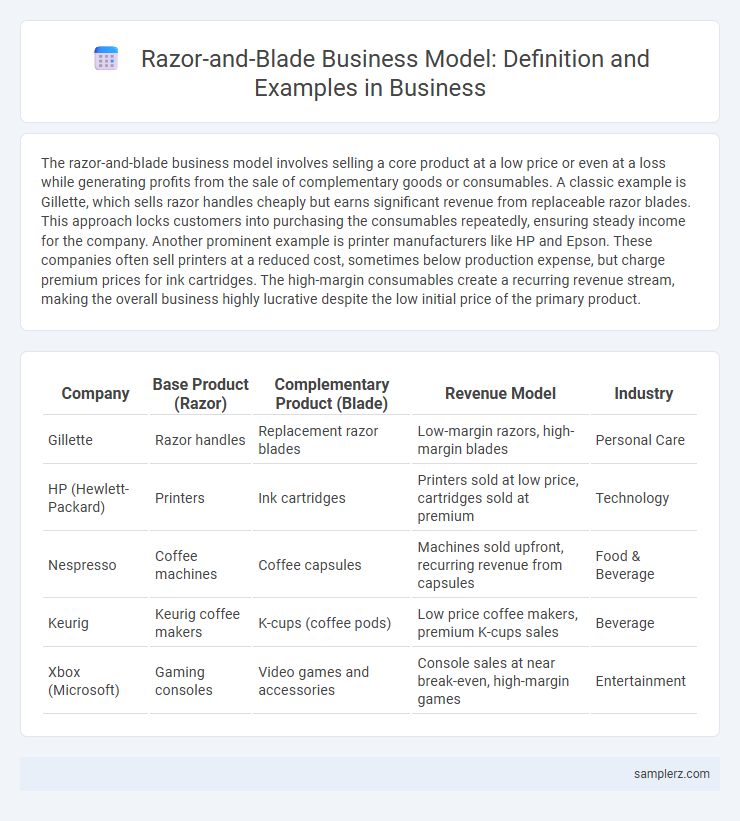
The razor-and-blade business model involves selling a core product at a low price or even at a loss while generating profits from the sale of complementary goods or consumables. A classic example is Gillette, which sells razor handles cheaply but earns significant revenue from replaceable razor blades. This approach locks customers into purchasing the consumables repeatedly, ensuring steady income for the company. Another prominent example is printer manufacturers like HP and Epson. These companies often sell printers at a reduced cost, sometimes below production expense, but charge premium prices for ink cartridges. The high-margin consumables create a recurring revenue stream, making the overall business highly lucrative despite the low initial price of the primary product.
Table of Comparison
| Company | Base Product (Razor) | Complementary Product (Blade) | Revenue Model | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gillette | Razor handles | Replacement razor blades | Low-margin razors, high-margin blades | Personal Care |
| HP (Hewlett-Packard) | Printers | Ink cartridges | Printers sold at low price, cartridges sold at premium | Technology |
| Nespresso | Coffee machines | Coffee capsules | Machines sold upfront, recurring revenue from capsules | Food & Beverage |
| Keurig | Keurig coffee makers | K-cups (coffee pods) | Low price coffee makers, premium K-cups sales | Beverage |
| Xbox (Microsoft) | Gaming consoles | Video games and accessories | Console sales at near break-even, high-margin games | Entertainment |
Understanding the Razor-and-Blade Business Model
The razor-and-blade business model generates recurring revenue by selling a primary product at a low price or loss, while profiting from the continuous sales of complementary consumables or accessories. Companies like Gillette dominate this strategy by offering affordable razors but pricing replacement blades significantly higher, ensuring steady customer reliance and long-term profitability. This model emphasizes customer lock-in and ongoing demand for essential supplementary products, driving sustained business growth.
Key Characteristics of Razor-and-Blade Strategies
Razor-and-blade business models focus on selling a primary product at a low price or loss while generating high-margin revenue from complementary consumables or accessories, such as printers and ink cartridges or gaming consoles and proprietary games. Key characteristics include initial customer lock-in through essential hardware, recurring purchases of disposable or refill items, and a strong emphasis on creating a durable competitive advantage via proprietary technology or brand loyalty. This strategy drives sustained profit growth by maximizing customer lifetime value and minimizing price sensitivity for the consumables.
Iconic Historical Examples: Gillette and Beyond
Gillette revolutionized the razor-and-blade business model by selling affordable razor handles while generating continuous revenue through the high-margin replacement blades. Other iconic examples include printer manufacturers like HP, which offer low-cost printers paired with expensive ink cartridges, and gaming consoles such as Sony PlayStation that rely on game sales and subscription services for sustained profits. This model emphasizes locking customers into purchasing consumables or complementary products repeatedly, ensuring long-term business success.
Modern Tech Applications: Printers and Ink Cartridges
Modern tech applications exemplify the razor-and-blade business model through printers and ink cartridges, where printers are sold at competitive prices while ink cartridges generate ongoing revenue. This strategy ensures continuous customer engagement and high-profit margins from recurring cartridge sales. Major brands like HP and Canon leverage this approach to sustain long-term profitability in the tech market.
Gaming Industry: Consoles and Game Sales
The gaming industry exemplifies the razor-and-blade business model through consoles and game sales, where companies like Sony and Microsoft sell gaming consoles at low or subsidized prices while generating substantial revenue from high-margin game titles and downloadable content. This strategy encourages consumer investment in proprietary ecosystems, increasing lifetime customer value through recurring software purchases and subscription services such as PlayStation Plus or Xbox Game Pass. The model drives profitability by leveraging hardware as an entry point and maximizing sales in digital and physical game markets.
Subscription Services: Coffee Machines and Pods
Subscription services for coffee machines and pods exemplify the razor-and-blade business model by selling the coffee machine at a low cost or for free, while generating consistent revenue through recurring sales of pods. Leading brands like Nespresso and Keurig leverage this model, creating customer lock-in with proprietary pod designs. This strategy ensures steady cash flow and maximizes lifetime customer value through ongoing subscription fees.
Digital Products: Razors and App Ecosystems
The razor-and-blade business model in digital products is exemplified by mobile operating systems like Apple's iOS and Google's Android, which offer free platforms (razors) while generating revenue through app stores (blades). Developers pay fees or commissions on in-app purchases and app sales, creating a continuous profit stream linked to the ecosystem. This model leverages network effects, as a larger user base attracts more developers, enhancing the app ecosystem and increasing customer lock-in.
Health and Wellness: Electric Toothbrushes and Replacement Heads
The health and wellness industry effectively employs the razor-and-blade business model through electric toothbrushes paired with replacement heads. Companies like Philips Sonicare and Oral-B generate recurring revenue by selling durable electric toothbrush handles alongside high-margin, frequently purchased replacement brush heads. This strategy enhances customer retention and drives sustained sales growth within the oral care market.
Automotive Sector: Vehicles and Consumable Parts
The razor-and-blade business model in the automotive sector exemplifies selling vehicles at competitive prices while generating recurring revenue through consumable parts like tires, brake pads, and oil filters. Automakers often offer durable cars with components designed for periodic replacement, ensuring continuous demand for aftermarket parts. This strategy maximizes lifetime customer value by combining initial vehicle sales with consistent consumable part purchases.
Evaluating Pros and Cons of the Razor-and-Blade Model
The razor-and-blade business model, exemplified by companies like Gillette, involves selling a core product at a low price while generating profits from consumable complementary products. This model creates recurring revenue streams and enhances customer loyalty but can lead to customer frustration due to perceived high costs of replacement parts or consumables. Evaluating this strategy requires balancing initial affordability with long-term profitability and customer satisfaction.
example of razor-and-blade in business model Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com