Burn rate in a startup refers to the rate at which a company spends its capital before generating positive cash flow. For example, a startup with $500,000 in funding that spends $50,000 per month has a burn rate of $50,000. This means the startup has a runway of 10 months before it needs additional funding or must become profitable. Investors closely monitor burn rate to assess the financial health and sustainability of a startup. High burn rates can indicate rapid growth but also increase the risk of running out of cash. Analyzing burn rate data helps founders make strategic decisions about spending, hiring, and fundraising to extend the company's operational timeframe.
Table of Comparison
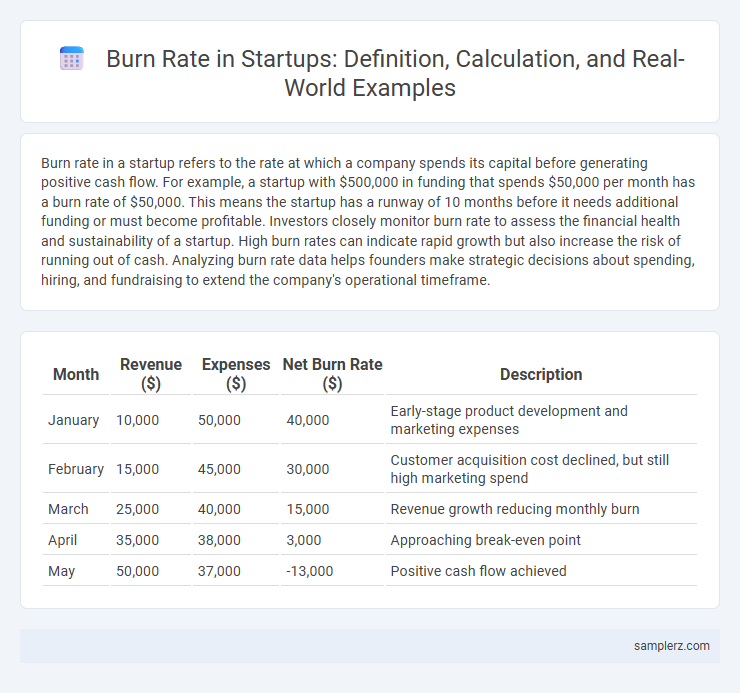
| Month | Revenue ($) | Expenses ($) | Net Burn Rate ($) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 10,000 | 50,000 | 40,000 | Early-stage product development and marketing expenses |
| February | 15,000 | 45,000 | 30,000 | Customer acquisition cost declined, but still high marketing spend |
| March | 25,000 | 40,000 | 15,000 | Revenue growth reducing monthly burn |
| April | 35,000 | 38,000 | 3,000 | Approaching break-even point |
| May | 50,000 | 37,000 | -13,000 | Positive cash flow achieved |
Understanding Burn Rate: A Key Startup Metric
Burn rate measures the rate at which a startup spends its capital to cover operating expenses before generating positive cash flow, often expressed monthly. For example, a startup with $500,000 in funding and monthly expenses of $50,000 has a burn rate of $50,000, indicating it will deplete its funds in 10 months if no additional revenue is generated. Tracking burn rate helps founders forecast runway and make informed decisions on budgeting, fundraising, and growth strategies.
Why Burn Rate Matters for Early-Stage Startups
Burn rate measures the speed at which a startup spends its capital, directly influencing its runway and survival chances. High burn rates can deplete cash reserves quickly, risking the inability to finance critical operations or secure future funding. Understanding burn rate helps founders manage expenses strategically to extend operational longevity and attract investors.
Calculating Burn Rate: Step-by-Step Example
Calculating burn rate in a startup involves tracking total monthly expenses against available cash reserves to determine how quickly funds are being depleted. For instance, if a startup spends $50,000 monthly and has $300,000 in the bank, the burn rate equals $50,000 per month, with a runway of six months before funding runs out. Monitoring burn rate helps optimize budget allocation, forecast financial needs, and attract investors by demonstrating fiscal responsibility.
Real-World Burn Rate Example: A SaaS Startup
A SaaS startup with a monthly revenue of $50,000 and operating expenses totaling $120,000 demonstrates a burn rate of $70,000, indicating how much capital is consumed monthly to sustain operations. This burn rate, typical during early growth phases, reflects costs such as employee salaries, server infrastructure, and marketing efforts. Understanding this real-world burn rate enables founders to strategize fundraising timelines and optimize expenditure to achieve profitability.
Monthly Burn Rate Breakdown for Founders
A startup's monthly burn rate typically includes fixed costs such as salaries averaging $50,000, office rent around $10,000, and marketing expenses near $15,000. Variable costs like software subscriptions and freelance services can add an additional $5,000 to $8,000 monthly. Founders should analyze each category to optimize cash flow and extend the runway during the initial growth phase.
How Burn Rate Impacts Startup Longevity
A startup with a monthly burn rate of $100,000 and a cash runway of 12 months will need to secure additional funding or achieve profitability before funds run out, directly impacting its longevity. Managing burn rate by controlling operating expenses and scaling revenue is critical to extend a startup's survival and growth potential. Investors closely monitor burn rate metrics to assess financial health and the sustainability of the business model.
Managing Burn Rate: Strategies for Startups
Startups managing burn rate often allocate funds primarily to product development, marketing, and operational expenses, with typical monthly costs ranging from $50,000 to $200,000 depending on growth stage and industry. Implementing strict cash flow monitoring tools and prioritizing customer acquisition efficiency helps extend runway and optimize resource allocation. Strategic actions like renegotiating vendor contracts and scaling headcount based on revenue milestones significantly reduce unsustainable spending, ensuring financial stability during critical growth phases.
Burn Rate Benchmarks by Industry
Startups in the technology sector often experience a monthly burn rate between $100,000 and $500,000, reflecting high research and development costs. In contrast, retail startups typically maintain lower burn rates around $50,000 to $200,000 due to less intensive capital requirements. Understanding industry-specific burn rate benchmarks enables startups to optimize cash flow management and extend runway duration effectively.
Burn Rate and Investor Decision-Making
A startup with a monthly burn rate of $100,000 signals to investors how quickly it is depleting its capital, influencing funding decisions and valuation. Investors closely analyze burn rate to assess runway, operational efficiency, and urgency for additional funding rounds. A manageable burn rate aligned with growth milestones enhances investor confidence and strategic support.
Reducing Burn Rate Without Sacrificing Growth
A startup with a $200,000 monthly burn rate can reduce expenses by renegotiating supplier contracts and automating key processes, lowering costs by 15% while maintaining a steady 10% monthly revenue growth. Implementing remote work policies cuts office expenses by $20,000 per month without affecting team productivity or customer acquisition. Strategic investment in scalable marketing channels ensures continued user base expansion even as operational costs decrease.
example of burn rate in startup Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com