Skunkworks projects in business refer to innovative initiatives developed by a small, autonomous team within a larger organization. These teams operate with minimal bureaucracy and freedom from traditional company processes, fostering rapid experimentation and creative problem-solving. A classic example is Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works division, responsible for developing advanced aircraft such as the U-2 and SR-71 Blackbird under tight secrecy and accelerated timelines. Another example comes from Google's X division, known as the "moonshot factory," which focuses on breakthrough technologies like self-driving cars and internet-beaming balloons. These projects emphasize disruptive innovation and often involve substantial risk but hold the potential to revolutionize markets. Skunkworks teams typically leverage cross-disciplinary expertise and agile methodologies to achieve breakthrough business outcomes efficiently.
Table of Comparison
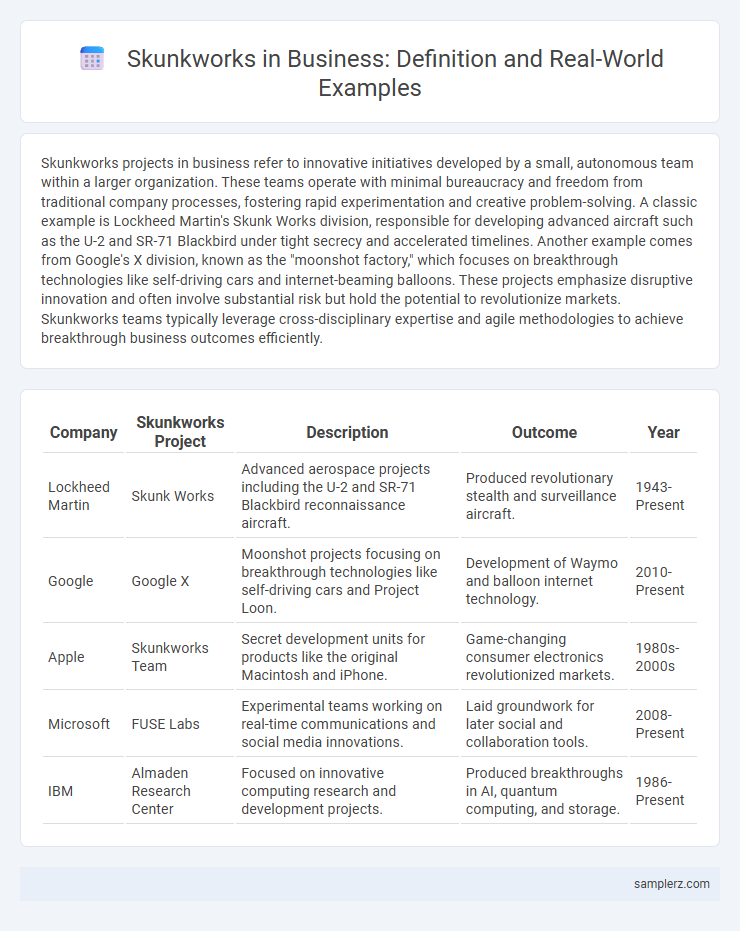
| Company | Skunkworks Project | Description | Outcome | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lockheed Martin | Skunk Works | Advanced aerospace projects including the U-2 and SR-71 Blackbird reconnaissance aircraft. | Produced revolutionary stealth and surveillance aircraft. | 1943-Present |
| Google X | Moonshot projects focusing on breakthrough technologies like self-driving cars and Project Loon. | Development of Waymo and balloon internet technology. | 2010-Present | |
| Apple | Skunkworks Team | Secret development units for products like the original Macintosh and iPhone. | Game-changing consumer electronics revolutionized markets. | 1980s-2000s |
| Microsoft | FUSE Labs | Experimental teams working on real-time communications and social media innovations. | Laid groundwork for later social and collaboration tools. | 2008-Present |
| IBM | Almaden Research Center | Focused on innovative computing research and development projects. | Produced breakthroughs in AI, quantum computing, and storage. | 1986-Present |
Origins of Skunkworks: A Brief Overview
Skunkworks originated at Lockheed Martin during World War II as a specialized group tasked with rapid development of advanced aircraft, notably the P-80 Shooting Star jet fighter. This initiative emphasized secrecy, innovation, and autonomy, allowing engineers to bypass standard corporate bureaucracy for accelerated project delivery. The success of Skunkworks inspired numerous corporations to adopt similar autonomous teams for cutting-edge research and development in business sectors.
Key Principles of Skunkworks Projects
Skunkworks projects in business emphasize small, autonomous teams operating with minimal bureaucracy to accelerate innovation and maintain secrecy. These projects prioritize rapid prototyping, iterative development, and empowered decision-making to swiftly address complex challenges. Critical principles include focused objectives, limited resources, and fostering a culture of trust and creative freedom to achieve breakthrough results.
Lockheed Martin: The Skunkworks Pioneer
Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works division revolutionized aerospace innovation by developing advanced aircraft like the U-2 and SR-71 Blackbird under tight secrecy and accelerated timelines. This elite team operates with minimal bureaucracy, fostering rapid prototyping and breakthrough technologies that give a strategic advantage in defense contracts. Skunk Works exemplifies how autonomous innovation labs within large corporations can deliver cutting-edge solutions while maintaining corporate agility.
Google X: Revolutionizing Innovation
Google X serves as a prime example of skunkworks in business, operating as a semi-secret research lab dedicated to breakthrough technologies like self-driving cars and Project Loon. Its unconventional approach fosters radical innovation by encouraging experimentation outside traditional corporate constraints, accelerating the development of disruptive solutions. This methodology has solidified Google X's reputation as a pioneer in transforming visionary ideas into market-ready products.
Apple’s Macintosh: A Skunkworks Success Story
Apple's Macintosh project exemplifies a successful skunkworks initiative, where a small, autonomous team developed the revolutionary personal computer in secrecy. This approach allowed for rapid innovation, bypassing traditional corporate bureaucracy and fostering creativity that ultimately transformed the computing industry. The Macintosh's breakthrough user interface and design set new standards, highlighting skunkworks as a powerful model for disruptive technology development in business.
IBM’s PC Development: Breaking Corporate Norms
IBM's PC development in the late 1970s exemplified skunkworks by challenging traditional corporate structures and accelerating innovation through a small, autonomous team. This group operated outside standard procedures to rapidly design and launch the IBM 5150, which redefined personal computing and disrupted industry standards. The project's success showcased how skunkworks can drive transformative products by emphasizing agility and independent decision-making within large corporations.
Microsoft’s Xbox: A Covert Creation
Microsoft's Xbox originated within a skunkworks project led by a small, secretive team aiming to enter the gaming market without corporate interference. This agile approach enabled rapid innovation and development outside traditional business structures, resulting in the successful launch that challenged established console manufacturers. The Xbox project exemplifies how skunkworks foster disruptive technology and strategic market expansion in competitive industries.
3M’s Post-it Notes: Innovation from Within
3M's Post-it Notes exemplify skunkworks innovation, where a small, autonomous team developed the low-tack adhesive technology independently in the 1970s. This secretive project allowed rapid experimentation and iteration without traditional corporate constraints. The result revolutionized office supplies, generating billions in revenue and demonstrating 3M's commitment to fostering internal innovation.
Atlassian’s ShipIt Days: Encouraging Internal Skunkworks
Atlassian's ShipIt Days exemplify an internal skunkworks approach by empowering employees to develop innovative projects outside regular workflows for 24 hours. This initiative fosters creativity, accelerates problem-solving, and often results in impactful product enhancements, driving business growth. Companies adopting similar programs benefit from increased employee engagement and rapid prototype development, which bolster competitive advantage.
Best Practices for Implementing Skunkworks in Business
Effective skunkworks projects in business prioritize autonomous teams empowered to innovate without bureaucratic constraints, fostering rapid prototyping and experimentation. Maintaining clear objectives aligned with overall corporate strategy ensures that skunkworks efforts deliver relevant and scalable innovations. Regular executive support and dedicated resources enhance accountability and enable swift decision-making throughout the innovation lifecycle.
example of skunkworks in business Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com