A bear hug in a business proposal occurs when a company offers to buy another firm at a significantly higher price than its current market value. This aggressive takeover tactic is designed to pressure the target company's board of directors and shareholders into accepting the offer quickly. For example, Company A might propose acquiring Company B at a 40% premium over its stock price, making it difficult for Company B to reject without risking shareholder dissatisfaction. In data-driven corporate transactions, bear hugs often involve detailed financial analysis highlighting synergy potentials and market expansion opportunities. These proposals frequently include a clear valuation model, cash or stock offer details, and potential strategic benefits to justify the premium price. Bear hugs rely on a combination of entity data, such as market capitalization and revenue growth, to make an irresistible bid that targets the board's responsibility to maximize shareholder value.
Table of Comparison
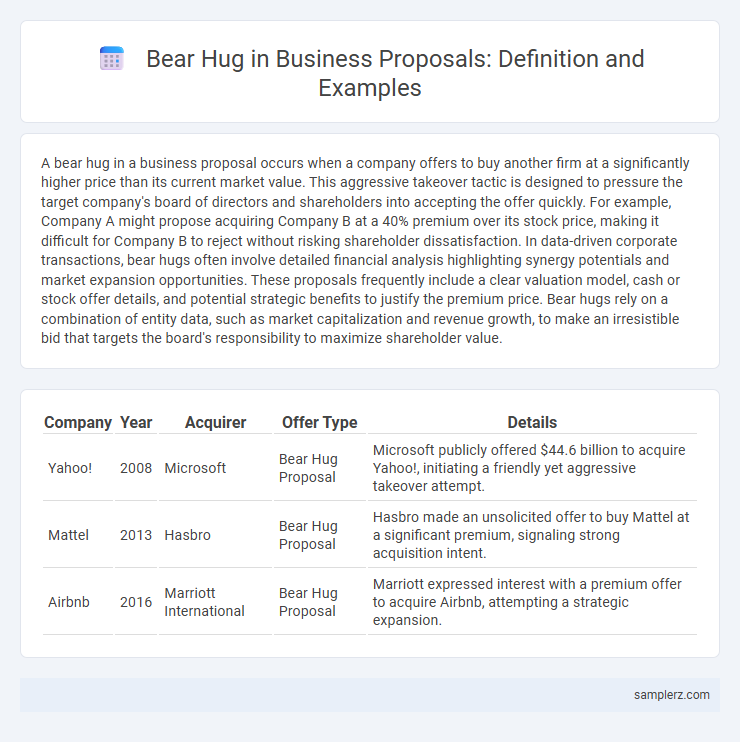
| Company | Year | Acquirer | Offer Type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yahoo! | 2008 | Microsoft | Bear Hug Proposal | Microsoft publicly offered $44.6 billion to acquire Yahoo!, initiating a friendly yet aggressive takeover attempt. |
| Mattel | 2013 | Hasbro | Bear Hug Proposal | Hasbro made an unsolicited offer to buy Mattel at a significant premium, signaling strong acquisition intent. |
| Airbnb | 2016 | Marriott International | Bear Hug Proposal | Marriott expressed interest with a premium offer to acquire Airbnb, attempting a strategic expansion. |
Understanding the Bear Hug Tactic in Business Proposals
A bear hug in business proposals occurs when a company offers an unsolicited, attractive acquisition bid with terms so favorable that the target company finds it difficult to reject. This tactic pressures the target's board by presenting a premium price, often above market value, to expedite acceptance and limit competitive bids. Recognizing the bear hug's strategic intent helps companies prepare defensive measures or negotiate better terms in hostile takeover scenarios.
Key Characteristics of Bear Hug Proposals
Bear hug proposals feature an unsolicited, generous offer with a premium price often above the current market value to incentivize acceptance. These proposals are typically direct, aimed at gaining quick approval by appealing to the target company's board with attractive financial terms. Key characteristics include urgency, a clear strategic rationale, and minimal negotiation to pressure swift agreement.
Classic Example: Corporate Takeover Offers
A classic example of a bear hug in corporate takeover offers involves Company A sending an unsolicited, high-premium proposal directly to Company B's board, pressuring them to accept the acquisition. This strategy leverages aggressive, publicly disclosed offers to sway shareholders and bypass management resistance. Bear hugs often lead to swift negotiation or forced sale, exemplifying high-stakes mergers and acquisitions tactics.
Bear Hug in Mergers and Acquisitions
A Bear Hug in mergers and acquisitions refers to an aggressive takeover strategy where the acquirer makes an unsolicited, premium offer directly to the target company's board or shareholders, often at a price significantly above the current market value. This tactic creates pressure on the target company to accept the offer quickly to maximize shareholder value and avoid protracted negotiations or hostile bids. Prominent examples include Qualcomm's $44 billion Bear Hug offer for NXP Semiconductors in 2016, illustrating the effectiveness of this approach in securing high-value deals.
How Bear Hug Proposals Influence Negotiations
Bear hug proposals exert significant pressure on target companies by offering an attractive premium, prompting swift consideration of the offer. This aggressive approach often accelerates negotiations, reduces the likelihood of competing bids, and signals strong buyer commitment. As a strategic tactic, bear hugs can disrupt standard negotiation dynamics, forcing board members and executives to quickly evaluate shareholder value and potential deal synergies.
Real-World Case Studies of Bear Hug Tactics
In 2015, Valeant Pharmaceuticals executed a notable bear hug for Allergan by delivering an unsolicited, high-premium offer that pressured Allergan's board to engage in negotiations, demonstrating the tactic's effectiveness in hostile acquisitions. This aggressive approach drove Allergan's share price up significantly, highlighting the financial impact of bear hug proposals in real-world scenarios. Such case studies illustrate how companies leverage bear hug tactics to force strategic discussions and influence shareholder value during merger and acquisition processes.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Bear Hug Proposals
Bear hug proposals, often characterized by an unsolicited, high-value offer to acquire a company, raise significant legal and ethical implications, including fiduciary duties of the target's board to act in shareholders' best interests and the risk of coercive tactics compromising fair market negotiation. Legal scrutiny focuses on antitrust laws and securities regulations to ensure transparency and prevent manipulative practices. Ethical concerns emphasize respecting corporate governance standards and avoiding undue pressure on management, safeguarding stakeholders' rights throughout the acquisition process.
Bear Hug vs. Hostile Takeover: Core Differences
A bear hug in a business proposal involves a friendly, high-premium offer to acquire a company, encouraging cooperation from the target's board of directors. Unlike a hostile takeover, which bypasses management through direct appeal to shareholders, a bear hug seeks negotiation and mutual agreement. The core difference lies in approach: bear hugs aim for collaboration and win-win outcomes, whereas hostile takeovers often provoke resistance and conflict.
Strategic Advantages of Using a Bear Hug Proposal
A bear hug proposal offers strategic advantages by applying immediate pressure on the target company's board, often prompting swift negotiations. This approach can limit competitive bids, giving the acquirer a stronger position to secure favorable terms quickly. Companies using bear hug proposals benefit from reduced deal uncertainty and enhanced chances of a successful takeover.
Responding Effectively to a Bear Hug Approach
Responding effectively to a bear hug approach in a business proposal requires swift evaluation of the offer's valuation and terms to ensure alignment with company goals. Engaging legal and financial advisors helps in identifying potential risks and structuring counteroffers that protect shareholder interests. Transparent communication with stakeholders during this process fosters trust and facilitates strategic decision-making.
example of bear hug in proposal Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com