A bear hug in business acquisition refers to an aggressive offer made by a company to purchase another firm at a premium price, often unsolicited. This tactic aims to pressure the target company's board into accepting the offer by making it financially attractive and difficult to refuse. For example, in 2006, Oracle made a bear hug offer to PeopleSoft by proposing a significant premium on the share price, initiating a hostile takeover attempt. This approach leverages the element of surprise and financial incentive to accelerate the acquisition process. The data shows that bear hug offers typically exceed 20% above the market price to entice shareholders while compelling the management to consider the proposal seriously. Companies employ this strategy to gain control quickly, especially when prior negotiations have failed or resistance is anticipated from the target firm's leadership.
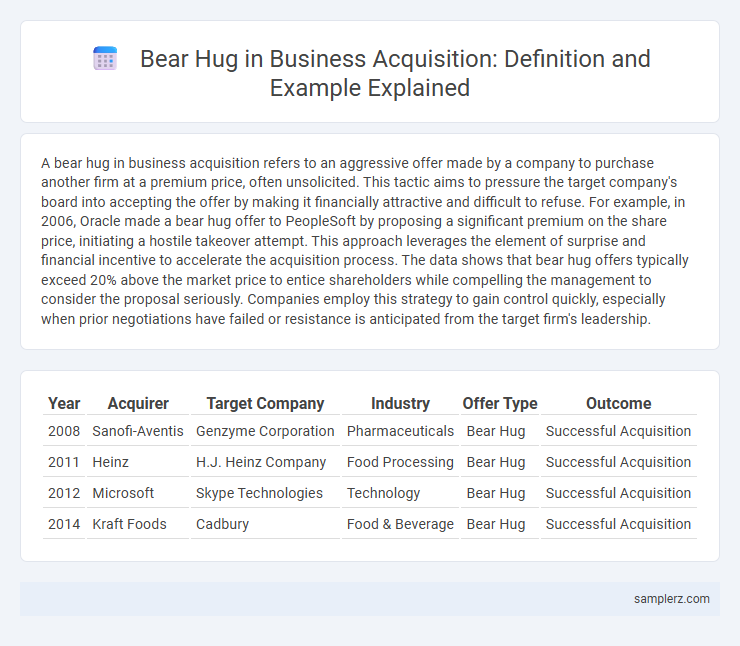
Table of Comparison
| Year | Acquirer | Target Company | Industry | Offer Type | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | Sanofi-Aventis | Genzyme Corporation | Pharmaceuticals | Bear Hug | Successful Acquisition |
| 2011 | Heinz | H.J. Heinz Company | Food Processing | Bear Hug | Successful Acquisition |
| 2012 | Microsoft | Skype Technologies | Technology | Bear Hug | Successful Acquisition |
| 2014 | Kraft Foods | Cadbury | Food & Beverage | Bear Hug | Successful Acquisition |
Understanding the Bear Hug Strategy in Business Acquisitions
The bear hug strategy in business acquisitions involves a company making an unsolicited, yet attractive, purchase offer directly to the target company's board, bypassing prolonged negotiation. This approach aims to pressure the target's management into accepting the proposal by offering a premium price significantly above the current market value. Successful examples include IBM's acquisition attempt of Sun Microsystems, where the acquirer used a bear hug to expedite the decision-making process and gain competitive advantage.
Key Features of a Bear Hug Offer
A bear hug offer in acquisitions is characterized by an unsolicited, highly attractive proposal made directly to a company's board, often exceeding current market value to pressure acceptance. Key features include a premium price, a firm deadline for response, and public disclosure to increase leverage. This strategy aims to compel swift action while limiting the target's ability to negotiate or seek alternative bids.
Real-World Bear Hug Acquisition Examples
In the business world, a notable example of a bear hug acquisition is when Microsoft approached Yahoo! in 2008 with an unsolicited bid of $44.6 billion, aiming to acquire the company by making an attractive public offer directly to Yahoo!'s board. This aggressive tactic forced Yahoo! to seriously consider the proposal despite initial resistance, exemplifying a bear hug's power in mergers and acquisitions. Other significant cases include Kraft's acquisition attempt of Cadbury in 2009, where the public offer created pressure to negotiate, highlighting how bear hug strategies can expedite deal-making.
Bear Hug vs. Hostile Takeover: Key Differences
A bear hug in acquisitions involves a friendly, unsolicited offer that pressures the target company's board to consider the deal, contrasting sharply with a hostile takeover where the acquirer bypasses management and directly appeals to shareholders. The bear hug typically aims to initiate negotiations and maintain a cooperative atmosphere, while hostile takeovers often provoke resistance and legal defenses from the target. This strategic difference impacts deal structure, timeline, and corporate relations, making bear hugs a softer alternative in acquisition tactics.
Legal Implications of a Bear Hug Approach
A bear hug in acquisition involves an acquirer making a firm, often unsolicited, offer directly to the target company's board or shareholders, pressuring them legally and publicly to accept the deal. This approach can trigger fiduciary duties, requiring the board to carefully evaluate the offer's fairness and potential conflict of interest, while exposure to shareholder litigation increases if the board rejects a financially compelling bid. The legal implications demand thorough due diligence and strategic communication to mitigate risks associated with hostile takeover tactics and regulatory compliance.
Benefits of Employing a Bear Hug in M&A
A bear hug in M&A involves an acquirer making an unsolicited, attractive offer to the target company's board, often at a premium price, compelling swift consideration. This strategy benefits the acquirer by expediting the negotiation process, reducing the risk of competitive bids, and signaling strong interest to stakeholders. Employing a bear hug can also pressure the target's management to seriously evaluate the offer, increasing the likelihood of a successful acquisition.
Risks and Challenges of Bear Hug Offers
A bear hug acquisition offer, often characterized by a high-premium unsolicited proposal, poses significant risks including strained relations between the acquiring and target companies. The aggressive nature of the offer can trigger defensive measures such as poison pills or legal battles, leading to prolonged uncertainty and operational disruptions. Investors may react negatively due to perceived coercion, impacting stock prices and overall market confidence.
Famous Companies That Used Bear Hug Strategies
In the 2008 acquisition attempt of Yahoo! by Microsoft, Microsoft employed a bear hug strategy by presenting an unsolicited but highly attractive offer directly to Yahoo!'s board, applying significant pressure to accept the bid. Another notable example is Kraft's hostile takeover of Cadbury in 2009, where Kraft used a bear hug approach by offering a premium price to shareholders, forcing Cadbury's management to consider the deal seriously. These tactics illustrate how major corporations use bear hugs to accelerate acquisition negotiations and influence board decisions effectively.
How Target Companies Respond to Bear Hug Proposals
Target companies often respond to bear hug proposals by conducting swift internal reviews to assess the attractiveness of the offer and potential strategic impacts. They may engage with financial advisors to evaluate the bid's fairness and negotiate terms that maximize shareholder value. Some targets reject bear hugs outright to maintain control, while others pursue counteroffers or seek alternative buyers to foster competitive tension.
Lessons Learned from Notable Bear Hug Acquisition Cases
The 2008 Kraft Foods bear hug acquisition of Cadbury highlights the importance of strategic timing and regulatory awareness, as Kraft's aggressive unsolicited offer eventually overcame initial resistance through effective negotiation and public appeal. Lessons learned emphasize the need for thorough due diligence and clear communication to manage stakeholder reactions and minimize reputational risks during hostile bids. This case also demonstrates how integrating cultural differences and operational synergies early can facilitate smoother post-acquisition transitions and value realization.
example of bear hug in acquisition Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com