A well-known example of a conglomerate in business is Berkshire Hathaway. This multinational holding company owns a diverse range of subsidiaries including insurance, utilities, railroads, and consumer goods. Its business model emphasizes acquiring companies across various industries to create a broad-based portfolio. Another prominent example is General Electric (GE), which has historically operated as a conglomerate. GE's holdings span sectors such as aviation, healthcare, power generation, and renewable energy. The company employs a strategy of diversification to reduce risk and capitalize on different market opportunities.
Table of Comparison
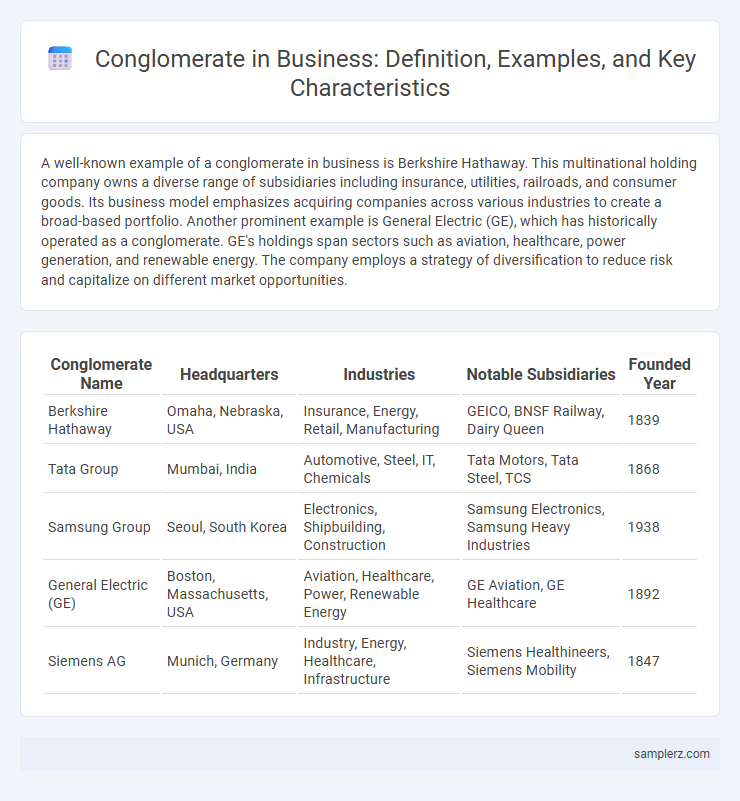
| Conglomerate Name | Headquarters | Industries | Notable Subsidiaries | Founded Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berkshire Hathaway | Omaha, Nebraska, USA | Insurance, Energy, Retail, Manufacturing | GEICO, BNSF Railway, Dairy Queen | 1839 |
| Tata Group | Mumbai, India | Automotive, Steel, IT, Chemicals | Tata Motors, Tata Steel, TCS | 1868 |
| Samsung Group | Seoul, South Korea | Electronics, Shipbuilding, Construction | Samsung Electronics, Samsung Heavy Industries | 1938 |
| General Electric (GE) | Boston, Massachusetts, USA | Aviation, Healthcare, Power, Renewable Energy | GE Aviation, GE Healthcare | 1892 |
| Siemens AG | Munich, Germany | Industry, Energy, Healthcare, Infrastructure | Siemens Healthineers, Siemens Mobility | 1847 |
What Is a Conglomerate?
A conglomerate is a large corporation composed of diverse and often unrelated businesses operating in multiple industries, such as Alphabet Inc., which owns Google, YouTube, and several other subsidiaries spanning technology, healthcare, and automotive sectors. These business entities operate independently but benefit from centralized corporate management and shared resources, allowing risk diversification and capital allocation advantages. Conglomerates like Berkshire Hathaway exemplify this model by acquiring companies across various industries, including insurance, energy, and manufacturing.
Key Characteristics of Conglomerates
Conglomerates are large corporations composed of diverse businesses operating in unrelated industries, exemplified by companies like Berkshire Hathaway and General Electric. Key characteristics include diversified revenue streams, risk reduction through varied investments, and centralized corporate management overseeing independent subsidiaries. This structure enables conglomerates to leverage financial strength and operational synergies while minimizing market volatility impact on overall performance.
Major Global Conglomerate Examples
Berkshire Hathaway, led by Warren Buffett, exemplifies a major global conglomerate with diversified holdings in insurance, utilities, railroads, and consumer goods. Samsung Group operates as a conglomerate with key subsidiaries spanning electronics, heavy industry, and financial services across international markets. Tata Group, headquartered in India, maintains a vast conglomerate portfolio including automotive, steel, information technology, and hospitality sectors worldwide.
Siemens: A German Conglomerate Success Story
Siemens AG stands as a prime example of a successful German conglomerate, operating across multiple industries including energy, healthcare, and industrial automation. With a diverse portfolio and global presence, Siemens leverages technological innovation and strategic acquisitions to maintain its position as a leader in industrial manufacturing and digitalization. The company's ability to integrate advanced engineering solutions with sustainable practices has driven long-term growth and resilience in competitive markets.
Berkshire Hathaway: The Iconic American Conglomerate
Berkshire Hathaway, led by Warren Buffett, exemplifies a successful American conglomerate with diversified holdings across insurance, utilities, manufacturing, and retail sectors. Its portfolio includes major subsidiaries like GEICO, BNSF Railway, and Dairy Queen, driving significant revenue and market influence. The conglomerate's strategic acquisitions and long-term investment approach have solidified its position as a dominant force in global business.
Tata Group: India’s Multinational Powerhouse
Tata Group, one of India's largest conglomerates, operates across over 100 countries with diversified business interests spanning steel, automotive, IT services, telecommunications, and hospitality. Its subsidiaries, including Tata Steel, Tata Motors, TCS, and Taj Hotels, collectively generate annual revenues exceeding $100 billion, making it a global business powerhouse. Tata Group's strategic acquisitions and innovation-driven approach have solidified its position as a leader in emerging and developed markets worldwide.
Samsung: Diversification in Action
Samsung exemplifies diversification as a leading conglomerate with business segments spanning electronics, heavy industries, financial services, and construction. Its extensive portfolio includes Samsung Electronics, a global leader in consumer technology, and Samsung Heavy Industries, one of the world's largest shipbuilders. This strategic diversification enables Samsung to mitigate risks and capitalize on varied market opportunities across different industries.
Alphabet Inc.: Technology as a Conglomerate
Alphabet Inc. exemplifies a technology conglomerate by managing diverse subsidiaries including Google, YouTube, Waymo, and Verily, spanning sectors from internet services to autonomous vehicles and life sciences. This corporate structure enables Alphabet to leverage cross-industry innovation and mitigate risks through diverse revenue streams. The conglomerate's market capitalization consistently ranks it among the world's most valuable and influential technology enterprises.
Benefits of Conglomerate Structure
A conglomerate structure, exemplified by companies like Berkshire Hathaway, offers significant benefits including diversified revenue streams and reduced business risk due to operating in multiple industries. This structure enables efficient capital allocation across subsidiaries, enhancing overall corporate growth and financial stability. It also fosters cross-sector innovation and competitive advantages by leveraging varied expertise within the conglomerate portfolio.
Challenges Faced by Modern Conglomerates
Modern conglomerates like Berkshire Hathaway and Siemens encounter challenges such as managing diverse business units with varying market dynamics and operational complexities. Coordinating strategic goals across industries while maintaining financial stability often demands sophisticated risk management and agile leadership. These companies also struggle with regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions, increasing overhead and operational risks.
example of conglomerate in business Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com