Holacracy is a management system that replaces traditional hierarchical structures with a decentralized framework. Companies like Zappos have adopted holacracy to distribute authority and decision-making across self-organizing teams. This approach allows for increased agility, employee engagement, and faster innovation by empowering individuals to take ownership of their roles. In a holacracy, roles are clearly defined with specific accountabilities and domains, enabling transparent communication and efficient collaboration. The system uses regular governance meetings to update roles and policies based on real-time organizational needs. By implementing holacracy, businesses can improve adaptability and responsiveness in dynamic markets while reducing bottlenecks caused by conventional management layers.
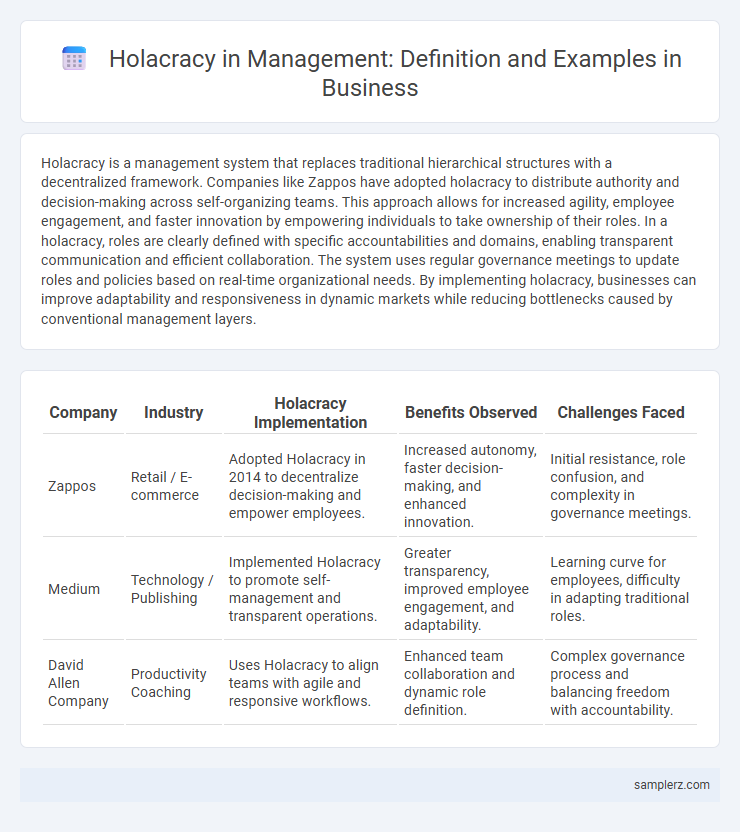
Table of Comparison
| Company | Industry | Holacracy Implementation | Benefits Observed | Challenges Faced |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zappos | Retail / E-commerce | Adopted Holacracy in 2014 to decentralize decision-making and empower employees. | Increased autonomy, faster decision-making, and enhanced innovation. | Initial resistance, role confusion, and complexity in governance meetings. |
| Medium | Technology / Publishing | Implemented Holacracy to promote self-management and transparent operations. | Greater transparency, improved employee engagement, and adaptability. | Learning curve for employees, difficulty in adapting traditional roles. |
| David Allen Company | Productivity Coaching | Uses Holacracy to align teams with agile and responsive workflows. | Enhanced team collaboration and dynamic role definition. | Complex governance process and balancing freedom with accountability. |
Understanding Holacracy: A Brief Overview
Holacracy transforms traditional management by distributing authority across self-organizing teams known as circles, enhancing agility and accountability within organizations. This system replaces hierarchical decision-making with transparent governance processes and role definitions, enabling rapid adaptation to changing business environments. Companies like Zappos have successfully implemented holacracy, demonstrating improved innovation and employee engagement through decentralized leadership.
Key Principles of Holacratic Management
Holacratic management decentralizes authority by distributing decision-making across self-organizing teams called circles, enhancing agility and innovation. Roles within circles are clearly defined with specific accountabilities, promoting transparency and accountability in operations. Continuous governance and tactical meetings ensure alignment with organizational goals while enabling rapid adaptation to changing business environments.
Real-World Companies Using Holacracy
Zappos, a leading online shoe retailer, implemented holacracy to foster employee autonomy and decentralized decision-making, enhancing innovation and adaptability. Medium, the online publishing platform, adopted holacracy to eliminate traditional hierarchies and empower teams with clarity in roles and accountabilities. Both companies demonstrate how holacracy can transform organizational structures to prioritize agility and collaborative governance.
Zappos: A Holacracy Success Story
Zappos implemented holacracy to decentralize authority and enhance employee autonomy, resulting in improved innovation and customer service. The company replaced traditional management hierarchies with self-organizing teams called circles, which empowered employees to take ownership of roles and responsibilities. This approach fostered a dynamic work environment that aligned with Zappos' core values and contributed to its sustained business growth.
Implementing Holacracy: Step-by-Step Example
Implementing Holacracy begins with defining clear roles and accountabilities within the organization, replacing traditional job descriptions with dynamic "circles" that govern specific functions. The process involves holding governance meetings where team members propose and integrate role changes to enhance agility and transparency. Continuous feedback loops and structured tactical meetings ensure iterative adjustments, fostering decentralized decision-making and empowering employees at all levels.
Role Assignment in Holacratic Organizations
In holacratic organizations, role assignment is decentralized, distributing authority across specific roles rather than individuals, which enhances flexibility and accountability. Each role has clear domains, accountabilities, and policies, ensuring that tasks are aligned with organizational purpose while allowing adaptability in dynamic business environments. This system promotes transparent decision-making and streamlines operations by continuously evolving roles based on ongoing governance meetings.
Decision-Making under Holacracy: Practical Illustration
In holacracy, decision-making is distributed across roles rather than centralized in a hierarchy, enabling faster and more adaptive responses to business challenges. For example, a marketing team operating under holacracy uses structured governance meetings to create or modify roles and policies, allowing members to propose changes and reach consent-based decisions without requiring top-level approval. This approach enhances accountability and transparency, empowering employees to address issues proactively and innovate within their defined domains.
Challenges Faced by Companies Adopting Holacracy
Companies adopting holacracy often struggle with role ambiguity and resistance to change from employees accustomed to traditional hierarchical structures. The lack of clear authority can slow decision-making processes and create confusion during the transition period. Difficulties in maintaining accountability and ensuring effective communication across distributed autonomous teams further complicate holacracy implementation.
Comparing Holacracy with Traditional Management Structures
Holacracy replaces hierarchical management with decentralized authority distributed across self-organizing teams called circles, enabling faster decision-making and increased employee autonomy compared to traditional top-down structures. Traditional management typically relies on rigid role definitions and centralized control, which can slow innovation and limit adaptability in dynamic markets. Holacracy's emphasis on transparent governance and role fluidity enhances organizational agility and responsiveness, fostering a resilient business environment.
Lessons Learned from Holacracy Implementation
Holacracy implementation in business organizations reveals critical lessons about decentralizing authority and enhancing agile decision-making by replacing traditional hierarchies with self-managing teams. Companies like Zappos demonstrate that successful holacracy adoption requires continuous communication, clear roles, and employee training to navigate the complexity and prevent role ambiguity. Emphasizing transparency and iterative adaptation promotes accountability and innovation, while also highlighting challenges in scaling holacracy across large, diverse organizations.
example of holacracy in management Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com