In business restructuring, a common example of turnaround is when a struggling company implements cost-cutting measures and operational improvements to restore profitability. The company may reduce workforce, renegotiate supplier contracts, and streamline production processes to improve cash flow and reduce debt. This strategic approach focuses on stabilizing financial health and positioning the company for sustainable growth. Turnaround efforts often involve leadership changes, such as appointing a new CEO with expertise in restructuring and crisis management. Data-driven decisions based on market analysis and internal performance metrics guide the prioritization of initiatives during the turnaround process. Successful restructuring can lead to enhanced investor confidence, improved competitive positioning, and long-term survival in a challenging market environment.
Table of Comparison
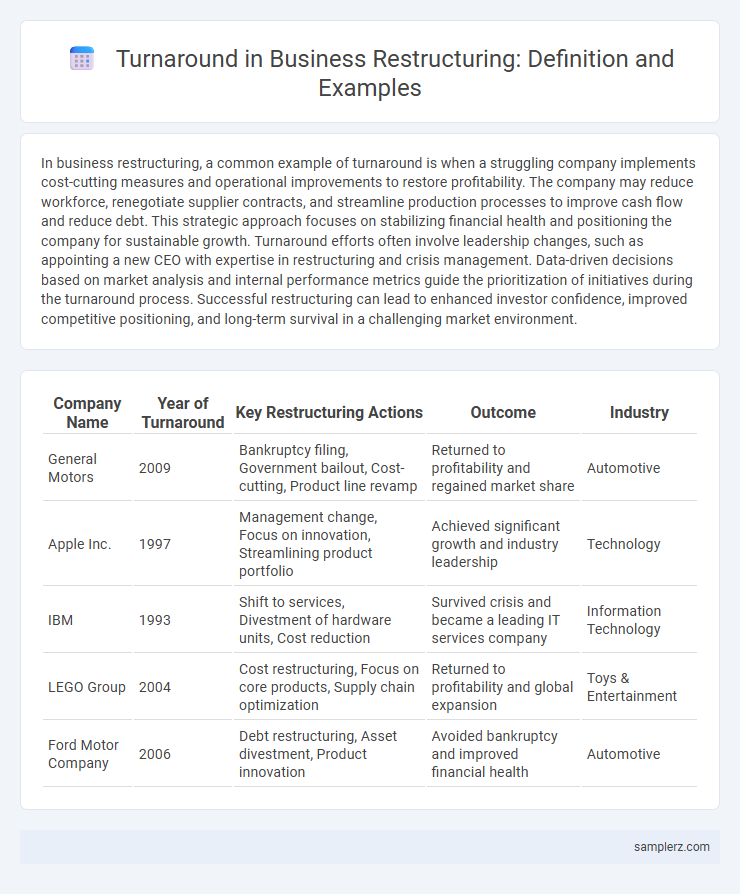
| Company Name | Year of Turnaround | Key Restructuring Actions | Outcome | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Motors | 2009 | Bankruptcy filing, Government bailout, Cost-cutting, Product line revamp | Returned to profitability and regained market share | Automotive |
| Apple Inc. | 1997 | Management change, Focus on innovation, Streamlining product portfolio | Achieved significant growth and industry leadership | Technology |
| IBM | 1993 | Shift to services, Divestment of hardware units, Cost reduction | Survived crisis and became a leading IT services company | Information Technology |
| LEGO Group | 2004 | Cost restructuring, Focus on core products, Supply chain optimization | Returned to profitability and global expansion | Toys & Entertainment |
| Ford Motor Company | 2006 | Debt restructuring, Asset divestment, Product innovation | Avoided bankruptcy and improved financial health | Automotive |
Understanding Turnaround in Business Restructuring
Turnaround in business restructuring involves reversing a company's decline through strategic changes such as cost reduction, asset optimization, and operational efficiency improvements. Key examples include implementing aggressive debt restructuring, divesting non-core assets, and enhancing cash flow management to stabilize finances. Understanding effective turnaround strategies enables businesses to regain profitability and sustainable growth amid financial distress.
Key Indicators Signaling the Need for a Turnaround
Declining cash flow, shrinking profit margins, and increasing debt levels are critical key indicators signaling the need for a business turnaround. Persistent negative EBITDA and deteriorating customer retention rates often highlight underlying operational inefficiencies requiring immediate restructuring. Monitoring these financial and performance metrics enables timely strategic decisions to stabilize and revitalize company operations during a turnaround process.
Notable Turnaround Case Studies in Corporate Restructuring
General Motors' 2009 bankruptcy marked a pivotal turnaround through extensive restructuring that included government-backed financing, asset divestiture, and streamlining operations to restore profitability. IBM's strategic pivot in the early 1990s involved refocusing on core technology services, shedding hardware divisions, and investing heavily in innovation, resulting in a sustained business revival. Xerox's transformation by shifting from a traditional copier manufacturer to a document management and business services provider illustrates effective restructuring driving renewed market relevance.
Essential Strategies for Successful Business Turnarounds
Implementing cost reduction through process optimization and renegotiating supplier contracts significantly enhances cash flow during business turnarounds. Focusing on core competencies by divesting non-core assets helps streamline operations and improve profitability. Engaging leadership in transparent communication fosters employee alignment and commitment to restructuring goals.
Leadership’s Role in Driving Turnaround Outcomes
Effective leadership plays a pivotal role in business turnaround by setting clear strategic directions, fostering a culture of accountability, and driving operational excellence. Leaders who demonstrate transparent communication, decisive decision-making, and stakeholder engagement can realign organizational goals and restore financial stability. Case studies of companies like Ford under Alan Mulally highlight how visionary leadership catalyzed successful restructuring and sustainable growth.
Impact of Financial Restructuring on Business Recovery
Financial restructuring transforms a company's balance sheet by reducing debt burdens and improving liquidity, directly enhancing operational stability and stakeholder confidence. By renegotiating loan terms and converting debt into equity, businesses can restore cash flow and invest in growth initiatives, accelerating recovery. This strategic adjustment often leads to improved credit ratings and renewed investor interest, driving long-term sustainability.
Operational Changes that Enable Turnarounds
Implementing lean manufacturing processes and streamlining supply chain management significantly enhance efficiency during business turnarounds. Reducing production bottlenecks and adopting advanced inventory tracking systems decrease operational costs and improve cash flow. These targeted operational changes empower companies to stabilize financial performance and regain competitive advantage.
Lessons Learned from Failed Turnaround Attempts
Failed turnaround attempts in business restructuring often reveal critical lessons such as the importance of realistic financial projections and early stakeholder engagement. Companies that neglect transparent communication or underestimate operational challenges risk deepening their financial distress and losing trust. These experiences emphasize the need for comprehensive due diligence and adaptive strategies to ensure successful restructuring outcomes.
Employee Engagement During Restructuring Turnarounds
Employee engagement during restructuring turnarounds is critical for maintaining productivity and morale, as seen in IBM's successful 1990s transformation where transparent communication and participatory decision-making improved workforce commitment. Companies like Ford also enhanced employee trust by involving staff in problem-solving initiatives, resulting in higher retention rates and smoother operational shifts. These examples demonstrate that prioritizing employee engagement strengthens organizational resilience and supports sustainable recovery during business turnarounds.
Measuring Long-Term Success After a Turnaround
Measuring long-term success after a business turnaround involves tracking key performance indicators such as sustained revenue growth, improved profit margins, and enhanced cash flow stability over multiple fiscal years. Evaluating customer retention rates and employee engagement scores provides insights into operational health and cultural transformation. Businesses that achieve consistent market share expansion and positive brand reputation metrics demonstrate effective restructuring outcomes.
example of turnround in restructuring Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com