A keiretsu is a Japanese business network consisting of interconnected companies, typically centered around a bank or trading company. An example of keiretsu in a conglomerate is the Mitsubishi Group, which includes diverse entities like Mitsubishi Motors, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and Mitsubishi Corporation. These companies maintain close relationships through cross-shareholdings, coordinated business strategies, and shared financial resources. The keiretsu structure strengthens collaboration and stability among member firms within the conglomerate. Each company benefits from mutual support in research, supply chain management, and market expansion. Data shows that this interconnected model helps reduce market risks and fosters innovation by leveraging the collective resources of the entire network.
Table of Comparison
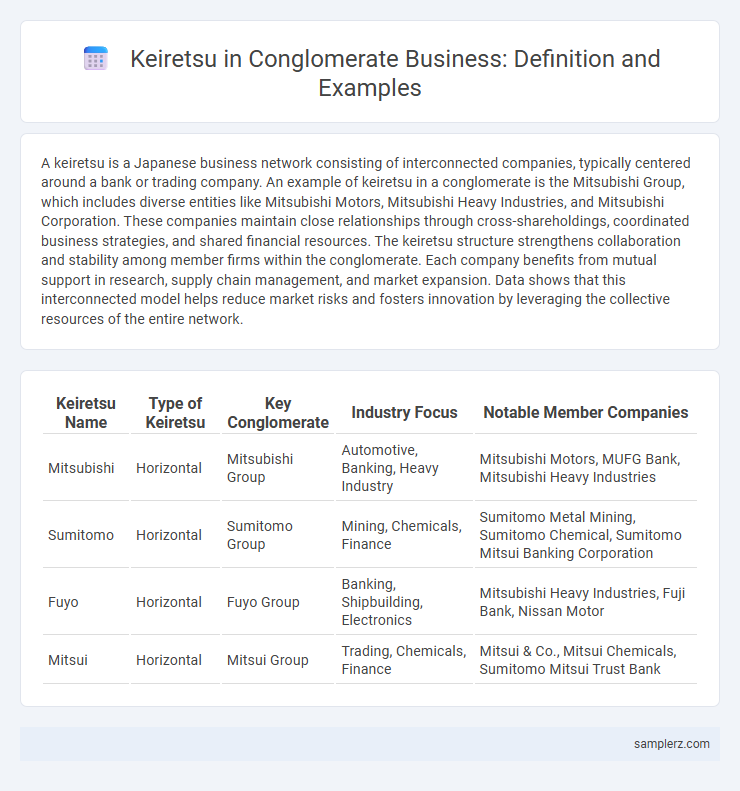
| Keiretsu Name | Type of Keiretsu | Key Conglomerate | Industry Focus | Notable Member Companies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitsubishi | Horizontal | Mitsubishi Group | Automotive, Banking, Heavy Industry | Mitsubishi Motors, MUFG Bank, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries |
| Sumitomo | Horizontal | Sumitomo Group | Mining, Chemicals, Finance | Sumitomo Metal Mining, Sumitomo Chemical, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation |
| Fuyo | Horizontal | Fuyo Group | Banking, Shipbuilding, Electronics | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Fuji Bank, Nissan Motor |
| Mitsui | Horizontal | Mitsui Group | Trading, Chemicals, Finance | Mitsui & Co., Mitsui Chemicals, Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Bank |
Introduction to Keiretsu in Modern Conglomerates
Keiretsu in modern conglomerates exemplify interconnected business groups, primarily rooted in Japanese corporate culture, where member companies maintain equity ties and collaborate closely across sectors like manufacturing, finance, and technology. These networks enhance stability and competitive advantage by fostering long-term relationships, shared resources, and coordinated business strategies. Prominent keiretsu include Mitsubishi and Sumitomo, which illustrate how conglomerates leverage integrated supply chains and cross-shareholding to sustain market dominance.
Historical Background of Keiretsu Structures
Keiretsu structures originated in post-World War II Japan to replace prewar zaibatsu conglomerates, enabling businesses to collaborate through cross-shareholding and long-term partnerships. These networks typically consist of manufacturers, suppliers, and financial institutions, fostering stability and mutual support within the corporate group. Notable examples include the Mitsubishi and Sumitomo keiretsu, which played significant roles in Japan's industrial growth during the mid-20th century.
Mitsubishi Group: A Classic Keiretsu Example
Mitsubishi Group exemplifies a classic keiretsu structure, consisting of interconnected companies across industries such as automotive, banking, and heavy industries. This Japanese conglomerate operates through cross-shareholding and long-term business relationships that enhance stability and collaboration among member firms. Its keiretsu model fosters integrated supply chains and mutual support, driving sustained economic growth within Japan's corporate landscape.
The Sumitomo Keiretsu: Interconnected Business Ecosystem
The Sumitomo Keiretsu exemplifies a tightly interconnected business ecosystem with core companies spanning banking, metal manufacturing, and chemical industries, promoting mutual support and long-term stability. Central institutions like Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation provide financial services that reinforce the group's cohesion and facilitate collaborative investment strategies. This keiretsu model enhances operational efficiency and risk management across its conglomerate through cross-shareholding and coordinated business planning.
Mitsui Group and Its Network of Subsidiaries
Mitsui Group exemplifies a keiretsu structure, integrating a network of diverse subsidiaries spanning finance, trading, manufacturing, and energy sectors. Its interlocking shareholdings and collaborative relationships enhance operational efficiency and foster long-term stability within Japan's conglomerate ecosystem. This strategic alliance enables Mitsui to leverage synergies and maintain competitive advantages across global markets.
Fuyo Group: Collaboration Within a Keiretsu Conglomerate
The Fuyo Group exemplifies a keiretsu conglomerate through its strategic collaboration among leading companies like Fuji Bank, Nissan Motor, and Hitachi. This network facilitates mutual shareholding and coordinated business strategies, enhancing financial stability and competitive advantage. Such integration allows member firms to leverage collective resources and innovation within Japan's corporate ecosystem.
Real-World Success Stories of Keiretsu in Business
Toyota Group exemplifies a successful keiretsu, integrating automotive manufacturing, parts suppliers, and financial services to create a resilient and efficient conglomerate. Mitsubishi Group's keiretsu structure leverages close-knit relationships among its industrial, banking, and trading companies to sustain long-term growth and innovation. Hitachi's keiretsu model drives technological advancements and market expansion through collaborative synergies across its diverse subsidiaries in electronics, engineering, and finance.
Keiretsu vs Traditional Conglomerate Models
Keiretsu, exemplified by Japan's Mitsubishi Group, integrates affiliated companies through cross-shareholding and long-term partnerships, fostering collaboration and mutual stability. Traditional conglomerate models, such as General Electric in the U.S., prioritize centralized control and diversified ownership to maximize financial performance and market reach. The keiretsu model emphasizes interdependence and resilience, contrasting with the hierarchical, profit-driven approach of conventional conglomerates.
Benefits of Keiretsu Associations in Conglomerate Strategy
Keiretsu associations in conglomerate strategy enhance business stability by fostering long-term partnerships among member companies, facilitating resource sharing and risk reduction. These alliances improve supply chain efficiency through coordinated procurement and production processes, leading to cost savings and innovation. Financial support within the keiretsu network ensures access to capital and mitigates market volatility, strengthening overall corporate resilience.
Future Trends of Keiretsu in Global Conglomerates
Future trends of keiretsu in global conglomerates emphasize digital integration and collaborative innovation among member firms to enhance supply chain resilience and market adaptability. Increasing adoption of AI-driven analytics fosters real-time decision-making, strengthening inter-company coordination within keiretsu networks. Expansion into emerging markets enables diversified investment portfolios, positioning keiretsu as pivotal structures in global economic growth and sustainability initiatives.
example of keiretsu in conglomerate Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com