Brownfield development in business refers to the process of redeveloping or upgrading previously used or underutilized commercial properties. An example of this is transforming an old industrial site into a mixed-use complex combining office spaces, retail shops, and residential units. This approach leverages existing infrastructure while addressing environmental concerns and urban revitalization. Another illustration of brownfield development involves refurbishing obsolete factory buildings into technology hubs or innovation centers. Companies often invest in these projects to capitalize on location advantages and reduce construction costs compared to building on undeveloped land. Brownfield projects contribute significantly to sustainable urban growth by reusing land and minimizing urban sprawl.
Table of Comparison
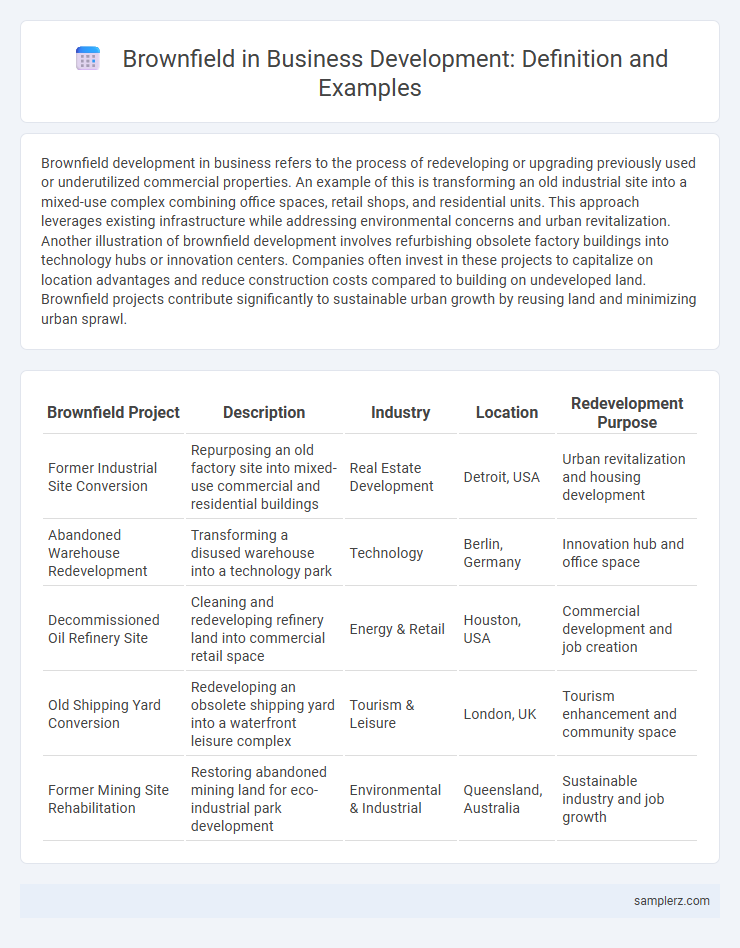
| Brownfield Project | Description | Industry | Location | Redevelopment Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Former Industrial Site Conversion | Repurposing an old factory site into mixed-use commercial and residential buildings | Real Estate Development | Detroit, USA | Urban revitalization and housing development |
| Abandoned Warehouse Redevelopment | Transforming a disused warehouse into a technology park | Technology | Berlin, Germany | Innovation hub and office space |
| Decommissioned Oil Refinery Site | Cleaning and redeveloping refinery land into commercial retail space | Energy & Retail | Houston, USA | Commercial development and job creation |
| Old Shipping Yard Conversion | Redeveloping an obsolete shipping yard into a waterfront leisure complex | Tourism & Leisure | London, UK | Tourism enhancement and community space |
| Former Mining Site Rehabilitation | Restoring abandoned mining land for eco-industrial park development | Environmental & Industrial | Queensland, Australia | Sustainable industry and job growth |
Understanding Brownfield Development in Business
Brownfield development in business involves repurposing previously used commercial or industrial sites, often contaminated or underutilized, into productive assets. This approach capitalizes on existing infrastructure, reducing costs and environmental impact compared to greenfield projects. By transforming these sites, companies can leverage location advantages, comply with sustainability goals, and stimulate local economic growth.
Key Characteristics of Brownfield Sites
Brownfield sites are previously developed lands, often former industrial or commercial properties, that may be contaminated but have existing infrastructure such as roads, utilities, and buildings. These sites typically require environmental remediation and pose challenges like soil contamination and regulatory compliance. Redeveloping brownfield areas leverages their strategic locations to revitalize urban spaces and promote sustainable growth.
Notable Global Examples of Brownfield Projects
The redevelopment of the London Olympic Park transformed a former industrial brownfield site into a world-class sports and residential complex, showcasing urban regeneration's potential. The High Line in New York City repurposed an abandoned elevated railway into a thriving public park, driving economic growth and tourism. In Asia, the redevelopment of Seoul's Cheonggyecheon Stream reclaimed a polluted urban stream, fostering environmental restoration and urban revitalization.
Successful Brownfield Redevelopment Case Studies
Successful brownfield redevelopment projects demonstrate how contaminated, underutilized industrial sites can be transformed into thriving commercial hubs, such as the revitalization of the London Docklands, which converted derelict docks into a vibrant financial district. The Detroit Michigan Brownfield Redevelopment Authority's efforts turned former manufacturing sites into mixed-use developments, enhancing urban renewal and economic growth. These case studies highlight the importance of public-private partnerships and comprehensive environmental remediation in driving sustainable economic development.
Economic Benefits of Brownfield Investments
Brownfield development projects, such as the revitalization of abandoned industrial sites, generate significant economic benefits by attracting new businesses and creating job opportunities. These investments stimulate local economies through increased property values and expanded tax bases, reducing urban decay and blight. Redeveloping brownfields also leverages existing infrastructure, resulting in cost efficiency compared to greenfield projects and promoting sustainable urban growth.
Environmental Impact of Brownfield Revitalization
Brownfield revitalization transforms contaminated industrial sites into valuable commercial or residential spaces, reducing urban sprawl and preserving greenfields. Environmental impact assessments guide remediation efforts, addressing soil contamination, groundwater pollution, and hazardous waste management to mitigate health risks. Successful brownfield redevelopment stimulates economic growth while promoting sustainable land use and improving ecosystem quality.
Public-Private Partnerships in Brownfield Development
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) in brownfield development often involve collaboration between government agencies and private developers to rehabilitate contaminated industrial sites for commercial or residential use. These partnerships leverage private investment and expertise while enabling public entities to address environmental hazards and regulatory compliance efficiently. Successful PPPs facilitate urban revitalization, generate economic growth, and improve community infrastructure by transforming underutilized land into productive assets.
Challenges in Brownfield Redevelopment Processes
Brownfield redevelopment projects often face significant challenges such as environmental contamination, which requires extensive site assessment and remediation to meet regulatory standards. Navigating complex zoning laws and securing financing further complicate development, impacting project timelines and costs. Stakeholder engagement and community opposition can also delay progress, necessitating transparent communication and strategic planning to ensure successful outcomes.
Brownfield vs. Greenfield: Business Considerations
Brownfield development involves upgrading or repurposing existing business infrastructure, offering cost savings and faster time-to-market compared to Greenfield projects, which start from scratch on undeveloped land. Companies choose Brownfield strategies to leverage established resources, reduce risk, and comply with zoning laws, while Greenfield ventures provide full design freedom but entail higher initial investment and longer timelines. Evaluating factors such as site conditions, regulatory environment, and capital availability is crucial for deciding between Brownfield and Greenfield business development.
Future Trends in Brownfield Business Development
Brownfield development in business increasingly integrates sustainable technologies and smart infrastructure to revitalize underutilized urban sites. Emerging trends emphasize adaptive reuse, where existing structures are transformed into innovative commercial or mixed-use spaces, reducing environmental impact and preserving cultural heritage. Investment in brownfield projects is expected to grow as demand for eco-friendly urban renewal and advanced data-driven planning tools rises.
example of brownfield in development Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com