In automotive design, a scuttle refers to the section of the chassis located between the engine compartment and the passenger cabin. This area often includes the firewall, which separates the engine bay from the interior, providing structural integrity and safety. The scuttle panel plays a key role in supporting the windshield and can also house components such as hinges for the hood or mounts for windshield wipers. Data from automotive manufacturers show that the scuttle's design impacts both vehicle rigidity and crash safety performance. Entities like OEMs and aftermarket suppliers focus on materials such as stamped steel or aluminum for the scuttle to reduce weight while maintaining strength. Innovations in scuttle construction contribute to better aerodynamics and noise insulation, enhancing overall vehicle quality.
Table of Comparison
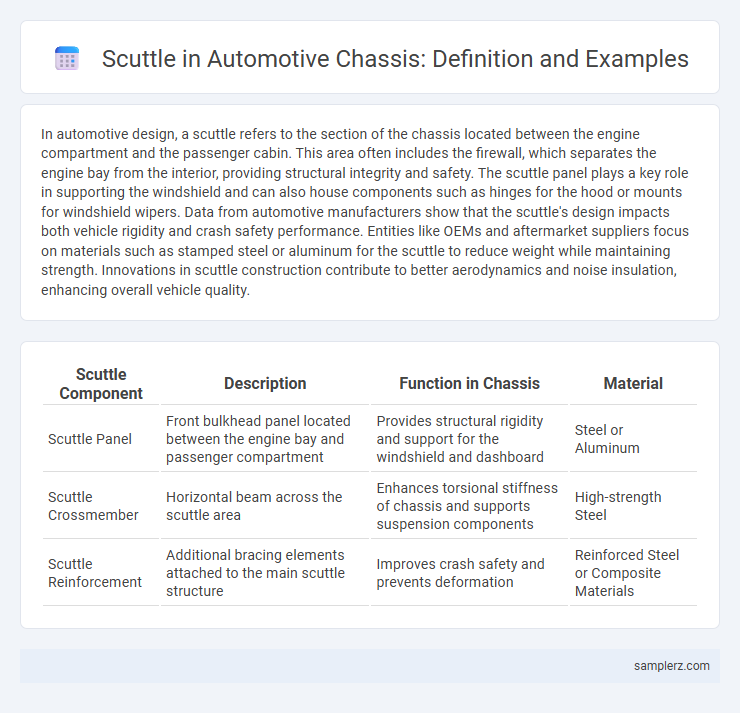
| Scuttle Component | Description | Function in Chassis | Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scuttle Panel | Front bulkhead panel located between the engine bay and passenger compartment | Provides structural rigidity and support for the windshield and dashboard | Steel or Aluminum |
| Scuttle Crossmember | Horizontal beam across the scuttle area | Enhances torsional stiffness of chassis and supports suspension components | High-strength Steel |
| Scuttle Reinforcement | Additional bracing elements attached to the main scuttle structure | Improves crash safety and prevents deformation | Reinforced Steel or Composite Materials |
Understanding the Scuttle in Automotive Chassis Design
The scuttle in automotive chassis design refers to the structural component located between the engine bay and the passenger compartment, providing crucial rigidity and crash protection. It serves as a mounting point for the dashboard, windshield, and A-pillars, contributing to overall vehicle safety and structural integrity. Proper design of the scuttle enhances torsional stiffness, improving handling and occupant safety during collisions.
Key Functions of a Scuttle in Vehicle Chassis
The scuttle in a vehicle chassis serves as a critical structural component that enhances rigidity between the engine compartment and passenger cabin, providing improved crash safety and reducing chassis flex. It supports mounting points for the windshield, dashboard, and firewall, ensuring proper alignment and integrity of these elements. By channeling airflow and housing wiring harnesses, the scuttle also contributes to vehicle aerodynamics and electrical system organization.
Materials Used for Scuttle Construction
The scuttle in automotive chassis is commonly constructed using high-strength steel or aluminum alloys to enhance durability and reduce weight, thereby improving overall vehicle performance. Composite materials like carbon fiber reinforced plastics are increasingly employed for their superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. These material choices contribute significantly to the structural integrity and crashworthiness of modern automotive chassis.
Scuttle Placement within the Car Chassis
Scuttle placement within the car chassis is typically located between the engine bay and the passenger compartment, serving as a structural barrier that enhances rigidity and safety. Positioned at the base of the windshield, the scuttle supports key components such as the dashboard assembly, steering column, and windshield wipers. Optimizing scuttle location improves impact absorption during collisions while contributing to overall vehicle aerodynamics and noise reduction.
Historical Evolution of Scuttle Design
The scuttle in automotive chassis design originally served as a structural partition between the engine compartment and passenger cabin, evolving from simple flat panels in early 20th-century vehicles to more aerodynamically contoured and reinforced forms by the mid-century. Advances in steel stamping and welding techniques during the 1930s and 1940s enabled the integration of scuttle panels with windshield frames, enhancing rigidity and crash safety. Modern scuttle designs incorporate high-strength materials and complex geometries to improve occupant protection, reduce noise and vibration, and optimize airflow for engine cooling and aerodynamics.
Modern Examples of Scuttle Integration
Modern automotive chassis designs integrate the scuttle as a reinforced panel between the engine compartment and the passenger cabin, enhancing structural rigidity and crash safety. In electric vehicles like the Tesla Model 3, the scuttle serves as a mounting point for sensors and electronic components, optimizing spatial efficiency. Advanced materials such as high-strength steel and aluminum alloys are commonly used to reduce weight while maintaining durability in scuttle construction.
Scuttle’s Role in Safety and Structural Integrity
The scuttle in automotive chassis serves as a critical structural component, enhancing the rigidity between the engine bay and passenger compartment to improve overall vehicle stability during a collision. It absorbs and redistributes impact forces, reducing cabin deformation and protecting occupants. Modern designs incorporate reinforced materials to optimize energy absorption and maintain the integrity of the safety cell.
Common Scuttle Types in Different Vehicle Classes
Scuttle types in automotive chassis vary across vehicle classes, including bulkhead scuttles commonly found in passenger cars that separate the engine compartment from the cabin to enhance noise and heat insulation. In SUVs and off-road vehicles, reinforced scuttle designs provide additional structural rigidity and improved crash protection. Commercial trucks often feature enlarged scuttles to accommodate larger engine bays and facilitate better airflow for heavy-duty cooling requirements.
Innovations in Scuttle Manufacturing
Innovations in scuttle manufacturing for automotive chassis include the integration of advanced composite materials such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, which enhance structural rigidity while reducing weight. Laser welding techniques have improved precision and strength in joining scuttle panels, contributing to improved crash safety and durability. Incorporating multifunctional designs that house sensor arrays and cable conduits within the scuttle area streamlines assembly and supports the advancement of autonomous driving systems.
Maintenance and Inspection of the Scuttle in Chassis
Regular maintenance and inspection of the scuttle in the chassis involve checking for corrosion, cracks, and structural integrity to ensure vehicle safety. Proper sealing and waterproofing around the scuttle prevent water ingress that can lead to rust and electrical issues. Timely repairs and rust treatment on the scuttle help maintain the chassis's strength and prolong the vehicle's lifespan.
example of scuttle in chassis Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com