Heel-and-toe downshifting is a driving technique used in performance and racing cars to match the engine speed with the transmission speed during a downshift. The driver uses the right foot to press the brake pedal while simultaneously using the edge or heel of the same foot to blip the throttle, increasing engine RPM. This method prevents drivetrain shock and maintains vehicle stability by ensuring smooth gear engagement. In an automotive context, heel-and-toe downshifting improves control during high-speed cornering and deceleration, especially in manual transmission vehicles. Data shows that this technique reduces wear on the clutch and transmission, enhancing overall vehicle longevity. Professional racers and driving enthusiasts often employ heel-and-toe to maintain optimal engine performance and improve lap times.
Table of Comparison
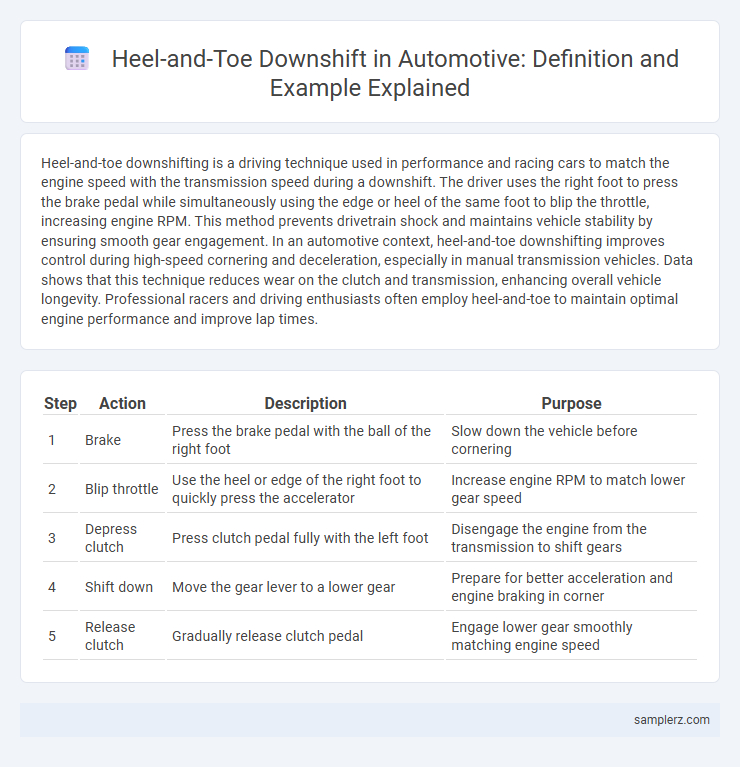
| Step | Action | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brake | Press the brake pedal with the ball of the right foot | Slow down the vehicle before cornering |
| 2 | Blip throttle | Use the heel or edge of the right foot to quickly press the accelerator | Increase engine RPM to match lower gear speed |
| 3 | Depress clutch | Press clutch pedal fully with the left foot | Disengage the engine from the transmission to shift gears |
| 4 | Shift down | Move the gear lever to a lower gear | Prepare for better acceleration and engine braking in corner |
| 5 | Release clutch | Gradually release clutch pedal | Engage lower gear smoothly matching engine speed |
Understanding the Heel-and-Toe Technique
The heel-and-toe technique in downshifting involves simultaneously braking and blipping the throttle to match engine speed with the lower gear, ensuring smooth deceleration and preventing drivetrain shock. Mastery of this technique is essential for high-performance driving, as it maintains vehicle stability and enhances control during corner entry. Practicing heel-and-toe downshifts improves overall shifting precision, reduces clutch wear, and optimizes engine response.
Why Heel-and-Toe Matters in Downshifting
Heel-and-toe downshifting improves vehicle stability and control by matching engine RPM to the lower gear, preventing drivetrain shock and rear-wheel lockup during braking. This technique enhances cornering precision and safety in high-performance driving scenarios by maintaining optimal traction and balance. Mastering heel-and-toe is essential for seamless gear transitions, reducing wear on the transmission and improving overall driving dynamics.
Step-by-Step Guide to Heel-and-Toe Downshifting
Heel-and-toe downshifting involves braking with the ball of the right foot while blipping the throttle with the heel to match engine RPM during a downshift, ensuring smooth gear engagement. Begin by pressing the brake pedal with the ball of your right foot, then pivot your foot to the right to press the gas pedal briefly while disengaging the clutch and shifting to a lower gear. This technique reduces drivetrain shock, maintains vehicle balance, and improves acceleration when entering corners or slowing down.
Common Mistakes in Heel-and-Toe Application
Common mistakes in heel-and-toe downshifting include improper timing between brake and throttle, which causes jerky transitions or engine stalling. Many drivers fail to match engine revs precisely, leading to excessive wear on the clutch and drivetrain components. Consistent practice in coordinating heel-and-toe can prevent these errors and ensure smoother, more efficient downshifts during spirited driving.
Real-World Scenarios for Heel-and-Toe Usage
Heel-and-toe downshifting is commonly used during aggressive cornering in motorsports, where drivers simultaneously brake and blip the throttle to match engine RPM with the lower gear. Real-world scenarios include navigating tight hairpin turns on a racetrack or managing steep descents in performance road cars, enhancing control and preventing drivetrain shock. This technique improves vehicle stability and acceleration response, crucial for both amateur enthusiasts and professional drivers in dynamic driving conditions.
Benefits of Heel-and-Toe Downshifting for Drivers
Heel-and-toe downshifting enables smooth, precise gear changes by matching engine speed with wheel speed, enhancing vehicle stability and control during deceleration. This technique reduces drivetrain shock, extends clutch and transmission life, and allows drivers to maintain optimal RPM for immediate acceleration out of corners. Skilled use of heel-and-toe downshifting increases driving precision, improves lap times in motorsports, and provides a more engaging and responsive driving experience.
Comparing Heel-and-Toe with Standard Downshifting
Heel-and-toe downshifting involves simultaneously braking and blipping the throttle to smoothly match engine speed with the lower gear, enhancing control and reducing drivetrain shock. Standard downshifting simply releases the brake and shifts gears without throttle modulation, often causing abrupt deceleration and increased wear on transmission components. This technique is essential for performance driving, as it improves vehicle stability and prolongs clutch life compared to conventional downshifts.
Expert Tips for Mastering Heel-and-Toe Techniques
Mastering the heel-and-toe downshift technique enhances smooth gear transitions and prevents driveline shock, essential for performance driving. Expert tips include practicing precise throttle blips with the right foot while braking, maintaining rev matching to match engine RPM with lower gear speed. Consistent heel-and-toe execution improves vehicle control during cornering and preserves clutch longevity in high-performance automotive applications.
How Heel-and-Toe Improves Track Performance
Heel-and-toe downshifting synchronizes engine speed with wheel speed during braking, allowing smoother gear transitions and preventing drivetrain shock. This technique maintains vehicle balance and stability through corners by enabling quicker deceleration and more precise throttle control. Improved cornering speed and reduced tire wear result in enhanced overall lap times and consistent track performance.
Practicing Heel-and-Toe: Drill and Example Sessions
Practicing heel-and-toe downshifting involves coordinating throttle blips with brake application to maintain engine revs and smooth gear changes. Drill sessions focus on gradually mastering heel blipping by using controlled speed environments and specific downshift scenarios, such as shifting from third to second gear while braking into a corner. Example exercises include simulating track-like conditions where timed heel-and-toe shifts optimize vehicle balance and avoid drivetrain shock, improving overall driving precision.
example of heel-and-toe in downshift Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com