Jounce in a shock absorber refers to the compression phase where the suspension fully compresses and the vehicle's chassis moves closer to the axle. This occurs when the shock absorber reaches the limit of its travel, absorbing the impact from sudden bumps or potholes. The jounce event is critical for preventing damage to the suspension components and maintaining vehicle stability. Shock absorbers use jounce bump stops or internal hydraulic cushions to control the jounce movement and reduce harsh impacts. These components ensure a smooth transition during high compression, protecting both the shock absorber and the vehicle frame. Effective jounce management improves ride comfort and extends the lifespan of automotive suspension systems.
Table of Comparison
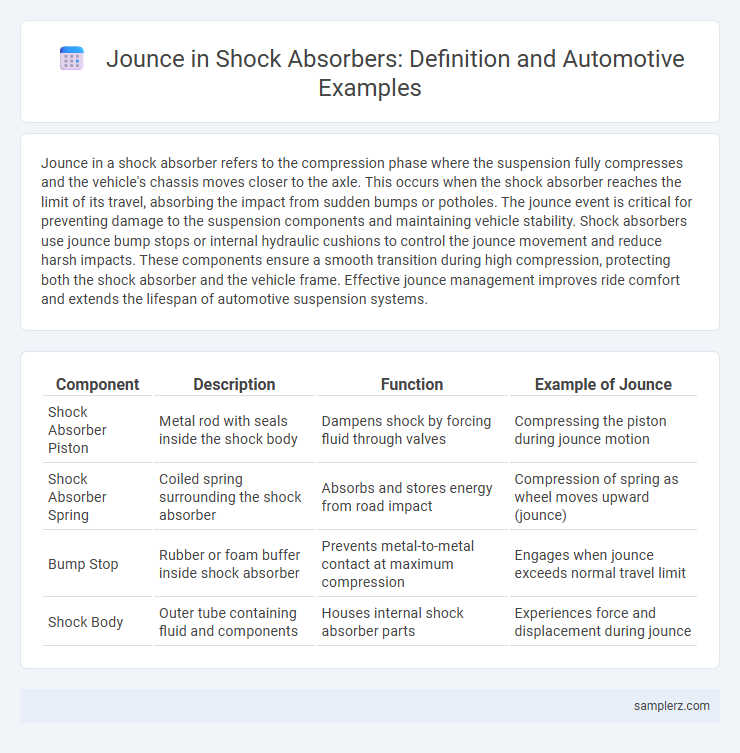
| Component | Description | Function | Example of Jounce |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shock Absorber Piston | Metal rod with seals inside the shock body | Dampens shock by forcing fluid through valves | Compressing the piston during jounce motion |
| Shock Absorber Spring | Coiled spring surrounding the shock absorber | Absorbs and stores energy from road impact | Compression of spring as wheel moves upward (jounce) |
| Bump Stop | Rubber or foam buffer inside shock absorber | Prevents metal-to-metal contact at maximum compression | Engages when jounce exceeds normal travel limit |
| Shock Body | Outer tube containing fluid and components | Houses internal shock absorber parts | Experiences force and displacement during jounce |
Understanding Jounce in Automotive Suspension Systems
Jounce in automotive suspension systems refers to the upward travel distance of a shock absorber when the wheel moves over a bump or obstacle, compressing the suspension. Proper understanding of jounce is critical for optimizing ride comfort, handling stability, and preventing suspension bottoming, which can cause damage. Engineers analyze shock absorber jounce characteristics through dynamic testing and simulations to calibrate damping rates and spring stiffness in vehicles.
What Happens During Jounce in Shock Absorbers
During jounce in shock absorbers, the suspension compresses as the vehicle wheel moves upward due to road irregularities or sudden impacts. This compression forces the shock absorber's piston to push through hydraulic fluid or gas, converting kinetic energy into heat and thereby damping vibrations. Efficient energy absorption during jounce enhances ride comfort and maintains tire contact with the road surface for improved vehicle stability.
Key Functions of Shock Absorbers During Jounce
Shock absorbers play a crucial role during jounce by controlling the upward movement of the suspension when the vehicle encounters a bump or pothole, preventing excessive body movement and maintaining tire contact with the road. They convert kinetic energy from the jounce motion into heat through hydraulic fluid damping, ensuring smooth and stable ride quality. Effective shock absorption during jounce enhances vehicle handling, reduces chassis vibration, and improves overall safety by stabilizing the suspension system.
Real-World Examples of Jounce Events
During high-speed cornering on rough terrain, the suspension system experiences jounce as the shock absorber compresses sharply to absorb impacts from uneven surfaces. Off-road vehicles frequently encounter jounce events when traversing obstacles such as rocks or deep ruts, causing rapid compression of the shock absorber to maintain tire contact and vehicle stability. Sports cars undergoing sudden braking maneuvers also demonstrate jounce as the front suspension compresses significantly to counteract forward weight transfer.
Impact of Jounce on Ride Quality and Vehicle Stability
Jounce in a shock absorber refers to the rapid compression of the suspension when the tire encounters a sudden bump or obstacle, directly affecting ride quality by absorbing and dissipating impact energy. Excessive jounce can lead to harsh ride experiences and reduced vehicle stability by causing frequent suspension bottoming, which compromises tire contact with the road. Properly calibrated jounce control ensures smoother handling, enhanced traction, and improved safety during dynamic driving conditions.
Signs of Jounce Issues in Shock Absorbers
Signs of jounce issues in shock absorbers include excessive bouncing, uneven tire wear, and reduced vehicle stability during turns or braking. Noticeable clunking noises when driving over bumps indicate worn jounce bumpers or degraded spring compression. Poor shock absorption leads to decreased ride comfort and potential damage to suspension components.
How Engineers Test Jounce Performance
Engineers test jounce performance in shock absorbers by using dynamic compression tests that simulate extreme road impacts and measure the absorber's response under high load. Advanced testing rigs apply rapid suspension travel to assess energy absorption, damping characteristics, and potential bottoming out behavior during jounce events. Data from these tests guides the calibration of shock absorbers to optimize ride comfort, handling stability, and component durability in automotive suspension systems.
Suspension Components Involved in Jounce Movement
Jounce movement in a shock absorber primarily involves the compression of suspension components such as coil springs, struts, and the shock absorber piston itself. The coil springs absorb and cushion the impact, while the struts provide structural support and help control the vehicle's ride height. Shock absorbers convert kinetic energy from jounce movement into thermal energy, stabilizing the vehicle by dampening excessive oscillations.
Solutions for Managing Excessive Jounce
Excessive jounce in automotive shock absorbers can be effectively managed using hydraulic bump stops and high-quality monotube dampers designed to absorb harsh impacts. Advanced multi-stage bumpers constructed from durable elastomers provide progressive resistance to compression, minimizing damage during extreme wheel travel. Incorporating adjustable valving systems also allows fine-tuning of shock response to optimize ride comfort while controlling jounce forces.
Innovations in Shock Absorbers for Better Jounce Control
Innovations in shock absorbers for jounce control include adaptive damping systems that adjust resistance in real time to absorb impact forces more efficiently, enhancing ride comfort and vehicle stability. Advanced materials like magnetorheological fluids enable shock absorbers to respond instantly to varying road conditions, reducing jounce-induced vibrations. Integration of electronic sensors and controllers ensures precise tuning of jounce response, improving overall suspension performance and extending component longevity.
example of jounce in shock absorber Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com