The double-clutch transmission system improves gear shifting in automotive vehicles by reducing synchronization time between gears. This method involves pressing the clutch twice during a gear change: once to disengage the current gear and again to engage the next gear smoothly. By matching engine speed to wheel speed, double-clutching minimizes wear on the transmission and enhances driving performance, especially in manual sports cars and heavy-duty trucks. A classic example of double-clutch shifting occurs in vehicles equipped with non-synchronized manual gearboxes, such as older Porsche 911 models and large commercial trucks. Drivers first press the clutch to move the gear lever out of the current gear, then release the clutch while revving the engine to the appropriate speed before pressing the clutch again to engage the next gear. This technical process aligns the rotational speeds of the input and output shafts, resulting in seamless gear transitions and improved control over the vehicle.
Table of Comparison
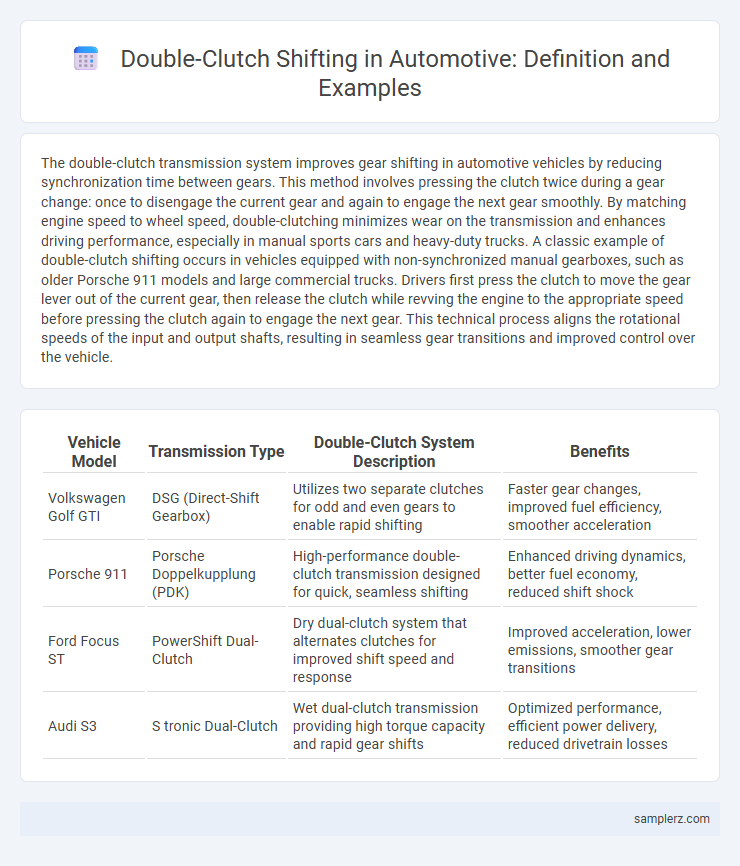
| Vehicle Model | Transmission Type | Double-Clutch System Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volkswagen Golf GTI | DSG (Direct-Shift Gearbox) | Utilizes two separate clutches for odd and even gears to enable rapid shifting | Faster gear changes, improved fuel efficiency, smoother acceleration |
| Porsche 911 | Porsche Doppelkupplung (PDK) | High-performance double-clutch transmission designed for quick, seamless shifting | Enhanced driving dynamics, better fuel economy, reduced shift shock |
| Ford Focus ST | PowerShift Dual-Clutch | Dry dual-clutch system that alternates clutches for improved shift speed and response | Improved acceleration, lower emissions, smoother gear transitions |
| Audi S3 | S tronic Dual-Clutch | Wet dual-clutch transmission providing high torque capacity and rapid gear shifts | Optimized performance, efficient power delivery, reduced drivetrain losses |
Understanding Double-Clutching in Automotive Transmissions
Double-clutching in automotive transmissions involves manually shifting gears by engaging and disengaging the clutch twice to match engine speed with the transmission input shaft, improving gear synchronization and reducing wear. This technique is commonly used in older non-synchronized manual transmissions and heavy-duty trucks to enable smoother gear changes and prevent gear grinding. Mastering double-clutching enhances driving performance by optimizing power delivery and extending transmission lifespan.
The Mechanics Behind Double-Clutch Shifting
Double-clutch shifting involves a specific sequence of clutch engagements to synchronize gear speeds, enhancing smoothness and control in manual transmissions. The first clutch press disengages the engine from the gearbox, enabling the driver to shift into neutral and rev-match by adjusting engine speed to the next gear's requirements. Re-engaging the clutch after selecting the desired gear ensures seamless power transfer, minimizing gear clash and wear.
Step-by-Step Example of Double-Clutch Shifting
During double-clutch shifting, the driver first presses the clutch pedal and shifts the transmission to neutral, releasing the clutch to match engine speed to the new gear. Next, the driver presses the clutch again to engage the lower or higher gear while adjusting engine RPM to synchronize with the transmission input shaft. This technique reduces gear clash and enhances smoothness during upshifts or downshifts, optimizing gear engagement in performance driving or classic manual transmissions.
Key Benefits of Double-Clutching for Drivers
Double-clutching improves gear synchronization by matching engine speed to transmission speed, resulting in smoother shifts and reduced wear on the clutch and gearbox. This technique enhances vehicle control during downshifts, particularly in manual transmissions without synchronized gears, by minimizing drivetrain shock and maintaining engine stability. Drivers benefit from prolonged transmission lifespan, increased driving precision, and a more engaging driving experience due to the seamless power delivery during gear changes.
Double-Clutching vs. Single-Clutch Shifting
Double-clutching improves gear engagement by matching engine and transmission speeds, reducing wear on the synchronizers compared to single-clutch shifting. In automotive applications, this technique is particularly effective in manual transmissions without synchromesh, enhancing smoothness and extending gearbox longevity. Single-clutch shifting relies solely on synchros, potentially causing gear clash and increased transmission stress under aggressive driving conditions.
When to Use Double-Clutch Shifting in Real Driving
Double-clutch shifting is particularly beneficial during low-speed, manual transmission gear changes, such as when driving on steep hills or in stop-and-go traffic where smooth gear engagement is crucial. It reduces wear on the synchronizers by matching the engine speed with the transmission input shaft, enhancing the longevity of the gearbox. Drivers often apply double-clutching when downshifting to prevent jerking and maintain vehicle stability in real driving conditions.
Double-Clutch Shifting Example: Downshifting on a Slope
Double-clutch shifting during downshifting on a slope involves pressing the clutch twice to match engine speed with the lower gear, preventing drivetrain shock. This technique enhances vehicle control and engine responsiveness when decelerating on steep inclines. Efficient double-clutching also reduces wear on the transmission synchronizers in manual automotive systems.
Common Double-Clutching Mistakes to Avoid
Common double-clutching mistakes to avoid include releasing the clutch too quickly, which can cause gear grinding and transmission wear. Failing to match engine RPM with the transmission speed during gear shifts often leads to jerky movements and accelerated clutch plate deterioration. Ensuring smooth throttle control and precise timing between clutch engagements enhances transmission longevity and driving performance.
Mastering Double-Clutch Shifting: Tips and Tricks
Mastering double-clutch shifting enhances gear changes by synchronizing engine speed with transmission input, reducing wear on the synchronizers. Key tips include releasing the clutch slowly during the first pedal engagement, blipping the throttle to match revs on the downshift, and smoothly re-engaging the clutch to avoid jerks. Consistent practice of these techniques improves control, fuel efficiency, and driving performance in manual transmission vehicles, particularly in high-performance and heavy-duty automotive applications.
The Role of Double-Clutching in Modern vs. Classic Cars
Double-clutching enhances gear synchronization by matching engine and transmission speeds, crucial in classic cars with non-synchronized manual gearboxes. Modern vehicles integrate dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) that automate this process, delivering faster shifts and improved fuel efficiency. The evolution from manual double-clutch techniques to advanced DCT systems reflects significant advancements in automotive transmission technology.
example of double-clutch in shifting Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com