A detent in an automotive transmission is a mechanical feature that helps hold the gear selector in a specific position. This component typically consists of a spring-loaded ball or pin that fits into notches or grooves along the shift gate. The detent ensures precise gear engagement and prevents the transmission from slipping out of gear during vehicle operation. In manual transmissions, detents provide tactile feedback to the driver, confirming successful gear changes. Automatic transmissions use detent mechanisms within the valve body or shift linkage to maintain proper gear positioning. The reliability of detents contributes to smoother shifting performance and longer transmission component life.
Table of Comparison
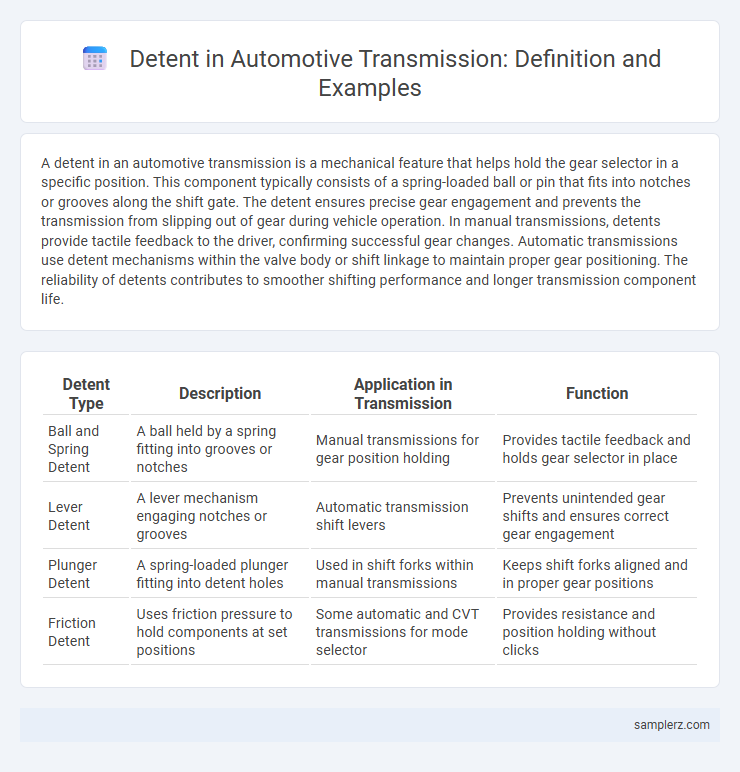
| Detent Type | Description | Application in Transmission | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball and Spring Detent | A ball held by a spring fitting into grooves or notches | Manual transmissions for gear position holding | Provides tactile feedback and holds gear selector in place |
| Lever Detent | A lever mechanism engaging notches or grooves | Automatic transmission shift levers | Prevents unintended gear shifts and ensures correct gear engagement |
| Plunger Detent | A spring-loaded plunger fitting into detent holes | Used in shift forks within manual transmissions | Keeps shift forks aligned and in proper gear positions |
| Friction Detent | Uses friction pressure to hold components at set positions | Some automatic and CVT transmissions for mode selector | Provides resistance and position holding without clicks |
Understanding Detents in Automotive Transmissions
Detents in automotive transmissions are mechanical features that provide precise positioning and tactile feedback for gear shifts by locking or holding the shift lever in place. These components commonly consist of spring-loaded balls or pawls that engage with grooves or notches on a shift shaft or drum, ensuring secure engagement and preventing unintentional gear movement. Understanding detents improves transmission reliability and enhances driver control by maintaining stable gear positions during vehicle operation.
Common Types of Detents Used in Transmissions
Detents in automotive transmissions commonly include ball detents, spring-loaded pawls, and notched plates, each designed to provide precise gear positioning and prevent unintentional gear shifts. Ball detents utilize a spring-loaded ball that locks into grooves to hold gears in place during operation, enhancing shift accuracy and stability. Spring-loaded pawls engage with teeth or notches on the shift shaft, offering tactile feedback and secure gear engagement in manual and automatic transmissions.
Role of Detents in Automatic vs. Manual Transmissions
Detents in automatic transmissions play a crucial role in maintaining gear position by using spring-loaded mechanisms to lock the gear lever, ensuring smooth and precise shifts during driving. In manual transmissions, detents provide tactile feedback and hold the gear lever in place by engaging notches or grooves within the shift assembly, preventing accidental gear disengagement. This differentiation enhances driving experience by optimizing gear stability and shift accuracy tailored to transmission type.
How Detents Assist Gear Selection
Detents in automotive transmissions provide precise positioning and tactile feedback during gear shifts by engaging notches or grooves within the shift mechanism. This mechanical locking system ensures that gears remain securely selected, reducing the likelihood of unintentional gear disengagement or slippage. Enhanced gear selection accuracy through detents contributes to smoother driving experiences and improved transmission reliability in both manual and automatic vehicles.
Examples of Detent Mechanisms in Modern Vehicles
Detent mechanisms in modern automotive transmissions commonly include ball-and-spring systems and notched gear designs that ensure precise gear engagement and prevent unintentional gear shifts. For instance, manual transmissions often employ a ball detent in the shift lever assembly to provide tactile feedback and secure gear positioning. Automatic transmissions use solenoid-controlled detents combined with hydraulic pressure to regulate gear selection smoothly and reliably.
Signs of Detent Malfunction in a Transmission
Signs of detent malfunction in a transmission include difficulty shifting gears, unusual noises such as clunking or grinding, and the transmission slipping out of gear unexpectedly. Drivers may also notice inconsistent gear engagement or a lack of tactile feedback when moving the gear lever. These symptoms indicate that the detent mechanism, responsible for holding the gear selector in place, may be worn or damaged, affecting transmission performance.
Detent Springs and Their Functionality
Detent springs in automotive transmissions play a critical role in maintaining gear position by applying consistent pressure on the detent mechanism, preventing unintended gear shifts and enhancing shift feel. These springs work in conjunction with ball bearings or notches to lock gears securely, ensuring smooth and precise gear engagement under various driving conditions. Properly calibrated detent springs contribute to transmission durability and driver control, reducing wear and improving overall shifting performance.
Innovations in Transmission Detent Technology
Innovations in transmission detent technology have introduced magnetic detents that enhance gear position accuracy and reduce wear on mechanical components. Advanced materials such as high-strength polymers and composite alloys improve durability and reduce friction during gear shifting. Integration of electronic sensors with detent mechanisms enables real-time gear position feedback, optimizing transmission performance and vehicle fuel efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Transmission Detent Systems
Regularly inspecting the transmission detent system for wear and ensuring the detent springs maintain optimal tension prevents gear slipping and maintains smooth shifting performance. Applying appropriate lubrication to the detent mechanism reduces friction and extends component lifespan while avoiding contamination that can cause malfunctions. Timely replacement of worn detent balls and pads supports precise gear engagement and reduces the risk of transmission damage.
Comparing Detent Designs Across Car Brands
Detent mechanisms in automotive transmissions vary significantly between car brands, with some using spring-loaded ball plungers for precise gear positioning while others integrate cam-based detents to enhance shift feel and reduce gear slippage. For instance, Honda transmissions often employ a robust ball and spring detent system in their manual gearboxes, offering distinct tactile feedback, whereas BMW favors a more complex cam and roller detent arrangement in their automatic transmissions to ensure smooth and secure gear engagement. These design differences reflect each brand's prioritization of driver experience, durability, and transmission performance.
example of detent in transmission Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com