Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) is a cryptographic method used in authentication to verify a user's identity without revealing any secret information. One practical example is its application in blockchain technology, where users prove they possess a private key without exposing it. This enhances security by preventing sensitive data from being transmitted or intercepted during the verification process. In authentication systems, zero-knowledge proofs enable password verification without sending the actual password over the network. For instance, the ZKP protocol can confirm that a user knows the password by responding correctly to cryptographic challenges. This approach reduces the risk of password theft and strengthens defenses against cyberattacks like phishing and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Table of Comparison
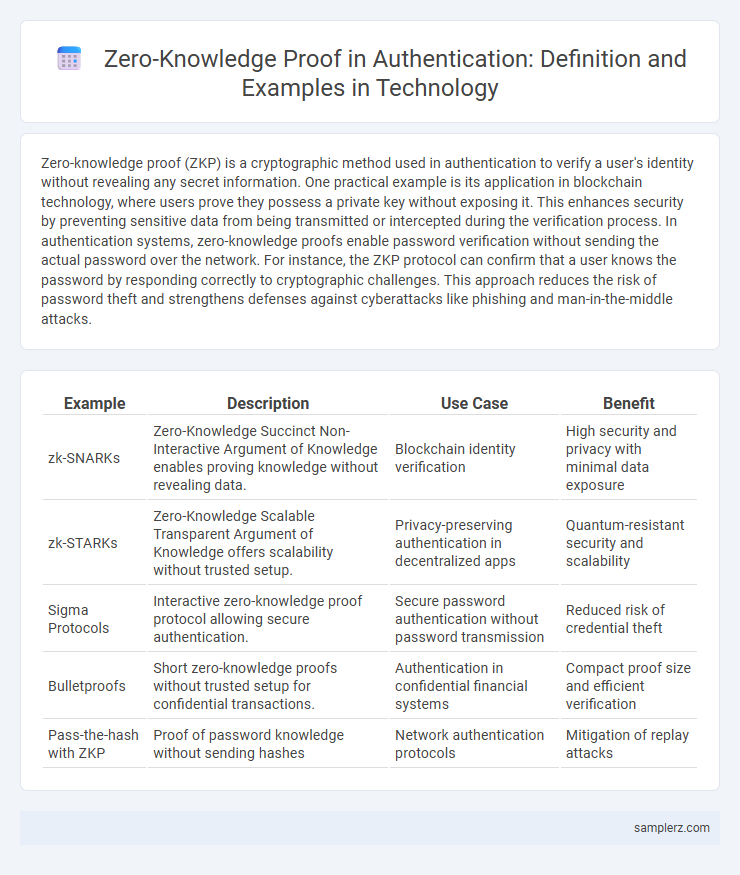
| Example | Description | Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| zk-SNARKs | Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge enables proving knowledge without revealing data. | Blockchain identity verification | High security and privacy with minimal data exposure |
| zk-STARKs | Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Argument of Knowledge offers scalability without trusted setup. | Privacy-preserving authentication in decentralized apps | Quantum-resistant security and scalability |
| Sigma Protocols | Interactive zero-knowledge proof protocol allowing secure authentication. | Secure password authentication without password transmission | Reduced risk of credential theft |
| Bulletproofs | Short zero-knowledge proofs without trusted setup for confidential transactions. | Authentication in confidential financial systems | Compact proof size and efficient verification |
| Pass-the-hash with ZKP | Proof of password knowledge without sending hashes | Network authentication protocols | Mitigation of replay attacks |
Introduction to Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Authentication
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) enable secure authentication by allowing users to prove their identity without revealing any sensitive information, enhancing privacy and security in digital systems. In authentication protocols, ZKPs verify the correctness of credentials without exposing passwords or biometric data, mitigating risks of data breaches and identity theft. Applications of zero-knowledge proofs include secure login processes, blockchain identity verification, and confidential transaction approvals in decentralized networks.
How Zero-Knowledge Proofs Enhance Security
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance security in authentication by allowing users to verify their identity without revealing any sensitive information, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches. For example, in passwordless login systems, zero-knowledge proofs enable a user to prove knowledge of a secret key without transmitting the key itself, preventing interception or replay attacks. This cryptographic method ensures secure access control in blockchain wallets and multi-factor authentication setups by maintaining privacy while confirming legitimacy.
Real-World Applications of Zero-Knowledge Authentication
Zero-knowledge proofs enable secure authentication without revealing passwords, as seen in blockchain technologies like Zcash, which uses zk-SNARKs to verify transactions privately. Apple employs zero-knowledge proofs in its private contact tracing framework to authenticate user data without compromising identity. In enterprise settings, Microsoft integrates zero-knowledge proofs within its Azure Confidential Ledger to ensure data integrity while maintaining confidentiality during authentication processes.
Passwordless Login with Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Passwordless login using zero-knowledge proofs enables users to authenticate without sharing their actual passwords, enhancing security by eliminating password transmission risks. This cryptographic method verifies a user's identity by proving knowledge of a secret without revealing the secret itself, protecting against phishing and credential theft. Leading technology firms implement zero-knowledge proof protocols to create seamless, secure login experiences, reducing reliance on traditional passwords.
Blockchain Authentication Using Zero-Knowledge Protocols
Blockchain authentication using zero-knowledge protocols enables users to verify identity without revealing sensitive information, enhancing privacy and security. This technology leverages cryptographic proofs to confirm possession of credentials without disclosing the actual data, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. Zero-knowledge proofs improve trust and efficiency in decentralized systems by allowing secure, anonymous authentication on blockchain networks.
Biometric Verification Secured by Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Biometric verification secured by zero-knowledge proofs enables authentication without revealing the underlying biometric data, enhancing user privacy and security. This technology allows systems to confirm identities by validating encrypted biometric templates such as fingerprints or iris scans without exposing the actual sensitive information. Implementing zero-knowledge proof protocols in authentication frameworks reduces the risk of data breaches and identity theft in biometric systems.
Internet of Things (IoT) Devices and Zero-Knowledge Authentication
Zero-knowledge proof enhances authentication in Internet of Things (IoT) devices by enabling secure verification without revealing sensitive data such as cryptographic keys or user credentials. This method mitigates risks associated with IoT vulnerabilities by ensuring devices authenticate each other through cryptographic protocols like zk-SNARKs or zk-STARKs. Implementing zero-knowledge authentication improves IoT security frameworks by minimizing attack surfaces and protecting data privacy in connected environments.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs for Multi-Factor Authentication
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) enhance Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) by enabling users to prove their identity without revealing sensitive information such as passwords or biometric data. This cryptographic method verifies possession of authentication factors like tokens or biometrics securely, reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft. Implementing ZKPs in MFA systems strengthens security while maintaining user privacy and minimizing attack surfaces in technology infrastructures.
Case Study: Zero-Knowledge Authentication in Financial Services
Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) enables secure authentication in financial services by allowing users to verify their identity without revealing sensitive information. A real-world case involves a major bank implementing ZKP to authenticate customers during online transactions, significantly reducing fraud and data breaches. This cryptographic method enhances privacy while maintaining regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
The Future of Authentication: Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Beyond
Zero-knowledge proofs are transforming authentication by enabling users to verify their identities without revealing sensitive information, enhancing privacy and security. Technologies like zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs power this innovation, supporting decentralized applications and blockchain networks. Future authentication systems will increasingly rely on zero-knowledge proofs to prevent data breaches and streamline user verification processes.
example of zero-knowledge proof in authentication Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com