A femtocell is a small, low-power cellular base station designed to improve indoor mobile network coverage by connecting to a user's broadband internet. It enhances data transmission quality and network capacity by offloading traffic from macrocell networks in dense urban areas or locations with poor signal strength. Telecommunications operators deploy femtocells to optimize network performance, reduce latency, and provide better user experience for voice and data services. Femtocells integrate seamlessly with existing mobile network infrastructure, supporting technologies such as 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G NR. They manage wireless communication within a limited range, usually up to 10 meters, catering primarily to residential or enterprise environments. Data collected from femtocell usage helps network providers analyze traffic patterns and optimize resource allocation for improved network efficiency.
Table of Comparison
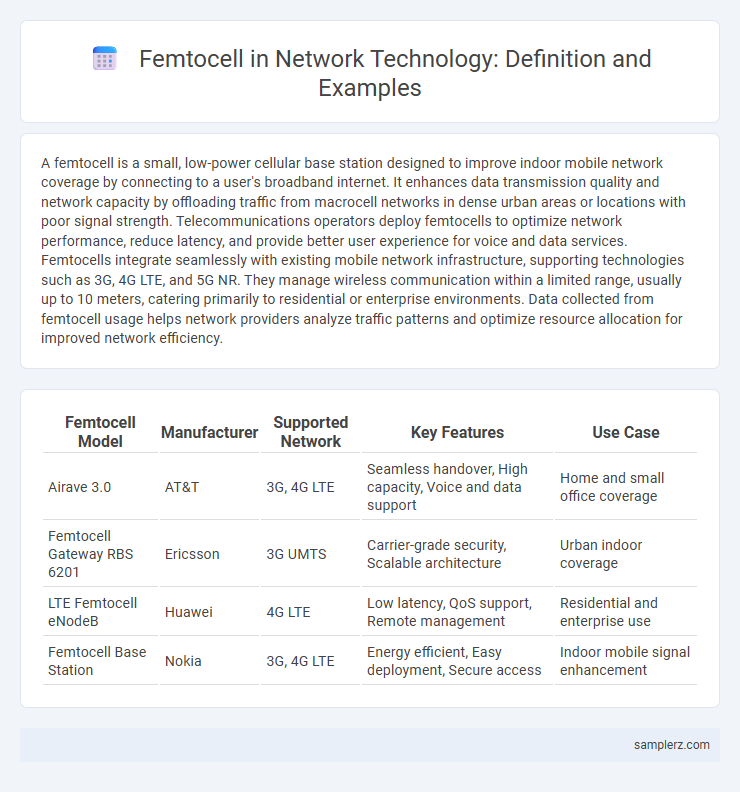
| Femtocell Model | Manufacturer | Supported Network | Key Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airave 3.0 | AT&T | 3G, 4G LTE | Seamless handover, High capacity, Voice and data support | Home and small office coverage |
| Femtocell Gateway RBS 6201 | Ericsson | 3G UMTS | Carrier-grade security, Scalable architecture | Urban indoor coverage |
| LTE Femtocell eNodeB | Huawei | 4G LTE | Low latency, QoS support, Remote management | Residential and enterprise use |
| Femtocell Base Station | Nokia | 3G, 4G LTE | Energy efficient, Easy deployment, Secure access | Indoor mobile signal enhancement |
Introduction to Femtocells in Modern Networks
Femtocells are small, low-power cellular access points designed to improve indoor mobile coverage by connecting to a user's broadband network. They enhance network capacity and reduce latency by offloading traffic from macrocells, resulting in better voice quality and faster data speeds. Widely deployed by telecom operators such as Verizon and AT&T, femtocells support 4G LTE and emerging 5G networks to optimize connectivity in homes and small businesses.
Key Features of Femtocell Technology
Femtocell technology enhances network coverage by utilizing small, low-power cellular base stations installed in homes or offices, delivering improved indoor signal strength and capacity. Key features include seamless integration with existing macrocell networks, advanced interference management to minimize signal disruption, and secure user authentication protocols ensuring reliable and private connections. These capabilities enable femtocells to support high data rates, reduce network congestion, and extend service reach in areas with weak cellular signals.
How Femtocells Enhance Indoor Mobile Coverage
Femtocells significantly enhance indoor mobile coverage by creating small, low-power cellular base stations within homes or offices that connect to the service provider's network via broadband internet. These devices reduce signal attenuations caused by thick walls and interference, delivering stronger and more reliable 4G or 5G signals indoors. Major telecom operators deploy femtocells to alleviate network congestion and improve voice quality and data speeds in areas with poor macrocell reception.
Real-World Examples of Femtocell Deployments
Femtocell deployments by major telecom operators such as Verizon and AT&T have significantly improved indoor cellular coverage in urban and suburban areas. In Japan, NTT Docomo utilized femtocells to enhance network capacity and signal strength in dense office buildings, reducing macrocell congestion. Small-scale femtocells from companies like Cisco have been integrated into smart homes to support seamless connectivity for IoT devices and mobile users.
Leading Femtocell Devices and Manufacturers
Leading femtocell devices include models like the Cisco Small Cell 3200 and the Huawei Sunwave LTE Femtocell, known for enhancing indoor cellular coverage and network capacity. Key manufacturers dominating the femtocell market are Cisco Systems, Ericsson, and Huawei Technologies, leveraging advanced small cell technology to improve wireless network performance. These companies integrate LTE and 5G capabilities into femtocells, addressing both residential and enterprise connectivity challenges effectively.
Femtocell Use Cases in Enterprise Networks
Femtocells enhance enterprise networks by providing improved indoor cellular coverage and capacity, especially in large office buildings where macrocell signals may be weak or obstructed. They support high-quality voice calls, seamless handoffs, and reliable data connections for employees, enabling better communication and productivity. Femtocell deployments also help reduce backhaul costs by offloading traffic from traditional cellular networks to the enterprise's broadband connection.
Residential Applications of Femtocells
Femtocells are small cellular base stations designed to improve indoor mobile coverage by connecting to a broadband internet connection, making them ideal for residential applications where signal strength is weak or inconsistent. These devices enhance voice quality and data speeds for smartphones by offloading traffic from macrocells, reducing network congestion and improving user experience in homes. Residential femtocells support multiple users simultaneously, facilitating seamless connectivity for voice calls, video streaming, and smart home devices within the household environment.
Femtocells in Rural and Remote Connectivity Solutions
Femtocells enhance rural and remote connectivity by providing localized cellular coverage through small, low-power base stations that connect to existing broadband networks. These devices improve signal strength and data speeds in areas where macrocell towers are sparse or unavailable, enabling reliable voice and data services. Deployment of femtocells reduces network congestion and extends cellular access to underserved populations, promoting digital inclusion and economic development.
Integration of Femtocells in 4G and 5G Networks
Femtocells enhance 4G and 5G networks by providing localized cellular coverage, improving indoor signal strength, and offloading traffic from macro cells to boost overall network capacity. Integration involves seamless handover protocols, secure IP backhaul connections, and coordination with the mobile core network to optimize resource allocation. Leading network operators deploy femtocells to support high-density urban environments and ensure consistent ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) in 5G.
Future Trends and Innovations in Femtocell Technology
Femtocell technology is evolving with the integration of 5G networks, enabling enhanced indoor coverage and higher data rates. Innovations such as self-organizing network (SON) capabilities and advanced interference management optimize femtocell performance in dense urban environments. Future trends include AI-driven resource allocation and seamless handover between macro and femtocell networks to support increasing IoT deployments.
example of femtocell in network Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com