A femtocell is a small, low-power cellular base station typically used to improve indoor mobile coverage. It connects to the service provider's network via broadband, such as DSL or cable, creating a localized cellular signal that supports voice, data, and SMS services. Femtocells are widely deployed in residential and enterprise environments to enhance network capacity and reduce call drops. In cellular networks, companies like Verizon and AT&T utilize femtocells to extend 4G LTE and 5G connectivity in areas with weak signals. These devices support multiple simultaneous users by creating a miniature cell site, reducing the load on nearby macrocells. Data throughput and network efficiency improve as femtocells offload traffic from traditional towers, optimizing overall network performance.
Table of Comparison
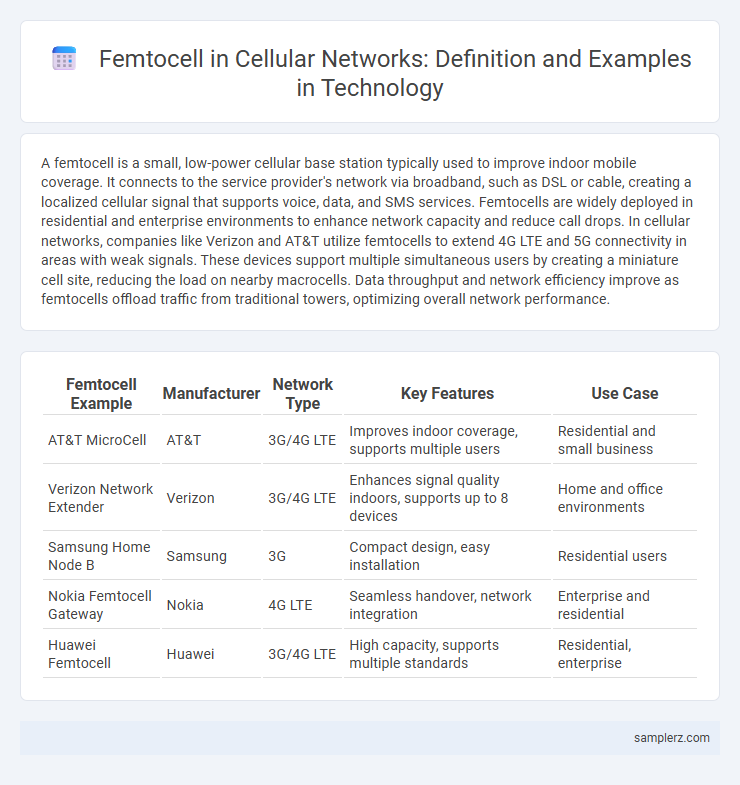
| Femtocell Example | Manufacturer | Network Type | Key Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT&T MicroCell | AT&T | 3G/4G LTE | Improves indoor coverage, supports multiple users | Residential and small business |
| Verizon Network Extender | Verizon | 3G/4G LTE | Enhances signal quality indoors, supports up to 8 devices | Home and office environments |
| Samsung Home Node B | Samsung | 3G | Compact design, easy installation | Residential users |
| Nokia Femtocell Gateway | Nokia | 4G LTE | Seamless handover, network integration | Enterprise and residential |
| Huawei Femtocell | Huawei | 3G/4G LTE | High capacity, supports multiple standards | Residential, enterprise |
Understanding Femtocells: A Brief Overview
Femtocells are low-power cellular base stations designed to enhance indoor cellular coverage by connecting to a service provider's network via broadband. These small-scale devices improve signal strength and data speeds within homes or offices, reducing network congestion and enhancing user experience. Common applications include improving 3G and 4G LTE connectivity in areas with poor macrocell coverage.
How Femtocells Enhance Cellular Network Coverage
Femtocells enhance cellular network coverage by providing localized, low-power cellular base stations that connect to the service provider's network via broadband. These small cellular units improve indoor signal strength, reducing dropped calls and increasing data speeds in areas with poor macrocell reception. By offloading traffic from macrocell networks, femtocells optimize overall network capacity and quality, particularly in densely populated or signal-challenged environments.
Real-World Example: Femtocells in Urban Environments
Femtocells are widely deployed in urban environments to enhance cellular network coverage, especially in high-density apartment complexes and office buildings where indoor signal penetration is challenging. Companies like Verizon and AT&T implement femtocell technology to offload mobile traffic from congested macrocell networks, ensuring faster data speeds and improved call quality. These small, low-power cellular base stations connect to the service provider's network via broadband, providing localized 3G or 4G LTE coverage and reducing network strain in metropolitan areas.
Leading Femtocell Solutions by Telecom Providers
Leading telecom providers such as AT&T, Vodafone, and Verizon have deployed femtocell technology to enhance indoor cellular coverage, leveraging small, low-power cellular base stations. These femtocell solutions improve network capacity and reduce call drops by routing voice and data traffic directly through existing broadband connections. Key benefits include seamless handoffs, reduced latency, and extended LTE access in homes and offices, significantly enhancing user experience in weak signal areas.
Residential Use Cases for Femtocell Technology
Femtocells are small cellular base stations designed to improve indoor coverage, commonly deployed in residential settings where macrocell signals are weak or inconsistent. These devices connect to the user's broadband internet and support multiple simultaneous voice and data connections, enhancing call quality and network capacity within homes. Residential femtocell use cases include reducing dropped calls, providing high-speed data access in remote or densely populated areas, and offloading traffic from congested macrocells to improve overall network efficiency.
Enterprise Deployment: Femtocells in Office Buildings
Femtocells in office buildings significantly enhance cellular coverage by creating localized, high-quality 4G or 5G signals within enterprise environments, reducing dropped calls and improving data speeds for employees. These small, low-power base stations connect to the enterprise internet and efficiently offload mobile traffic from macro networks, optimizing overall network capacity. Leading telecom providers deploy femtocell solutions in corporate campuses and multi-story office complexes to support seamless mobile communication and increase network reliability in dense workspaces.
Integrating Femtocells with Existing Cellular Infrastructure
Integrating femtocells with existing cellular infrastructure enhances network coverage and capacity by providing localized, high-quality indoor signals that offload traffic from macrocells. This integration relies on seamless handoff protocols and secure IP-based backhaul connections to the mobile operator's core network. Femtocells use standard interfaces like the S1 or X2 to maintain interoperability with LTE and 5G architectures, supporting efficient resource management and user authentication.
Key Benefits of Femtocell Implementation
Femtocell implementation in cellular networks significantly enhances indoor coverage by creating localized, low-power cellular base stations that improve signal strength and user experience. This technology reduces network congestion by offloading traffic from macrocell towers, leading to higher data speeds and lower latency for mobile users. Femtocells also contribute to energy efficiency and cost savings for operators by minimizing the need for extensive macrocell infrastructure upgrades.
Challenges and Limitations of Femtocell Deployment
Femtocell deployment in cellular networks faces challenges such as interference with macrocell signals, limited backhaul capacity, and complex handover management. Signal attenuation within buildings can reduce femtocell coverage, leading to inconsistent user experience. Ensuring security and privacy in untrusted residential environments also presents significant limitations for widespread femtocell adoption.
Future Trends: Evolving Roles of Femtocells in 5G Networks
Femtocells in 5G networks are evolving to enhance indoor coverage and capacity by supporting ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) and massive machine-type communication (mMTC). Integration of femtocells with edge computing enables real-time data processing and reduces network congestion, improving user experience in smart homes and IoT environments. Advanced network slicing techniques leverage femtocell deployments to provide dedicated resources for diverse 5G applications, optimizing performance and operational efficiency.
example of femtocell in cellular network Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com