Nosocomephobia, the intense fear of hospitals, often manifests in patients experiencing anxiety, panic attacks, or avoidance behaviors when confronted with hospital settings. This phobia can lead to delayed medical treatments, worsening health outcomes, and increased stress for both patients and healthcare providers. For example, a patient with severe nosocomephobia may refuse necessary surgeries or diagnostic tests despite medical advice, fearing the hospital environment. In clinical settings, healthcare professionals recognize nosocomephobia as a significant barrier to effective treatment and emphasize the importance of empathetic communication and personalized care plans. Data indicates that about 5-15% of the population may experience some degree of hospital-related anxiety, affecting their willingness to seek timely medical intervention. Hospitals have started implementing calming techniques, such as guided relaxation and environmental modifications, to alleviate this phobia and enhance patient compliance.
Table of Comparison
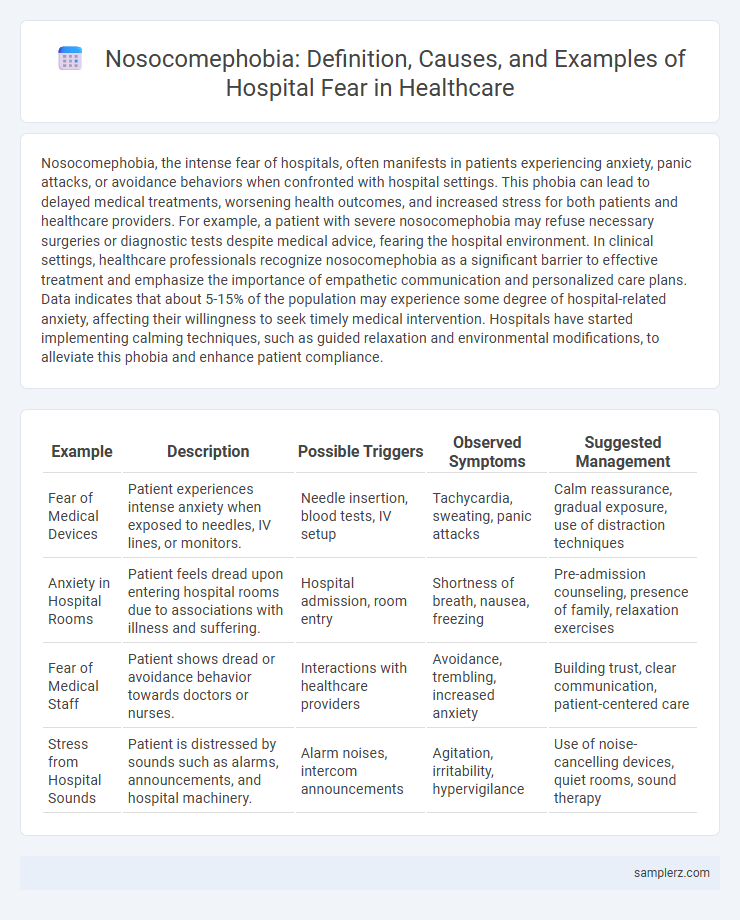
| Example | Description | Possible Triggers | Observed Symptoms | Suggested Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fear of Medical Devices | Patient experiences intense anxiety when exposed to needles, IV lines, or monitors. | Needle insertion, blood tests, IV setup | Tachycardia, sweating, panic attacks | Calm reassurance, gradual exposure, use of distraction techniques |
| Anxiety in Hospital Rooms | Patient feels dread upon entering hospital rooms due to associations with illness and suffering. | Hospital admission, room entry | Shortness of breath, nausea, freezing | Pre-admission counseling, presence of family, relaxation exercises |
| Fear of Medical Staff | Patient shows dread or avoidance behavior towards doctors or nurses. | Interactions with healthcare providers | Avoidance, trembling, increased anxiety | Building trust, clear communication, patient-centered care |
| Stress from Hospital Sounds | Patient is distressed by sounds such as alarms, announcements, and hospital machinery. | Alarm noises, intercom announcements | Agitation, irritability, hypervigilance | Use of noise-cancelling devices, quiet rooms, sound therapy |
Overview of Nosocomephobia in Healthcare Settings
Nosocomephobia, the intense fear of hospitals, significantly impacts patient experiences and healthcare outcomes by causing avoidance of necessary medical treatment. Symptoms include anxiety, panic attacks, and physiological distress when confronted with hospital environments or the thought of hospitalization. Healthcare providers must recognize and address nosocomephobia through patient-centered communication and anxiety-reduction strategies to improve treatment adherence and overall patient well-being.
Common Triggers of Nosocomephobia in Hospitals
Common triggers of nosocomephobia in hospitals include the sterile and unfamiliar environment, the presence of invasive medical equipment such as IV lines and monitors, and the fear of medical procedures like surgeries or injections. Patients often experience heightened anxiety due to the loss of control and the anticipation of potential pain or discomfort. Sounds of alarms and the sight of other distressed patients can further exacerbate this phobia.
Real-Life Patient Experiences with Hospital Phobia
Patients with nosocomephobia often report intense anxiety and panic attacks when approaching hospital environments, fearing invasive procedures or negative outcomes. One real-life example involves a middle-aged woman who avoided essential treatments for diabetes due to overwhelming dread of hospital stays, resulting in worsened health conditions. Such cases highlight the critical need for tailored psychological support and gradual exposure therapies to help patients overcome hospital-related fears.
How Medical Environments Intensify Nosocomephobia
Nosocomephobia, the intense fear of hospitals, often worsens in medical environments due to sterile rooms, intrusive sounds of medical equipment, and constant presence of healthcare staff. Bright, clinical lighting and unfamiliar medical procedures can trigger anxiety and panic attacks, making patients avoid necessary treatments. Crowded waiting areas and exposure to other patients in distress further amplify feelings of dread and helplessness associated with this phobia.
The Role of Hospital Staff in Recognizing Nosocomephobia
Hospital staff play a crucial role in recognizing nosocomephobia by observing patients' extreme anxiety, avoidance behaviors, and physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat or sweating during hospital visits. Early identification allows nurses and doctors to implement tailored communication strategies, provide emotional support, and coordinate mental health referrals. Effective staff training in recognizing these signs improves patient outcomes by reducing fear and enhancing cooperation with medical treatments.
Behavioral Signs of Nosocomephobia During Hospital Visits
Patients exhibiting nosocomephobia during hospital visits often display intense anxiety manifested through avoidance behaviors, such as reluctance to enter treatment areas or refusal of medical procedures. Repetitive questioning about safety protocols and excessive need for reassurance signal heightened fear responses. Physiological symptoms like sweating, rapid heartbeat, and trembling further indicate acute distress related to hospital environments.
Impact of Nosocomephobia on Patient Care and Recovery
Nosocomephobia, the intense fear of hospitals, can significantly hinder patient care by causing avoidance of necessary medical treatment and delayed diagnosis. This phobia increases anxiety and stress during hospitalization, negatively affecting patients' compliance with medical procedures and prolonging recovery times. Healthcare providers must recognize and address Nosocomephobia to improve patient outcomes and ensure effective treatment adherence.
Communication Strategies for Patients with Nosocomephobia
Patients with nosocomephobia experience intense fear of hospitals, requiring tailored communication strategies to ease anxiety and improve care engagement. Healthcare providers should use calm, reassuring language, provide clear explanations about procedures, and avoid medical jargon to foster trust and reduce fear. Visual aids, pre-admission consultations, and allowing patients to express concerns can also enhance communication effectiveness and patient comfort.
Hospital Design Adaptations to Ease Nosocomephobia
Hospital design adaptations to ease nosocomephobia focus on creating calming environments through natural light, soothing color schemes, and noise reduction strategies. Incorporating private patient rooms and easily navigable layouts minimizes stress and anxiety associated with medical settings. Use of biophilic design elements, such as indoor plants and views of nature, further reduces fear and promotes psychological comfort.
Therapeutic Approaches for Treating Nosocomephobia in Hospitals
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a primary therapeutic approach for nosocomephobia, aiming to reframe negative thoughts associated with hospital environments. Exposure therapy gradually introduces patients to hospital settings to reduce anxiety and build coping mechanisms. Complementary methods such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and psychoeducation enhance treatment efficacy and patient comfort during hospital stays.
example of Nosocomephobia in hospital Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com