Ring fencing in investment refers to the practice of isolating certain assets or funds within a separate portfolio to protect them from financial risks associated with other parts of a company or investment group. This strategy is commonly used by financial institutions and corporations to ensure that specific assets, such as those related to customer deposits or critical infrastructure projects, remain secure regardless of the organization's overall financial health. By creating a ring-fenced entity, investors can safeguard these assets from creditor claims or market volatility. A notable example of ring fencing occurs in the banking sector, where regulatory requirements mandate that retail banking operations be separated from riskier investment banking activities. For instance, the United Kingdom's ring-fencing rules, implemented after the 2008 financial crisis, require major banks to create distinct legal entities that isolate everyday customer deposits from trading operations. This regulatory framework enhances financial stability by minimizing the risk that losses in high-risk ventures will impact consumer banking services.
Table of Comparison
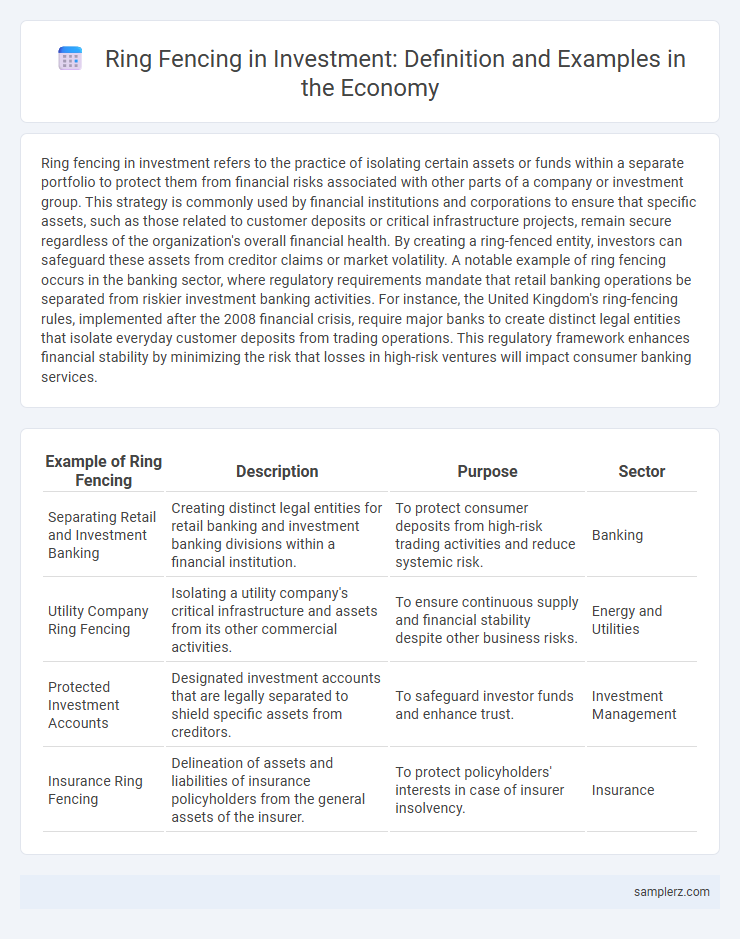
| Example of Ring Fencing | Description | Purpose | Sector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Separating Retail and Investment Banking | Creating distinct legal entities for retail banking and investment banking divisions within a financial institution. | To protect consumer deposits from high-risk trading activities and reduce systemic risk. | Banking |
| Utility Company Ring Fencing | Isolating a utility company's critical infrastructure and assets from its other commercial activities. | To ensure continuous supply and financial stability despite other business risks. | Energy and Utilities |
| Protected Investment Accounts | Designated investment accounts that are legally separated to shield specific assets from creditors. | To safeguard investor funds and enhance trust. | Investment Management |
| Insurance Ring Fencing | Delineation of assets and liabilities of insurance policyholders from the general assets of the insurer. | To protect policyholders' interests in case of insurer insolvency. | Insurance |
Understanding Ring Fencing: Key Concepts in Investment
Ring fencing in investment involves segregating certain assets or funds to protect them from risks associated with other parts of a portfolio or business operations. This strategy is commonly used by financial institutions to isolate high-risk ventures, ensuring that losses in one area do not affect the overall financial health or investor capital. Key examples include regulatory ring fencing in banks to separate retail banking assets from investment banking risks, safeguarding consumer deposits while allowing riskier trading activities to continue.
Real-World Examples of Ring Fencing in Investment Funds
Ring fencing in investment funds is exemplified by the creation of segregated portfolios within umbrella funds, where assets and liabilities are legally separated to protect investors from cross-contamination of risk. The Cayman Islands and Luxembourg are notable jurisdictions employing ring fencing structures to safeguard offshore mutual funds and private equity investments, ensuring creditor claims against one portfolio do not affect others. This mechanism enhances investor confidence by maintaining distinct financial boundaries and mitigating systemic risk within multi-asset funds.
How Ring Fencing Protects Investor Capital
Ring fencing in investment isolates specific assets or funds to shield investor capital from broader financial risks, ensuring protection against losses from other parts of the portfolio or external liabilities. This strategy is commonly used in structured finance, such as in special purpose vehicles (SPVs), where cash flows from the ring-fenced assets are dedicated solely to servicing investor obligations. By legally restricting access to these assets, ring fencing enhances capital preservation and reduces exposure during economic downturns or company insolvencies.
Ring Fencing in Private Equity: Case Studies
Ring fencing in private equity involves legally isolating assets or funds to protect investors and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. A notable case study is the Blackstone Group's use of ring fencing to separate high-risk portfolio companies from core assets, enhancing risk management and investor confidence. Another example is KKR's implementation of ring fencing strategies to safeguard fund liquidity during market downturns while maintaining operational agility.
The Role of Ring Fencing in Real Estate Investments
Ring fencing in real estate investments involves legally isolating specific assets or cash flows to protect investors from financial risks associated with other parts of a portfolio. This strategy enhances asset security by segregating high-value properties or income streams, ensuring that liabilities in other investments do not impact the ring-fenced assets. Real estate developers and fund managers often employ ring fencing to attract investment by providing clearer risk boundaries and improving capital allocation efficiency.
Corporate Structures Utilizing Investment Ring Fencing
Corporate structures utilizing investment ring fencing often establish separate subsidiaries or special purpose vehicles (SPVs) to isolate financial risks and protect core assets from potential losses. For example, large multinational corporations create ring-fenced entities to channel high-risk investments or foreign operations, ensuring that adverse outcomes do not affect the parent company's overall financial stability. This approach enhances capital allocation efficiency and mitigates systemic risk within diversified investment portfolios.
Regulatory Approaches to Ring Fencing in the Investment Sector
Regulatory approaches to ring fencing in the investment sector involve isolating client assets from a firm's proprietary holdings to protect investors during financial distress. Jurisdictions such as the United Kingdom enforce strict client asset segregation rules under the FCA's Client Asset Sourcebook (CASS), ensuring investor funds are safeguarded. These frameworks enhance market stability by minimizing contagion risk and bolstering confidence in financial institutions.
Impact of Ring Fencing on Risk Management in Investments
Ring fencing in investments involves legally isolating assets or funds to protect them from financial risks associated with other parts of a portfolio. This practice enhances risk management by ensuring that potential losses in one segment do not spread across the entire investment portfolio, preserving capital and stabilizing returns. By segregating high-risk investments, ring fencing mitigates systemic risk and improves regulatory compliance, thereby fostering investor confidence and financial stability.
Global Perspectives: Ring Fencing in International Investment
Ring fencing in international investment involves separating assets or profits within multinational corporations to protect them from political risk, taxation, or regulatory changes in foreign jurisdictions. A prominent example is how global tech firms establish subsidiaries in countries with favorable tax regimes, effectively isolating revenues to minimize tax liabilities and regulatory exposure. This strategic allocation of resources enhances financial stability and compliance across diverse economic environments.
Future Trends: Evolving Use of Ring Fencing in Investment Strategies
Ring fencing in investment strategies is increasingly being applied to isolate high-risk assets from core portfolios, protecting investors from potential volatility. This approach is gaining traction in sectors such as renewable energy and technology startups, where regulatory environments and rapid innovation create uncertain risk profiles. Advanced data analytics and AI-driven risk assessment tools are expected to enhance the precision of ring fencing, enabling more dynamic and adaptive investment management.
example of ring fencing in investment Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com