Leapfrogging in economic development refers to the process where emerging economies bypass traditional stages of growth by adopting advanced technologies directly. A prominent example is the rapid expansion of mobile banking in Kenya through M-Pesa, which allowed millions of unbanked individuals to access financial services without needing conventional banking infrastructure. This technological leapfrogging accelerated economic inclusion and facilitated the growth of small businesses and digital commerce. Another example can be observed in the renewable energy sector in parts of Africa and Asia, where countries have jumped straight to solar power installations rather than building extensive fossil fuel-based electricity grids. This shift has enabled these regions to increase energy access rapidly while promoting sustainable development. The adoption of cutting-edge technologies in energy and finance highlights how leapfrogging can drive faster and more inclusive economic progress in developing countries.
Table of Comparison
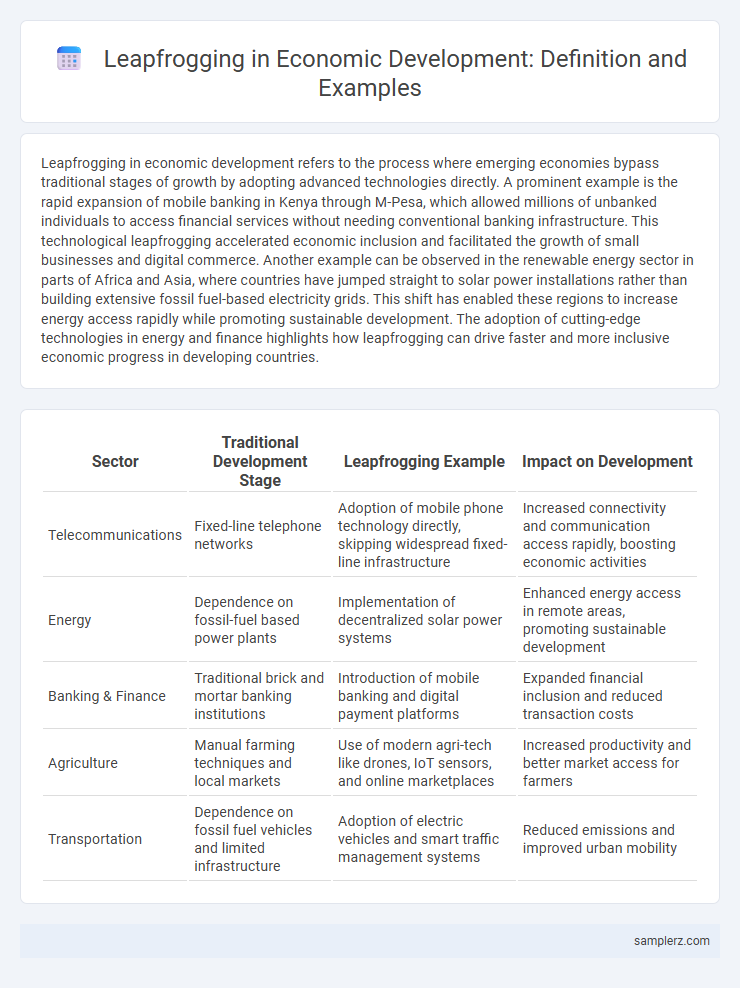
| Sector | Traditional Development Stage | Leapfrogging Example | Impact on Development |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Fixed-line telephone networks | Adoption of mobile phone technology directly, skipping widespread fixed-line infrastructure | Increased connectivity and communication access rapidly, boosting economic activities |
| Energy | Dependence on fossil-fuel based power plants | Implementation of decentralized solar power systems | Enhanced energy access in remote areas, promoting sustainable development |
| Banking & Finance | Traditional brick and mortar banking institutions | Introduction of mobile banking and digital payment platforms | Expanded financial inclusion and reduced transaction costs |
| Agriculture | Manual farming techniques and local markets | Use of modern agri-tech like drones, IoT sensors, and online marketplaces | Increased productivity and better market access for farmers |
| Transportation | Dependence on fossil fuel vehicles and limited infrastructure | Adoption of electric vehicles and smart traffic management systems | Reduced emissions and improved urban mobility |
Leapfrogging Defined: Transformative Economic Strategies
Leapfrogging in development refers to countries bypassing traditional stages of industrialization by adopting advanced technologies and innovative economic strategies directly, thereby accelerating growth. This approach is exemplified by African nations leveraging mobile banking to enhance financial inclusion without extensive banking infrastructure. Such transformative strategies enable economies to jump to higher levels of productivity and global competitiveness rapidly.
Case Study: Mobile Banking Revolution in Africa
The mobile banking revolution in Africa exemplifies leapfrogging in development by bypassing traditional banking infrastructure through widespread use of mobile phones, enabling millions to access financial services. Kenya's M-Pesa platform has transformed the economy by facilitating secure, low-cost transactions and promoting financial inclusion among unbanked populations. This technological adoption has driven economic growth, increased savings rates, and empowered small businesses across the continent.
Renewable Energy Leapfrogging in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets are rapidly adopting renewable energy technologies, bypassing traditional fossil fuel infrastructure to achieve sustainable growth. Countries like Kenya have implemented expansive off-grid solar power systems, providing electricity access to millions of rural households while reducing carbon emissions. This renewable energy leapfrogging accelerates economic development by lowering energy costs and fostering green job creation.
Digital Infrastructure Skipping Traditional Stages
Leapfrogging in economic development is evident in countries like Kenya, where mobile banking platforms such as M-Pesa have enabled rapid digital financial inclusion without relying on traditional brick-and-mortar banking infrastructure. This strategy accelerates access to financial services and stimulates economic growth by bypassing conventional stages like widespread physical bank branches. Enhanced digital infrastructure investments, including mobile networks and internet connectivity, facilitate this leapfrogging, positioning emerging economies to compete globally in the digital age.
Educational Technology Leapfrogging in Developing Nations
Educational technology leapfrogging in developing nations accelerates access to quality learning through mobile devices and online platforms, bypassing traditional infrastructure limitations like scarce schools and qualified teachers. Countries like Kenya and India have implemented mobile-based education apps and low-cost tablets, significantly increasing literacy rates and digital skills among rural populations. This rapid adoption of EdTech solutions fosters human capital development, driving economic growth and reducing inequality in emerging economies.
Sustainable Agriculture: Bypassing Conventional Methods
Leapfrogging in sustainable agriculture enables developing regions to bypass conventional, resource-intensive farming practices by adopting precision agriculture technologies and agroecological methods. Utilizing drone-based soil analysis and AI-driven irrigation systems significantly increases crop yields while conserving water and reducing chemical inputs. This approach accelerates economic growth by enhancing food security and promoting environmental sustainability without the intermediate stages of traditional agricultural development.
Urban Development: Smart Cities in Fast-Tracking Economies
Smart cities in fast-tracking economies harness advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics to optimize urban infrastructure and services, boosting efficiency and sustainability. By leapfrogging traditional development stages, these urban areas accelerate economic growth, improve quality of life, and reduce environmental impact. Examples include Shenzhen's rapid transformation into a tech-driven metropolis and Bangalore's rise as an innovation hub leveraging digital connectivity.
E-Government Services Streamlining Public Administration
E-Government services exemplify leapfrogging in development by enabling countries to bypass traditional bureaucratic inefficiencies and adopt digital platforms for public administration. Nations like Estonia have harnessed blockchain technology and digital IDs to streamline service delivery, enhance transparency, and reduce operational costs. This digital transformation accelerates governance efficiency and citizen engagement, fostering economic growth through improved institutional performance.
Health Tech Innovations: Telemedicine Adoption Examples
Telemedicine adoption has accelerated healthcare access in remote regions by enabling real-time consultations and reducing the need for physical infrastructure. Countries like India and Rwanda have leapfrogged traditional healthcare models by integrating mobile health platforms, enhancing patient outcomes through smartphone-based diagnostics and AI-powered symptom checkers. These innovations demonstrate how technology-driven leapfrogging can bridge gaps in healthcare delivery and promote inclusive economic development.
Policy Frameworks Enabling Leapfrogging Success
Policy frameworks that prioritize innovation, regulatory flexibility, and targeted investment enable countries to leapfrog traditional development stages, accelerating economic growth and technological adoption. Examples include Rwanda's proactive ICT policies fostering rapid digital transformation and Costa Rica's incentives for renewable energy, attracting green technology investments. Such strategic governance creates conducive environments for leapfrogging by reducing barriers and leveraging emerging technologies efficiently.
example of leapfrogging in development Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com