The gig economy represents a labor market characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work instead of permanent jobs. Platforms like Uber, Lyft, and TaskRabbit exemplify this model by connecting workers with customers seeking on-demand services. These companies rely heavily on digital technology to facilitate flexible work arrangements, contributing to the growing share of gig workers in the overall employment landscape. Data from economic studies show that gig workers now account for a significant portion of the workforce in many developed countries. The gig economy generates billions in revenue annually, influencing consumer behavior and reshaping traditional employment structures. Analysts observe that the gig model drives both economic efficiency and labor market fluidity by leveraging digital platforms and individual entrepreneurship.
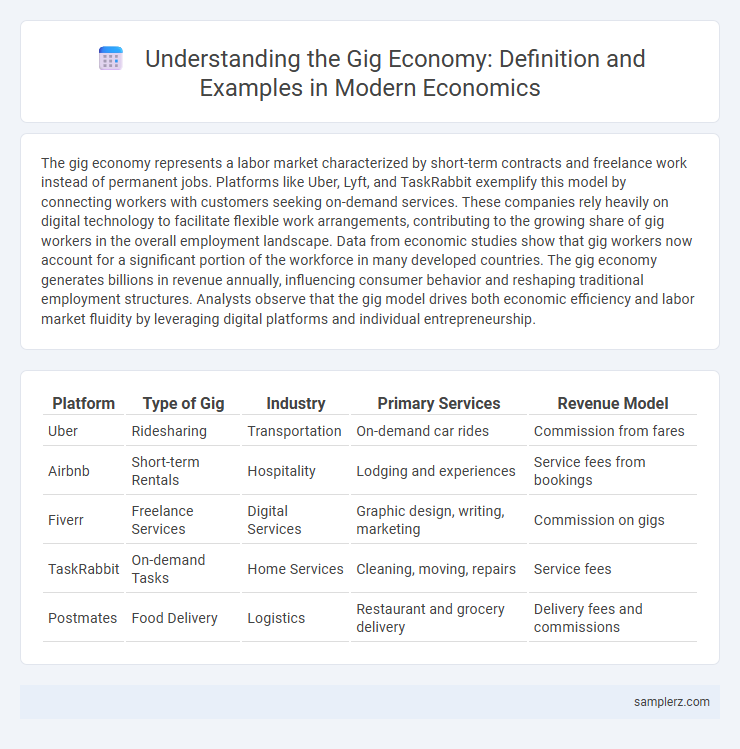
Table of Comparison
| Platform | Type of Gig | Industry | Primary Services | Revenue Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uber | Ridesharing | Transportation | On-demand car rides | Commission from fares |
| Airbnb | Short-term Rentals | Hospitality | Lodging and experiences | Service fees from bookings |
| Fiverr | Freelance Services | Digital Services | Graphic design, writing, marketing | Commission on gigs |
| TaskRabbit | On-demand Tasks | Home Services | Cleaning, moving, repairs | Service fees |
| Postmates | Food Delivery | Logistics | Restaurant and grocery delivery | Delivery fees and commissions |
Understanding the Gig Economy in Modern Economies
The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, plays a crucial role in modern economies by providing flexible employment opportunities and fostering innovation. Platforms like Uber, Airbnb, and Upwork exemplify how digital marketplaces connect gig workers with consumers, driving economic activity while reshaping traditional labor markets. This shift enhances workforce adaptability but also raises important discussions on job security and regulatory frameworks in evolving economic landscapes.
Popular Gig Economy Platforms Transforming Work
Popular gig economy platforms like Uber, Airbnb, and Upwork are transforming traditional work by enabling flexible, on-demand employment across transportation, accommodation, and freelance services. These platforms leverage digital technology to connect millions of workers with clients globally, creating new income opportunities and disrupting conventional labor markets. The rapid growth of gig economy marketplaces is reshaping economic participation and driving innovation in workforce management.
Freelancing: The Backbone of the Gig Economy
Freelancing drives the gig economy by allowing professionals to offer specialized skills such as graphic design, writing, and programming on flexible terms. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr connect millions of freelancers with clients worldwide, facilitating a dynamic marketplace. This model boosts economic activity by promoting entrepreneurship and enabling income generation outside traditional employment structures.
Ridesharing Services Driving Economic Change
Ridesharing services like Uber and Lyft exemplify the gig economy by transforming traditional transportation markets and creating flexible employment opportunities. These platforms leverage digital technologies to connect drivers with passengers, generating substantial income for millions of gig workers worldwide. The expansion of ridesharing has spurred local economic growth by increasing consumer mobility and stimulating related industries such as vehicle maintenance and fuel sales.
Food Delivery Apps Boosting Local Economies
Food delivery apps like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub have revolutionized the gig economy by creating flexible earning opportunities for thousands of local drivers and couriers. These platforms stimulate local economies by increasing demand for restaurant services, supporting small businesses, and generating additional income streams for workers outside traditional employment. The rapid growth of food delivery services contributes significantly to urban economic activity and employment rates in metropolitan areas.
Short-Term Rental Platforms Impacting Housing Markets
Short-term rental platforms like Airbnb significantly influence housing markets by increasing demand for rental properties, often driving up prices and reducing long-term rental availability. Research indicates that neighborhoods with a high concentration of short-term listings experience accelerated rent inflation and decreased housing affordability for residents. This trend challenges urban housing policies aimed at maintaining balanced rental markets and affordable living conditions.
Remote Work and Digital Gigs in the Global Economy
Remote work and digital gigs drive the global gig economy by enabling flexible employment across diverse industries such as IT, graphic design, and digital marketing. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr facilitate seamless connections between freelancers and clients worldwide, boosting economic participation in regions with limited traditional job opportunities. This digital transformation enhances productivity and supports economic resilience by decentralizing work and fostering global talent exchange.
Microtasking and the Rise of On-Demand Labor
Microtasking platforms like Amazon Mechanical Turk enable workers to complete small, discrete tasks for flexible pay, exemplifying the gig economy's shift toward on-demand labor. This model allows businesses to outsource numerous tiny tasks efficiently while providing workers with opportunities for supplemental income. The rise of on-demand labor reflects a growing trend of decentralizing work through digital platforms, transforming traditional employment structures.
The Impact of Gig Economy on Traditional Employment
The gig economy has transformed traditional employment by introducing flexible work arrangements through platforms like Uber, Airbnb, and TaskRabbit, enabling workers to monetize skills without long-term contracts. This shift has increased workforce participation but also led to concerns over job security, lack of benefits, and income instability for gig workers. Companies are adapting by integrating gig roles alongside full-time positions, reshaping labor market dynamics and prompting regulatory discussions worldwide.
The Future of Work: Gig Economy Trends in the Global Economy
The gig economy, defined by short-term contracts and freelance work, is reshaping the global labor market with tech platforms such as Uber, TaskRabbit, and Fiverr leading the shift. Projections estimate that by 2027, over 50% of the global workforce will engage in gig-based employment, driven by advances in digital platforms and changing worker preferences for flexibility. This trend significantly influences economic structures by fostering decentralized job markets and increasing income diversification worldwide.
example of gig economy in economy Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com