A roll-up in business refers to the strategy of acquiring multiple smaller companies in the same industry and combining them into a larger entity. This approach helps create economies of scale, increase market share, and enhance operational efficiencies. For instance, a private equity firm might execute a roll-up by purchasing several regional healthcare providers to build a nationwide network. This consolidation process often involves integrating data systems, streamlining management, and unifying branding to maximize value. Companies pursuing roll-ups typically focus on fragmented industries where smaller players dominate and growth through acquisition is more effective than organic expansion. The success of a roll-up depends on the ability to extract synergies and reduce costs while maintaining consistent service quality across all acquired businesses.
Table of Comparison
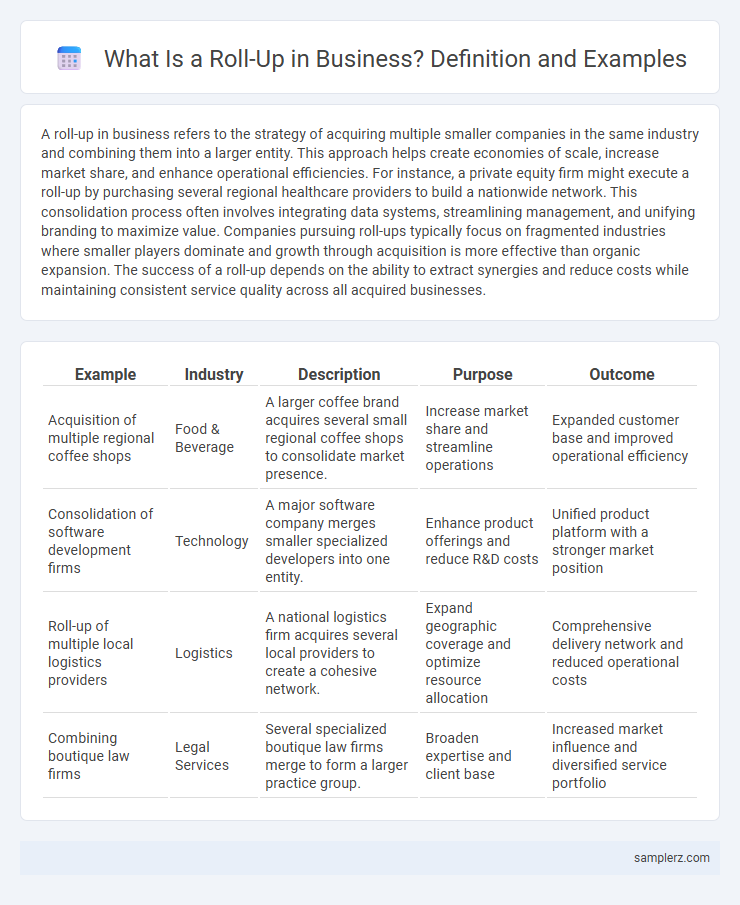
| Example | Industry | Description | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition of multiple regional coffee shops | Food & Beverage | A larger coffee brand acquires several small regional coffee shops to consolidate market presence. | Increase market share and streamline operations | Expanded customer base and improved operational efficiency |
| Consolidation of software development firms | Technology | A major software company merges smaller specialized developers into one entity. | Enhance product offerings and reduce R&D costs | Unified product platform with a stronger market position |
| Roll-up of multiple local logistics providers | Logistics | A national logistics firm acquires several local providers to create a cohesive network. | Expand geographic coverage and optimize resource allocation | Comprehensive delivery network and reduced operational costs |
| Combining boutique law firms | Legal Services | Several specialized boutique law firms merge to form a larger practice group. | Broaden expertise and client base | Increased market influence and diversified service portfolio |
Introduction to Roll-Ups in Business
Roll-ups in business involve the strategic acquisition of multiple smaller companies within the same industry to create a larger, more competitive entity. This approach allows for economies of scale, improved market share, and increased operational efficiencies. Prominent examples include private equity firms consolidating regional healthcare providers to streamline services and boost profitability.
Key Benefits of Roll-Up Strategies
Roll-up strategies in business involve acquiring multiple smaller companies within the same industry to create a larger, more competitive entity. Key benefits include economies of scale, increased market share, and enhanced operational efficiencies. This consolidation also drives higher valuation multiples and stronger negotiating power with suppliers and customers.
Classic Roll-Up Case Studies
Classic roll-up case studies often highlight the consolidation of fragmented industries, such as the acquisition spree by Waste Management Inc. in the 1980s, which unified numerous small waste disposal companies to create market dominance. Another prime example is the roll-up strategy employed by the dental services industry, where firms like Smile Brands expanded rapidly by acquiring local dental practices. These cases demonstrate how roll-ups drive economies of scale, operational efficiencies, and increased bargaining power within competitive markets.
Roll-Up Example: The Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry demonstrates a clear example of a roll-up strategy through mergers and acquisitions of smaller medical practices into larger healthcare groups or hospital systems. This consolidation enhances operational efficiency, expands patient services, and increases negotiating power with suppliers and insurers. Companies like UnitedHealth Group have successfully utilized roll-ups to create extensive healthcare networks, driving economies of scale and improved market share.
Roll-Up Success Story: Professional Services Firms
A prominent roll-up success story in the professional services sector is the merger of smaller consulting firms into a single, larger entity, enabling enhanced market reach and diversified service offerings. By consolidating resources, these firms achieve economies of scale, improved client acquisition, and increased operational efficiency. The resulting firm often captures a significant market share, driving sustained revenue growth and competitive advantage.
How Tech Companies Use Roll-Ups
Tech companies use roll-ups by acquiring multiple smaller startups with complementary technologies to create a unified platform, enhancing market reach and reducing operational costs. For example, a cloud service provider might roll up several specialized SaaS startups to offer an integrated suite of solutions. This strategy accelerates innovation and scales customer acquisition while consolidating competitive advantages.
Roll-Ups in the Retail Sector: A Closer Look
Roll-ups in the retail sector involve acquiring multiple smaller stores to create a larger, more competitive entity, enhancing purchasing power and operational efficiency. Companies like Dollar General have successfully implemented roll-up strategies to expand their footprint and market share rapidly. This consolidation often leads to economies of scale, improved supply chain coordination, and stronger brand recognition.
Private Equity and Roll-Up Examples
Private equity firms often execute roll-up strategies by acquiring multiple smaller companies within the same industry to create a larger, more competitive entity, as seen in Constellation Software's acquisition of numerous software firms. Roll-ups enhance operational efficiencies, increase market share, and improve valuation multiples by consolidating fragmented markets. Prominent examples include JAB Holding Company's consolidation of various consumer brands and Vista Equity Partners' aggregation of enterprise software businesses.
Risk Factors in Roll-Up Business Models
Roll-up business models aggregate multiple smaller companies to increase market share and operational efficiency, but they carry significant risk factors such as integration challenges, cultural clashes, and financial strain from acquisition costs. Failure to align disparate systems and processes can lead to operational inefficiencies and lost synergies, affecting overall profitability. Overleveraging to finance acquisitions increases debt risk, potentially jeopardizing cash flow and long-term business stability.
Future Trends in Roll-Up Strategies
Future trends in roll-up strategies emphasize leveraging technology to enhance operational synergies and data integration across acquired companies. Increasingly, artificial intelligence and machine learning are used to optimize consolidation processes and improve decision-making efficiency. Market dynamics also indicate a shift towards roll-ups in emerging industries such as renewable energy and fintech, where rapid scalability and innovation drive competitive advantage.
example of roll-up in business Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com