A golden parachute in a business contract refers to a substantial financial compensation package promised to top executives if they are terminated or forced to leave the company due to a merger or acquisition. This package typically includes cash severance, stock options, bonuses, and other benefits designed to provide financial security. One notable example is the contract of former Yahoo CEO Marissa Mayer, which included a golden parachute valued at approximately $23 million in the event of termination after a sale or merger. Golden parachutes serve as a protective mechanism for executives, ensuring they receive significant compensation despite potential job loss during corporate restructuring. These agreements often feature in the contracts of CEOs, CFOs, and other key executives to retain talent and prevent resistance during corporate takeovers. Data shows that the average golden parachute package in Fortune 500 companies ranges from 2 to 4 times the executive's annual salary, indicating the magnitude of these contractual protections.
Table of Comparison
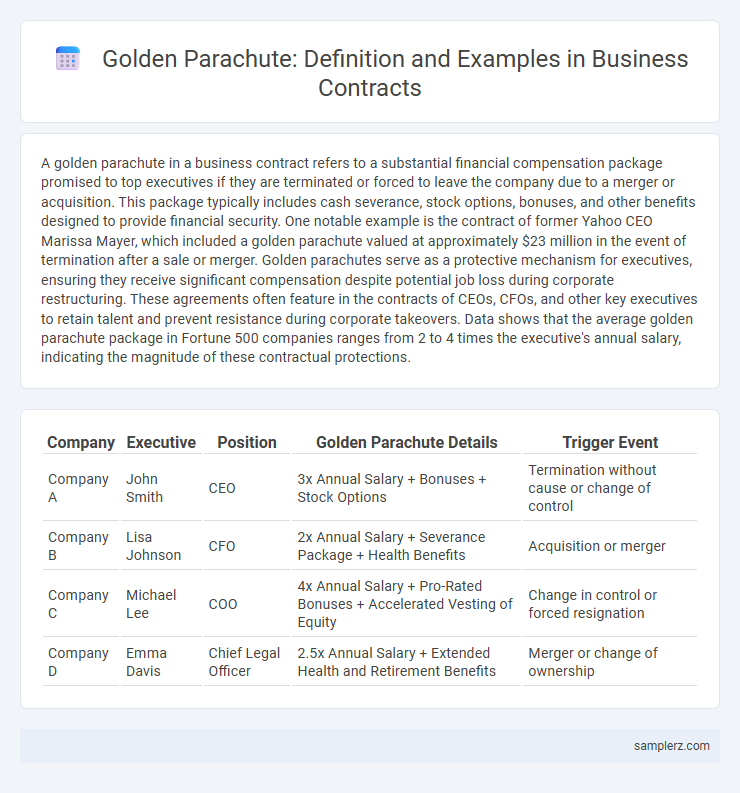
| Company | Executive | Position | Golden Parachute Details | Trigger Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | John Smith | CEO | 3x Annual Salary + Bonuses + Stock Options | Termination without cause or change of control |
| Company B | Lisa Johnson | CFO | 2x Annual Salary + Severance Package + Health Benefits | Acquisition or merger |
| Company C | Michael Lee | COO | 4x Annual Salary + Pro-Rated Bonuses + Accelerated Vesting of Equity | Change in control or forced resignation |
| Company D | Emma Davis | Chief Legal Officer | 2.5x Annual Salary + Extended Health and Retirement Benefits | Merger or change of ownership |
Understanding Golden Parachutes: Definition and Purpose
Golden parachutes are contractual agreements that provide top executives with significant financial benefits if they are terminated due to mergers or acquisitions. They typically include cash bonuses, stock options, and severance packages designed to protect executives from the risks of corporate restructuring. These provisions serve both to attract high-level talent and to ensure executive stability during transitional periods in business operations.
Key Elements of a Golden Parachute Clause
A golden parachute clause typically includes key elements such as a predetermined severance package, which may consist of cash bonuses, stock options, or other financial benefits triggered by termination following a merger or acquisition. It often specifies conditions under which the benefits are paid, including involuntary termination without cause or resignation for good reason within a defined period after a change in control. These provisions aim to protect executives' financial interests and incentivize leadership stability during corporate transitions.
Real-World Examples of Golden Parachute Contracts
Amazon's former CEO Jeff Bezos reportedly received a golden parachute worth approximately $90 million following his transition to Executive Chairman in 2021. Another notable example is Elon Musk, whose Tesla contract included a golden parachute valued at over $2.6 billion tied to company performance milestones. These contracts protect executives financially in scenarios of mergers, acquisitions, or significant role changes, ensuring stability and retention.
Notable Companies with Famous Golden Parachutes
Notable companies like Apple and JPMorgan Chase have famously included golden parachutes in their executive contracts, ensuring substantial severance packages for top executives in the event of mergers or acquisitions. Apple's agreement with former CEO Steve Jobs included millions in stock options and cash benefits, exemplifying a high-profile golden parachute. JPMorgan Chase secured a $69 million golden parachute for CEO Jamie Dimon, highlighting the significant financial protections companies provide to retain leadership during corporate transitions.
Golden Parachute Payout Structures Explained
Golden parachute payout structures typically include lump-sum cash payments, accelerated stock options vesting, and extended healthcare benefits for executives in the event of termination following a merger or acquisition. These contracts often define a multiple of the executive's annual salary or bonus, ranging from two to five times, ensuring significant financial security. The specificity of payout triggers and components varies by company but centers on safeguarding top executives from abrupt dismissal consequences.
Legal Considerations in Drafting Golden Parachute Agreements
Legal considerations in drafting golden parachute agreements include ensuring compliance with securities laws such as Rule 301 of Regulation S-K and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act to prevent excessive executive compensation that may harm shareholder interests. Contracts must clearly define trigger events, such as change of control or termination without cause, to avoid ambiguity and litigation risks. Careful attention to tax implications under Section 280G of the Internal Revenue Code is essential to minimize penalties and maximize tax efficiency for both the company and the executive.
Tax Implications of Golden Parachute Provisions
Golden parachute provisions in executive contracts often trigger significant tax implications, including the excise tax under Section 4999 of the Internal Revenue Code, which imposes a 20% tax on the amount exceeding three times the executive's base compensation. Payments classified as golden parachutes may also cause the loss of deductibility for the company under Section 162(m), affecting corporate tax liabilities. Executives receiving such payments should carefully assess the interplay between federal taxes and potential state income tax obligations to optimize their financial outcomes.
Controversies and Criticisms of Golden Parachute Contracts
Golden parachute contracts often face criticism for providing excessively large severance packages to top executives even when company performance declines or shareholder value drops. Controversies arise over perceived misalignment between executive rewards and company success, leading to public backlash and shareholder dissent. Critics argue these contracts can encourage risky managerial behavior by reducing accountability during mergers or acquisitions.
Golden Parachute Clauses in Mergers and Acquisitions
Golden parachute clauses in mergers and acquisitions guarantee lucrative exit packages for top executives if their employment is terminated following a change in company control, ensuring financial security and incentivizing leadership continuity during transitions. These agreements typically include severance pay, bonuses, stock options, and other benefits triggered by mergers or hostile takeovers. Corporations use golden parachutes to attract and retain executive talent while protecting against potential disruptions caused by ownership changes.
Best Practices for Implementing Golden Parachutes in Executive Contracts
Best practices for implementing golden parachutes in executive contracts include clearly defining severance terms linked to specific trigger events such as mergers or acquisitions, ensuring transparency to prevent shareholder disputes. Contracts should balance generous payouts with performance-based conditions to align executive incentives with company success. Incorporating tax-efficient structures and regular legal reviews helps maintain compliance and protect both the executive and the company's financial interests.
example of golden parachute in contract Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com