A black swan event in business refers to an unpredictable and rare occurrence that has severe consequences on a company or industry. The 2008 financial crisis is a prime example, where the collapse of major financial institutions led to a global economic downturn. This event highlighted the vulnerability of financial systems to unforeseen risk factors and the lack of preparedness within many organizations. Another notable black swan incident was the COVID-19 pandemic, which disrupted supply chains and forced businesses worldwide to adapt rapidly. Companies faced unprecedented challenges such as sudden drops in demand, workforce disruptions, and changes in consumer behavior. These examples emphasize the critical need for robust risk management strategies that account for low-probability yet high-impact scenarios in business planning.
Table of Comparison
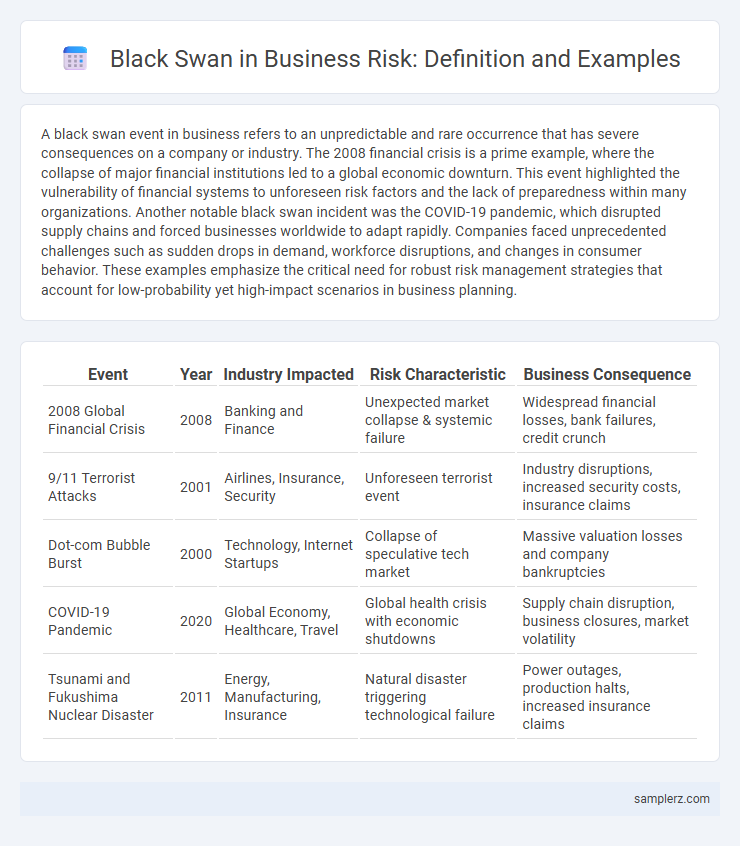
| Event | Year | Industry Impacted | Risk Characteristic | Business Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 Global Financial Crisis | 2008 | Banking and Finance | Unexpected market collapse & systemic failure | Widespread financial losses, bank failures, credit crunch |
| 9/11 Terrorist Attacks | 2001 | Airlines, Insurance, Security | Unforeseen terrorist event | Industry disruptions, increased security costs, insurance claims |
| Dot-com Bubble Burst | 2000 | Technology, Internet Startups | Collapse of speculative tech market | Massive valuation losses and company bankruptcies |
| COVID-19 Pandemic | 2020 | Global Economy, Healthcare, Travel | Global health crisis with economic shutdowns | Supply chain disruption, business closures, market volatility |
| Tsunami and Fukushima Nuclear Disaster | 2011 | Energy, Manufacturing, Insurance | Natural disaster triggering technological failure | Power outages, production halts, increased insurance claims |
Defining Black Swan Events in Business Risk
Black Swan events in business risk are rare, unpredictable incidents with severe consequences that significantly disrupt markets or industries. Examples include the 2008 global financial crisis, which stemmed from unforeseen systemic failures, and the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused unprecedented supply chain disruptions and demand shocks. These events expose vulnerabilities in risk management frameworks and highlight the need for robust contingency planning.
Characteristics of Black Swan Incidents
Black Swan incidents are characterized by their extreme rarity, severe impact, and retrospective predictability, such as the 2008 global financial crisis triggered by the collapse of Lehman Brothers. These events defy conventional risk models due to their unforeseen nature and disproportionate consequences on markets and industries. Their unpredictability challenges traditional risk management, emphasizing the need for adaptive strategies to mitigate potential catastrophic losses.
Financial Market Crashes as Black Swan Examples
Financial market crashes such as the 2008 Global Financial Crisis serve as quintessential black swan events characterized by their extreme rarity and profound impact on global economies. These crashes expose vulnerabilities in financial systems, triggered by unforeseen factors like the collapse of major institutions and the bursting of asset bubbles. Investors and policymakers often underestimate such events, leading to significant losses and prompting a reevaluation of risk management strategies.
Global Pandemics Disrupting Business Operations
Global pandemics such as COVID-19 exemplify black swan events by causing unprecedented disruptions in business operations worldwide, leading to supply chain breakdowns, sudden shifts in consumer behavior, and extensive workforce challenges. These unforeseen crises force companies to rapidly adapt through digital transformation, diversification of supply sources, and enhanced risk management strategies. Pandemic-induced volatility highlights the critical need for resilient business models capable of withstanding extreme and unpredictable risks.
Sudden Regulatory Changes Impacting Industries
Sudden regulatory changes, such as the unexpected implementation of stringent environmental laws or trade restrictions, can act as black swan events by drastically disrupting entire industries overnight. These unforeseen regulations often lead to significant financial losses, supply chain challenges, and forced operational overhauls for businesses unprepared for such abrupt shifts. Companies in sectors like energy, manufacturing, and finance are especially vulnerable to regulatory black swan risks, emphasizing the need for agile compliance strategies and robust risk management frameworks.
Supply Chain Failures from Unexpected Events
Supply chain failures stemming from unexpected events, such as the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, exemplify black swan risks by causing global disruptions in manufacturing and logistics. The sudden halt in semiconductor production during this disaster led to widespread shortages across automotive and electronics industries, highlighting vulnerabilities in supply chain dependencies. Companies lacking diversified suppliers faced prolonged recovery times and significant financial losses due to this unanticipated systemic shock.
Technological Failures and Cybersecurity Breaches
A prominent black swan event in business risk is the 2017 Equifax data breach, which exposed the personal information of 147 million people and caused massive financial and reputational damage. Technological failures such as system outages at major financial institutions can disrupt markets and client operations globally, highlighting the unpredictability and severity of these incidents. Cybersecurity breaches remain a critical black swan risk due to evolving threats and the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure in business operations.
Natural Disasters Affecting Global Commerce
The 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan exemplified a black swan event, severely disrupting global supply chains and causing massive financial losses across industries. This natural disaster halted production of key electronic components, impacting multinational corporations and slowing global trade. Its unpredictability and widespread economic effects highlight the critical need for robust risk management strategies in global commerce.
Corporate Scandals and Unforeseen Collapses
Corporate scandals like Enron's accounting fraud and unforeseen collapses such as Lehman Brothers' bankruptcy exemplify black swan events in business risk. These occurrences defy traditional risk models due to their rarity and massive impact, disrupting markets and eroding stakeholder trust. Companies often face significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory consequences following such unpredictable crises.
Strategies for Managing Black Swan Risks
Black swan events, such as the 2008 global financial crisis or the COVID-19 pandemic, reveal the critical importance of risk management strategies focused on unpredictability and high-impact disruptions. Effective approaches include scenario planning, building organizational resilience through diversified portfolios, and maintaining flexible liquidity reserves to absorb sudden shocks. Implementing advanced data analytics and fostering a culture of adaptive risk awareness enable businesses to better anticipate and respond to these rare but consequential events.
example of black swan in risk Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com