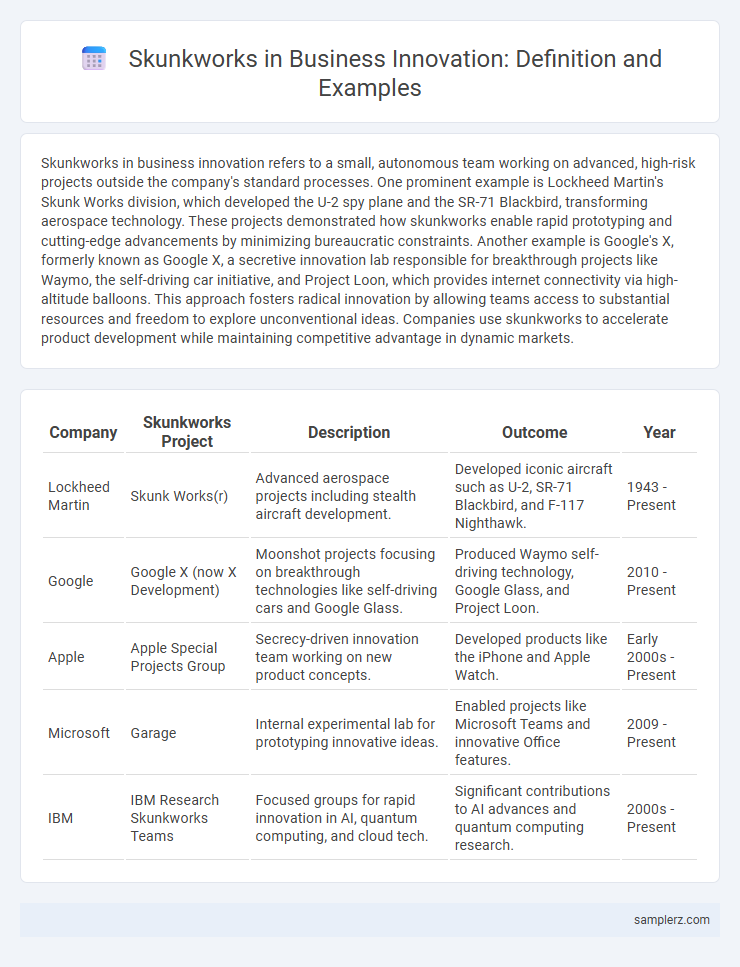
Skunkworks in business innovation refers to a small, autonomous team working on advanced, high-risk projects outside the company's standard processes. One prominent example is Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works division, which developed the U-2 spy plane and the SR-71 Blackbird, transforming aerospace technology. These projects demonstrated how skunkworks enable rapid prototyping and cutting-edge advancements by minimizing bureaucratic constraints. Another example is Google's X, formerly known as Google X, a secretive innovation lab responsible for breakthrough projects like Waymo, the self-driving car initiative, and Project Loon, which provides internet connectivity via high-altitude balloons. This approach fosters radical innovation by allowing teams access to substantial resources and freedom to explore unconventional ideas. Companies use skunkworks to accelerate product development while maintaining competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Table of Comparison
| Company | Skunkworks Project | Description | Outcome | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lockheed Martin | Skunk Works(r) | Advanced aerospace projects including stealth aircraft development. | Developed iconic aircraft such as U-2, SR-71 Blackbird, and F-117 Nighthawk. | 1943 - Present |
| Google X (now X Development) | Moonshot projects focusing on breakthrough technologies like self-driving cars and Google Glass. | Produced Waymo self-driving technology, Google Glass, and Project Loon. | 2010 - Present | |
| Apple | Apple Special Projects Group | Secrecy-driven innovation team working on new product concepts. | Developed products like the iPhone and Apple Watch. | Early 2000s - Present |
| Microsoft | Garage | Internal experimental lab for prototyping innovative ideas. | Enabled projects like Microsoft Teams and innovative Office features. | 2009 - Present |
| IBM | IBM Research Skunkworks Teams | Focused groups for rapid innovation in AI, quantum computing, and cloud tech. | Significant contributions to AI advances and quantum computing research. | 2000s - Present |
Iconic Skunkworks Projects That Changed Industries
Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works division revolutionized aerospace with the development of the U-2 spy plane and the SR-71 Blackbird, setting new standards in stealth and speed. Google X's Project Loon transformed global internet access by using high-altitude balloons to provide connectivity in remote areas. Tesla's secretive Roadster project accelerated the electric vehicle market, driving innovation in battery technology and sustainable transportation.
How Skunkworks Teams Drive Business Innovation
Skunkworks teams accelerate business innovation by operating with agility and autonomy outside traditional corporate constraints, enabling rapid prototyping and disruptive solutions. Companies like Lockheed Martin have demonstrated how focused, small teams can deliver breakthrough aerospace technologies efficiently. These innovative units leverage cross-functional expertise and a fail-fast culture to transform bold ideas into market-ready products, driving competitive advantage.
Famous Corporate Examples of Skunkworks in Action
Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works division revolutionized aerospace innovation by developing the U-2 and SR-71 Blackbird spy planes under strict secrecy and accelerated timelines. Google's Area 120 functions as an internal incubator, fostering experimental projects like Google Duplex and enabling rapid prototyping outside the company's traditional hierarchy. Microsoft Garage promotes employee-driven innovation by supporting skunkworks projects that lead to products such as Microsoft Launcher and Seeing AI, demonstrating corporate commitment to agile development and disruptive technologies.
Skunkworks Success Stories in Modern Enterprises
Skunkworks projects have led to groundbreaking innovations in modern enterprises, such as Lockheed Martin's development of the U-2 and SR-71 Blackbird aircraft, showcasing advanced aerospace technologies. Google X labs pioneered self-driving car technology and Project Loon, revolutionizing transportation and global internet access. These examples highlight how autonomous, focused teams accelerate innovation by bypassing traditional corporate processes and fostering rapid prototyping.
Startups and Their Skunkworks Approach to Disruption
Startups often adopt the skunkworks approach by creating small, autonomous teams dedicated to rapid innovation and disruptive technology development outside of the main organizational structure. This method enables agile experimentation and minimizes traditional bureaucratic constraints, accelerating the path from concept to market-ready products. Notable examples include startups in Silicon Valley leveraging skunkworks teams to pioneer breakthrough solutions in AI, biotech, and fintech industries.
Hidden Skunkworks Initiatives in Tech Giants
Hidden skunkworks initiatives at tech giants like Google and Apple drive breakthrough innovation by operating autonomously from core business units. These secretive projects focus on cutting-edge technologies such as AI, quantum computing, and advanced hardware, often leading to products like Google Glass and the Apple M1 chip. By maintaining a low profile, hidden skunkworks avoid bureaucratic constraints and rapidly prototype disruptive solutions that redefine market standards.
Skunkworks in Product Development: Real-World Cases
Skunkworks initiatives in product development have driven breakthrough innovations such as Lockheed Martin's development of the U-2 and SR-71 Blackbird aircraft, where small, autonomous teams operated with minimal oversight to accelerate design and testing. Another example is Google X, which fostered projects like Google Glass and self-driving cars through experimental teams detached from core business units, promoting rapid prototyping and disruptive technology development. These real-world cases demonstrate how skunkworks enable companies to circumvent traditional bureaucratic constraints, reduce time-to-market, and achieve radical innovation in competitive industries.
Cross-Industry Skunkworks Examples Fueling Growth
Cross-industry skunkworks projects like Google X and Lockheed Martin's Advanced Development Programs exemplify innovation by rapidly developing breakthrough technologies in isolated environments. These teams focus on high-risk, high-reward initiatives enabling accelerated growth and competitive advantages across sectors such as aerospace, technology, and automotive. By fostering collaboration among diverse expertise, cross-industry skunkworks drive transformative advancements and market expansion.
Lessons From Legendary Skunkworks Business Models
Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works exemplifies groundbreaking innovation through autonomous teams rapidly developing advanced aerospace technologies under strict secrecy and tight deadlines. This model highlights the importance of fostering a culture of trust, empowering small, agile groups with significant decision-making authority to accelerate product development. Emulating such skunkworks approaches enables businesses to disrupt markets by prioritizing speed, creativity, and iterative problem-solving over traditional bureaucratic processes.
Measuring Impact: Skunkworks Innovations in Business
Skunkworks projects in business often drive breakthrough innovations by operating in agile, low-bureaucracy environments, enabling rapid prototyping and testing. Measuring the impact of these innovations involves tracking key performance indicators such as time-to-market reduction, increased revenue from new product lines, and enhanced customer satisfaction metrics. Successful skunkworks initiatives typically show a measurable boost in competitive advantage and market share within 12 to 18 months post-launch.
example of skunkworks in innovation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com