The bore in a piston refers to the diameter of the cylinder in which the piston moves. For instance, in a typical 2.0-liter four-cylinder engine, the bore size might measure around 86 millimeters. This dimension directly impacts the engine's displacement and power output. Another example is found in performance engines where the bore can be larger, such as 100 millimeters in a 3.0-liter V6 engine. Increasing the bore size allows for greater air and fuel mixture intake, enhancing combustion efficiency. Bore measurements are critical data for engine design and tuning in automotive engineering.
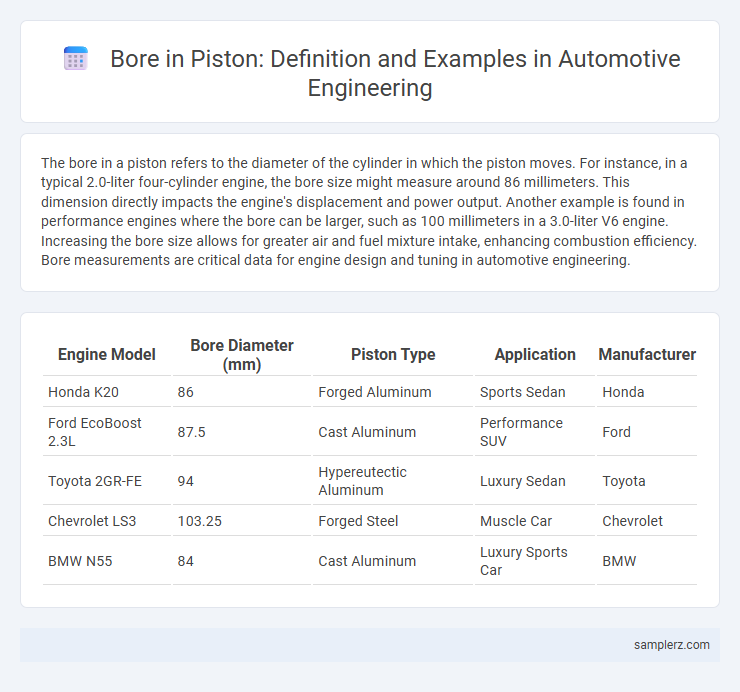
Table of Comparison
| Engine Model | Bore Diameter (mm) | Piston Type | Application | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honda K20 | 86 | Forged Aluminum | Sports Sedan | Honda |
| Ford EcoBoost 2.3L | 87.5 | Cast Aluminum | Performance SUV | Ford |
| Toyota 2GR-FE | 94 | Hypereutectic Aluminum | Luxury Sedan | Toyota |
| Chevrolet LS3 | 103.25 | Forged Steel | Muscle Car | Chevrolet |
| BMW N55 | 84 | Cast Aluminum | Luxury Sports Car | BMW |
Understanding Bore in Piston: Definition and Importance
Bore in a piston refers to the diameter of the cylinder in which the piston moves, typically measured in millimeters or inches. This dimension is crucial for determining the engine's displacement and directly influences power output and efficiency. Accurate bore sizing ensures optimal combustion, minimizing friction and wear, thereby enhancing engine performance and longevity.
Key Functions of Piston Bore in Engine Performance
The piston bore in an engine cylinder plays a critical role in maintaining optimal compression and combustion efficiency by providing a precise, smooth surface for the piston to move within. Its dimensions directly impact engine displacement, power output, and fuel efficiency, as a well-maintained bore ensures minimal friction and proper sealing. High-quality bore finishes reduce wear and heat buildup, enhancing overall engine durability and performance.
Common Materials Used for Piston Bores
Piston bores are commonly machined from cast iron or aluminum alloys due to their excellent wear resistance and thermal conductivity. Hypereutectic aluminum alloys, containing up to 16% silicon, are favored for their reduced thermal expansion and improved durability under high combustion pressures. Advanced coatings such as nikasil or ceramic layers are often applied to enhance surface hardness and reduce friction, extending the lifespan of piston bores in automotive engines.
Standard Bore Sizes in Automotive Pistons
Standard bore sizes in automotive pistons typically range from 70 mm to 100 mm, depending on the engine type and application. Common bore dimensions include 75 mm, 82 mm, and 90 mm, which influence engine displacement and performance characteristics. Precise bore sizing ensures optimal combustion efficiency and piston fit within the cylinder.
How Piston Bore Affects Engine Displacement
The piston bore refers to the diameter of the cylinder in which the piston moves, directly influencing engine displacement by determining the volume swept during a single piston stroke. A larger piston bore increases the cylinder volume, resulting in higher engine displacement and potentially more power output. Engine designers must balance bore size with stroke length to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions in internal combustion engines.
Example Measurements of Bore in Different Engines
Bore measurements in automotive pistons vary significantly across engine types, with typical passenger car engines ranging from 70mm to 100mm in diameter, while high-performance sports cars often feature bores exceeding 100mm to increase displacement and power output. For instance, a standard inline-4 engine might have a bore of 85mm, whereas a V8 engine used in muscle cars can have bores up to 103mm or more, directly impacting engine capacity and combustion efficiency. These bore variations play a crucial role in optimizing engine performance, fuel economy, and emissions standards in modern automotive engineering.
Techniques for Measuring Piston Bore Accurately
Precision in measuring piston bore diameter is achieved using bore gauges and micrometers, which provide exact internal dimensions essential for maintaining engine performance. Laser scanning technology offers high-resolution, non-contact measurement, enabling detection of minute surface irregularities and tapering. Employing coordinate measuring machines (CMM) ensures comprehensive three-dimensional analysis, facilitating optimal piston fit and reducing wear.
Impact of Bore Size on Engine Power and Efficiency
Bore size directly influences engine displacement, determining the volume of air-fuel mixture combusted, which impacts power output and thermal efficiency. A larger bore increases cylinder volume, enhancing horsepower but may reduce fuel efficiency due to greater heat loss and increased surface area. Optimizing bore size balances power delivery with fuel consumption, crucial for achieving desired engine performance and emissions standards.
Bore and Stroke: Their Relationship in Engine Design
Bore refers to the diameter of a piston inside the cylinder, while stroke is the distance the piston travels up and down. The relationship between bore and stroke directly impacts engine displacement, power output, and torque characteristics. A larger bore combined with a shorter stroke typically enables higher engine speeds and increased horsepower, whereas a smaller bore with a longer stroke enhances torque and fuel efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Piston Bore Performance
Regular inspection of the piston bore for wear and scoring is essential to maintain engine efficiency and prevent costly repairs. Using bore gauges and micrometers ensures precise measurement, helping to detect any deviations from manufacturer specifications early. Applying proper lubrication and adhering to recommended maintenance schedules extends the lifespan of the piston bore, maintaining optimal compression and reducing the risk of engine overheating.
example of bore in piston Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com